Aim of killing for disease control Why
... – Report depopulation operations – Number and species killed – Methods used – Description of difficulties encountered and solutions to alleviate or minimise animal suffering – Derogations from routine welfare slaughter ...
... – Report depopulation operations – Number and species killed – Methods used – Description of difficulties encountered and solutions to alleviate or minimise animal suffering – Derogations from routine welfare slaughter ...
CAT-SCRATCH FEVER Overview Cat-scratch disease is a slowly
... manifestations of headache, tonicclonic seizures, combative behavior, and coma. These symptoms typically occur suddenly, 1–8 weeks after the onset of lymphadenopathy. ...
... manifestations of headache, tonicclonic seizures, combative behavior, and coma. These symptoms typically occur suddenly, 1–8 weeks after the onset of lymphadenopathy. ...
BASIC TERMINOLOGY AND DEFINITIONS IN PLANT PATHOLOGY
... distribution, and spread usually refers to local distribution. Vectors are active agents of transmission such as insects, mites, nematodes and other animals. The dissemination of pathogenic organisms can also be accomplished by wind, rain, irrigation, contaminated seeds and transplants. A few pathog ...
... distribution, and spread usually refers to local distribution. Vectors are active agents of transmission such as insects, mites, nematodes and other animals. The dissemination of pathogenic organisms can also be accomplished by wind, rain, irrigation, contaminated seeds and transplants. A few pathog ...
Headache ‘THE RED FLAGS’
... – Occasionally difficult to differentiate from Chronic Migraine • Newly Persistent Daily Headache – New headache becomes daily within 3 days – Not caused by another disorder – Evaluation for secondary causes – Triggers: Viral illness, minor head trauma, surgery ...
... – Occasionally difficult to differentiate from Chronic Migraine • Newly Persistent Daily Headache – New headache becomes daily within 3 days – Not caused by another disorder – Evaluation for secondary causes – Triggers: Viral illness, minor head trauma, surgery ...
Lecture 6
... feces of ‘kissing bug’ – Enters through skin or wound – Enters tissue near wound and differentiates – Gametes multiply by binary fusion ...
... feces of ‘kissing bug’ – Enters through skin or wound – Enters tissue near wound and differentiates – Gametes multiply by binary fusion ...
Reading Guide for Week 1
... how to describe the rate of disease in a population using the words endemic, epidemic, pandemic, and outbreak the reservoirs of infection, or the natural habitat of a microbe, and that people carrying the microbe can have symptomatic infections or be asymptomatic carriers. The portals of entry and e ...
... how to describe the rate of disease in a population using the words endemic, epidemic, pandemic, and outbreak the reservoirs of infection, or the natural habitat of a microbe, and that people carrying the microbe can have symptomatic infections or be asymptomatic carriers. The portals of entry and e ...
recommended puppy - SouthCare Animal Medical Center
... disease that is transmissible to humans. In Washington, this vaccine is administered as a single vaccine which lasts 1 year the first time they are vaccinated and lasts 3 years thereafter. You will be given a Rabies tag and certificate with each vaccine. This certificate is needed for licensing and ...
... disease that is transmissible to humans. In Washington, this vaccine is administered as a single vaccine which lasts 1 year the first time they are vaccinated and lasts 3 years thereafter. You will be given a Rabies tag and certificate with each vaccine. This certificate is needed for licensing and ...
Milwaukee Journal Sentinel Safety Training Presentations
... • May lead to chronic liver disease, liver cancer, and death • Vaccination available since 1982 • HBV can survive for at least one week in dried blood ...
... • May lead to chronic liver disease, liver cancer, and death • Vaccination available since 1982 • HBV can survive for at least one week in dried blood ...
Student Application
... 2. I am able to list and locate protective equipment I need to prevent exposure to blood borne pathogen I am able to identify duties I perform that may expose me to a blood borne pathogen. 3. I am able to identify infectious waste and sharps and located the proper place to dispose of them. I am able ...
... 2. I am able to list and locate protective equipment I need to prevent exposure to blood borne pathogen I am able to identify duties I perform that may expose me to a blood borne pathogen. 3. I am able to identify infectious waste and sharps and located the proper place to dispose of them. I am able ...
Infection Control Quiz #1 Your client is a 40 year old man who has
... c. Moisture will not collect or cause rust ...
... c. Moisture will not collect or cause rust ...
CHRONIC WASTING DISEASE - PROTECTING SCOTLAND`S DEER
... to the United States of America and Canada. CWD is caused by a prion and belongs to the same group of diseases as scrapie, which affects sheep and goats, and ‘mad cow disease’ (bovine spongiform encephalopathy or ‘BSE’). This group of diseases are known collectively as ‘transmissible spongiform ence ...
... to the United States of America and Canada. CWD is caused by a prion and belongs to the same group of diseases as scrapie, which affects sheep and goats, and ‘mad cow disease’ (bovine spongiform encephalopathy or ‘BSE’). This group of diseases are known collectively as ‘transmissible spongiform ence ...
Duke in Darwin
... Decision to treat Is based on the occurrence of typical symptoms in patients from endemic areas Duke retrospective study of 94 patients with RMSF, those treated within 5 days of symptom onset were much less likely to die vs. those treated after 5 days (6.5% vs. 22.9%) Over 90% of patients saw a Dr. ...
... Decision to treat Is based on the occurrence of typical symptoms in patients from endemic areas Duke retrospective study of 94 patients with RMSF, those treated within 5 days of symptom onset were much less likely to die vs. those treated after 5 days (6.5% vs. 22.9%) Over 90% of patients saw a Dr. ...
Parasites - the uninvited dinner guests
... phological forms in multiple hosts, with intermediate hosts required for some parts of the life cycle, definitive hosts in which sexual maturity is achieved, vectors for transmission (can be intermediate or definitive hosts) and sometimes an optional paratenic (transport) host, in which the parasit ...
... phological forms in multiple hosts, with intermediate hosts required for some parts of the life cycle, definitive hosts in which sexual maturity is achieved, vectors for transmission (can be intermediate or definitive hosts) and sometimes an optional paratenic (transport) host, in which the parasit ...
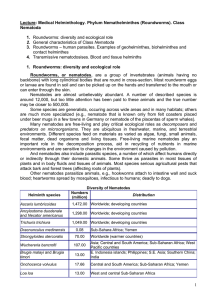
Lecture 13: “Roundworms (Nemathelminthes)
... can, under certain circumstances, be picked up by humans. In dogs and cats, these wormss have a migratory cycle similar to that of A. lumbricoides. In humans, however, they fail to reach the intestine. Instead they remain active in other body tissue for some time. This state of larval migration is k ...
... can, under certain circumstances, be picked up by humans. In dogs and cats, these wormss have a migratory cycle similar to that of A. lumbricoides. In humans, however, they fail to reach the intestine. Instead they remain active in other body tissue for some time. This state of larval migration is k ...
Bloodborne Pathogens
... Carrier state can lead to chronic liver disease, cirrhosis (10 year latency), or cancer (alcohol is strong co-factor) Leading cause of liver transplant in U.S. ...
... Carrier state can lead to chronic liver disease, cirrhosis (10 year latency), or cancer (alcohol is strong co-factor) Leading cause of liver transplant in U.S. ...
Insights from Economic-Epidemiology
... infections is < 0.5% after an intensive ‘‘search-and-destroy’’ campaign, compared with 50% in some areas In Siouxland (Iowa, Nebraska, S. Dakota), an epidemic of VRE was reversed Regionally coordinated response to epidemic Does this explain higher prevalence of ARB in areas with high concentration o ...
... infections is < 0.5% after an intensive ‘‘search-and-destroy’’ campaign, compared with 50% in some areas In Siouxland (Iowa, Nebraska, S. Dakota), an epidemic of VRE was reversed Regionally coordinated response to epidemic Does this explain higher prevalence of ARB in areas with high concentration o ...
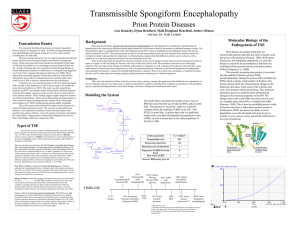
Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathies
... Lisa Kennedy, Dylan Bradford, Madi Hoagland Henefield, Anders Ohman Advisor: Dr. Todd Livdahl ...
... Lisa Kennedy, Dylan Bradford, Madi Hoagland Henefield, Anders Ohman Advisor: Dr. Todd Livdahl ...
Document
... – Administration of antigens so patient actively mounts a protective immune response ...
... – Administration of antigens so patient actively mounts a protective immune response ...
STD/STI Outline 1. STD/STI – Sexually transmitted disease or
... On genitals b. On cervix 2. Appear 1-3 month after infection 3. Once the warts appear the virus is with you for life ...
... On genitals b. On cervix 2. Appear 1-3 month after infection 3. Once the warts appear the virus is with you for life ...
Disease and Globalization
... continue to spread. AIDS, tuberculomillion people now diagnosed with people Health Organization and America’s sis, and malaria kill approximately 6 AIDS worldwide, for example, 95 halfway Center for Disease Control and million people a year, which is about percent live in the developing world around ...
... continue to spread. AIDS, tuberculomillion people now diagnosed with people Health Organization and America’s sis, and malaria kill approximately 6 AIDS worldwide, for example, 95 halfway Center for Disease Control and million people a year, which is about percent live in the developing world around ...
Control
... bacteria are most commonly introduced into a planting site on or in planting material. Wounds that commonly serve as infection sites are those made during pruning, machinery operations, freezing injury, growth cracks, soil insects and any other factor that causes injury to plant tissues. Bacteria ar ...
... bacteria are most commonly introduced into a planting site on or in planting material. Wounds that commonly serve as infection sites are those made during pruning, machinery operations, freezing injury, growth cracks, soil insects and any other factor that causes injury to plant tissues. Bacteria ar ...
Lyme Disease
... Also called: TB Tuberculosis (TB) is a bacterial infection caused by a germ called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The bacteria usually attack the lungs, but they can also damage other parts of the body. TB spreads through the air when a person with TB of the lungs or throat coughs, sneezes or talks. If ...
... Also called: TB Tuberculosis (TB) is a bacterial infection caused by a germ called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The bacteria usually attack the lungs, but they can also damage other parts of the body. TB spreads through the air when a person with TB of the lungs or throat coughs, sneezes or talks. If ...
infectious diseases
... Other diseases, including certain forms of hepatitis, can be transmitted among users of injected drugs through blood from shared syringes. HIV can be transmitted through blood or sexual contact. ...
... Other diseases, including certain forms of hepatitis, can be transmitted among users of injected drugs through blood from shared syringes. HIV can be transmitted through blood or sexual contact. ...
Bloodborne Pathogens
... Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is the pathogen that causes HIV infection and is transmitted from one person to another by blood, semen, vaginal secretions and breast milk. HIV attacks the immune system and cause AIDS. The infected person can be without symptoms or illness for 10-20 years and fee ...
... Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is the pathogen that causes HIV infection and is transmitted from one person to another by blood, semen, vaginal secretions and breast milk. HIV attacks the immune system and cause AIDS. The infected person can be without symptoms or illness for 10-20 years and fee ...
Chagas disease

Chagas disease, also known as American trypanosomiasis, is a tropical parasitic disease caused by the protozoan Trypanosoma cruzi. It is spread mostly by insects known as triatominae or kissing bugs. The symptoms change over the course of the infection. In the early stage, symptoms are typically either not present or mild and may include fever, swollen lymph nodes, headaches, or local swelling at the site of the bite. After 8–12 weeks, individuals enter the chronic phase of disease and in 60–70% it never produces further symptoms. The other 30 to 40% of people develop further symptoms 10 to 30 years after the initial infection, including enlargement of the ventricles of the heart in 20 to 30%, leading to heart failure. An enlarged esophagus or an enlarged colon may also occur in 10% of people.T. cruzi is commonly spread to humans and other mammals by the blood-sucking ""kissing bugs"" of the subfamily Triatominae. These insects are known by a number of local names, including: vinchuca in Argentina, Bolivia, Chile and Paraguay, barbeiro (the barber) in Brazil, pito in Colombia, chinche in Central America, and chipo in Venezuela. The disease may also be spread through blood transfusion, organ transplantation, eating food contaminated with the parasites, and by vertical transmission (from a mother to her fetus). Diagnosis of early disease is by finding the parasite in the blood using a microscope. Chronic disease is diagnosed by finding antibodies for T. cruzi in the blood.Prevention mostly involves eliminating kissing bugs and avoiding their bites. Other preventative efforts include screening blood used for transfusions. A vaccine has not been developed as of 2013. Early infections are treatable with the medication benznidazole or nifurtimox. Medication nearly always results in a cure if given early, but becomes less effective the longer a person has had Chagas disease. When used in chronic disease, medication may delay or prevent the development of end–stage symptoms. Benznidazole and nifurtimox cause temporary side effects in up to 40% of people including skin disorders, brain toxicity, and digestive system irritation.It is estimated that 7 to 8 million people, mostly in Mexico, Central America and South America, have Chagas disease as of 2013. In 2006, Chagas was estimated to result in 12,500 deaths per year. Most people with the disease are poor, and most people with the disease do not realize they are infected. Large-scale population movements have increased the areas where Chagas disease is found and these include many European countries and the United States. These areas have also seen an increase in the years up to 2014. The disease was first described in 1909 by Carlos Chagas after whom it is named. It affects more than 150 other animals.