![L 28 Electricity and Magnetism [5]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001656095_1-d86df1170441e2fe1ff7746d81978139-300x300.png)
L 28 Electricity and Magnetism [5]
... Magnetic materials • some materials are naturally magnetic or can be magnetized and retain their magnetism ferromagnetic materials • other materials (iron) can be magnetized temporarily by placing them near magnets • some materials have essentially no magnetic properties copper, aluminum, plast ...
... Magnetic materials • some materials are naturally magnetic or can be magnetized and retain their magnetism ferromagnetic materials • other materials (iron) can be magnetized temporarily by placing them near magnets • some materials have essentially no magnetic properties copper, aluminum, plast ...
View File
... The materials are all “soft” ferromagnets. The external field temporarily aligns the domains so there is a net dipole, which is then attracted to the bar magnet. - The effect vanishes with no applied B field - It does not matter which pole is used. ...
... The materials are all “soft” ferromagnets. The external field temporarily aligns the domains so there is a net dipole, which is then attracted to the bar magnet. - The effect vanishes with no applied B field - It does not matter which pole is used. ...
EARTH`S MAGNETIC FIELD
... geographic south pole (see Magnetic South Pole). This makes the compass usable for navigation. The cause of the field can be explained by dynamo theory. A magnetic fieldextends infinitely, though it weakens with distance from its source. The Earth's magnetic field, also called the geomagnetic field ...
... geographic south pole (see Magnetic South Pole). This makes the compass usable for navigation. The cause of the field can be explained by dynamo theory. A magnetic fieldextends infinitely, though it weakens with distance from its source. The Earth's magnetic field, also called the geomagnetic field ...
Electrification of Bodies
... As if alive when legs touched iron railing. Lab Experiment - fork with Fe and Cu prong Therefore - “animal electricity” (1791) - fork Released electricity from frog legs ? Nephew - Giovanni Aldini - awarded Copley Medal Of Royal Society for using electrical discharge to Briefly reanimate decapitated ...
... As if alive when legs touched iron railing. Lab Experiment - fork with Fe and Cu prong Therefore - “animal electricity” (1791) - fork Released electricity from frog legs ? Nephew - Giovanni Aldini - awarded Copley Medal Of Royal Society for using electrical discharge to Briefly reanimate decapitated ...
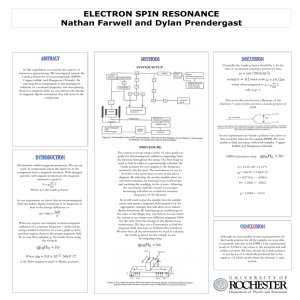
Poster: ESR
... easily in compounds where the electrons in the compound have a magnetic moment. With charged particles with angular momentum the magnetic moment is equal to: Where g is the Lande g-factor. In our experiment we know that an electromagnetic field can induce dipole transitions if its frequency is near ...
... easily in compounds where the electrons in the compound have a magnetic moment. With charged particles with angular momentum the magnetic moment is equal to: Where g is the Lande g-factor. In our experiment we know that an electromagnetic field can induce dipole transitions if its frequency is near ...
Exam 2 Solutions
... At r = R / 2, we find the B field from the cylinder from Ampere’s law, where the enclosed current is clearly 1/4 the total current. Since the point is equidistant from the center of the cylinder and the wire, the current in the wire must be the same, or I / 4. Simple application of the right hand ru ...
... At r = R / 2, we find the B field from the cylinder from Ampere’s law, where the enclosed current is clearly 1/4 the total current. Since the point is equidistant from the center of the cylinder and the wire, the current in the wire must be the same, or I / 4. Simple application of the right hand ru ...
AP Physics Daily Problem #140
... A wire loop, 2meters by 4 meters, of negligible resistance is in the plane of the page with its left end in a uniform 0.5-tesla magnetic field directed into the page, as shown above. A 5-ohm resistor is connected between points X and Y. The field is zero outside the region enclosed by the dashed lin ...
... A wire loop, 2meters by 4 meters, of negligible resistance is in the plane of the page with its left end in a uniform 0.5-tesla magnetic field directed into the page, as shown above. A 5-ohm resistor is connected between points X and Y. The field is zero outside the region enclosed by the dashed lin ...
ppt
... are made by towing a magnetometer behind the ship. • These instruments measure the magnitude of the magnetic field, but not the direction. • The magnetic anomaly is obtained by subtracting the regional field from the measured field. • The magnetic stripes run parallel to the ridges and are symmetric ...
... are made by towing a magnetometer behind the ship. • These instruments measure the magnitude of the magnetic field, but not the direction. • The magnetic anomaly is obtained by subtracting the regional field from the measured field. • The magnetic stripes run parallel to the ridges and are symmetric ...
Carlos Garcia Canal: Monopolium: the key to monopoles?
... - 1269 PETRUS PEREGRINUS DE MAHARNCURIA (Pierre Pèlerin de Maricourt) Epistola Petri Peregrini de Maricourt ad Sygerum de Foucancourt, militem, de magnete ...
... - 1269 PETRUS PEREGRINUS DE MAHARNCURIA (Pierre Pèlerin de Maricourt) Epistola Petri Peregrini de Maricourt ad Sygerum de Foucancourt, militem, de magnete ...
Exam 2 Solutions
... The parallel combination yields a resistance of 4 Ω and thus the total resistance is 6.0 Ω. The total current is thus 24 / 6.0 = 4 A. To find the current in the 6 Ω branch, first find the voltage across it, which is the same as the voltage across the parallel combination. This voltage is determined ...
... The parallel combination yields a resistance of 4 Ω and thus the total resistance is 6.0 Ω. The total current is thus 24 / 6.0 = 4 A. To find the current in the 6 Ω branch, first find the voltage across it, which is the same as the voltage across the parallel combination. This voltage is determined ...
Magnetic effect of electric current class 10 notes
... The region surrounding a magnet, in which a magnetic force can be experienced is known as magnetic field. Magnetic field lines: A graphical representation of the magnitude and the direction of a magnetic field. Properties of magnetic field lines 1. The field lines starts from north pole and merge at ...
... The region surrounding a magnet, in which a magnetic force can be experienced is known as magnetic field. Magnetic field lines: A graphical representation of the magnitude and the direction of a magnetic field. Properties of magnetic field lines 1. The field lines starts from north pole and merge at ...
Chapter 7 Electrodynamics 7.1 Electromotive Force
... claim that this is the only solution. Example: In vacuum-tube diodes, electrons are emitted from a hot cathode at zero potential and collected by an anode maintained at a potential V0, resulting in a convection current flow. Assuming that the cathode and the anode are parallel conducting plates and ...
... claim that this is the only solution. Example: In vacuum-tube diodes, electrons are emitted from a hot cathode at zero potential and collected by an anode maintained at a potential V0, resulting in a convection current flow. Assuming that the cathode and the anode are parallel conducting plates and ...
Magnetic field lines and flux
... Is there something like Gauss’ law for magnetic flux Yes, and it surprisingly simple with deep fundamental meaning Remember Gauss law for electric flux and let’s apply it by enclosing electric dipoles: ...
... Is there something like Gauss’ law for magnetic flux Yes, and it surprisingly simple with deep fundamental meaning Remember Gauss law for electric flux and let’s apply it by enclosing electric dipoles: ...
Giant magnetoresistance
Giant magnetoresistance (GMR) is a quantum mechanical magnetoresistance effect observed in thin-film structures composed of alternating ferromagnetic and non-magnetic conductive layers. The 2007 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Albert Fert and Peter Grünberg for the discovery of GMR.The effect is observed as a significant change in the electrical resistance depending on whether the magnetization of adjacent ferromagnetic layers are in a parallel or an antiparallel alignment. The overall resistance is relatively low for parallel alignment and relatively high for antiparallel alignment. The magnetization direction can be controlled, for example, by applying an external magnetic field. The effect is based on the dependence of electron scattering on the spin orientation.The main application of GMR is magnetic field sensors, which are used to read data in hard disk drives, biosensors, microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) and other devices. GMR multilayer structures are also used in magnetoresistive random-access memory (MRAM) as cells that store one bit of information.In literature, the term giant magnetoresistance is sometimes confused with colossal magnetoresistance of ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic semiconductors, which is not related to the multilayer structure.