* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download STD/STI Outline 1. STD/STI – Sexually transmitted disease or
Cryptosporidiosis wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
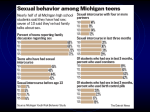
STD/STI Outline STD/STI – Sexually transmitted disease or infection A. Infectious diseases spread from person to person through sexual contact 2. STI - Sexually transmitted Infection A. For infection to occur they must come in contact with STD B. Vaginal, Anal, Oral or skin to skin contact 3. High risk behaviors A. Being sexually active with more than one person 1. Typically unaware of partners past 2. Even one partner may be risky B. Unprotected sex 1. Even condoms are only 85% effective in preventing pregnancy 2. Not effective against HPV, Pubic Lice, Scabies, etc. 3. Abstinence is only 100% C. Selecting high risk partners 1. History of activity 2. Intravenous drug users D. Using alcohol & other drugs 1. Inhibitions are lowered 2. Study 25% of SA teens were under the influence 4. Must understand the causes and consequences of these activities A. Most people (including you) do not know the consequences of these diseases B. They are serious infections and can alter the rest of your life C. STD 1. Some are incurable a. Genital Herpes b. HIV c. HPV d. Hepatitis B (HBV) e. HCV 2. Some cause cancer a. Hepatitis B 1. Liver Cancer b. HPV 1. Cervical Cancer 3. Can create reproductive problems a. PID 1. Can cause sterility 2. Damages reproductive organs 3. Can be treated with antibiotics 4. Ectopic Pregnancy a. is a pregnancy that develops outside a woman's uterus (womb) 4. Can be passed to child a. Before birth b. During birth c. After Birth 1. Damage may occur to variety of systems 2. Premature birth may occur 3. Death d. Examples 1. Chlamydia Gonorrhea HPV (genital warts) a. Warts in throat 4. Genital Herpes a. Can be fatal for infants or cause nerve damage 5. Syphilis 5. Protection (may not protect you from all STD’s) A. Condom B. Use a moisture barrier, such as a dental dam, cut-open latex condom or plastic wrap, when having oral intercourse with a female partner. 6. Abstinence A. Use of Refusal skills B. Associate with friends who share your views C. Keep in mind 1. Sexual activity is the cause 2. The STD is the effect 1. 2. 3. 7. Diseases and their symptoms/treatments A. HPV 1. Virus a. Most common STD in US 1. Can Cause Genital warts 2. Can be asymptomatic a. 50-75% of males and female acquire this during their life b. 30 different types of this virus can infect the genitals b. Pap Test can determine in females 2. Affects a. Genital Area b. Is cause for Cervical, Penile and anal cancers 3. Symptoms a. Warts 1. Pink or reddish wart a. On genitals b. On cervix 2. Appear 1-3 month after infection 3. Once the warts appear the virus is with you for life 4. Treatment a. Only for warts not HPV b. Asymptomatic cases can be cleared by immune system B. Chlamydia 1. Bacterium 2. Affects a. Urethra-males b. Vagina – females 3. More than 4 million cases reported each year a. Common cause of sterility b. If left Untreated 1. Nongonococcal Urethritis (NGU) a. Affects both males & Females Symptoms (if symptoms occur) a. Males 1. Pain and burning during urination 2. Discharge b. Females 1. Less obvious symptoms 2. May have discharge 3. Pain in pelvic region 4. Pain during urination 5. Can lead to PID a. Painful infection of 1. Ovaries 2. Fallopian Tubes 3. Uterus 5. Treatment a. Antibiotics C. Gonorrhea 1. Bacteria 2. Affects (mucous membranes) a. Lining of urethra in Males b. Vagina, Cervix in females 3. Symptoms a. Males 1. Pain and burning during urination 2. Whitish Discharge b. Females 1. Discharge from vagina 2. Burning during urination 3. Irregular menstruation 4. Abdominal pain c. Appearance of symptoms 1. 3days to 3 weeks after contact 2. May subside and go away a. But disease stays in body 4. Treatment a. Antibiotics D. Trichomoniasis 1. Protozoan 2. Affects a. Females 1. Vaginal & Bladder Infections 2. Can lead to NGU b. Males 1. Rarely infected 2. Carriers 3. Symptoms a. Females 1. Vaginal burning, itching 2. Painful urination 3. Greenish/yellow discharge 4. Can cause vaginitis a. Inflammation 4. Carried by males in semen other bodily fluids Secondary infection a. Bacteria, protozoa, virus 5. Can be discovered in a Pap Test 4. Treatment a. prescription drugs, either metronidazole or tinidazole E. Genital Herpes 1. Virus a. Simplex Type 1 = cold sores b. Simplex Type 2 = Genital Sores 1. Both can cause sore in mouth or on genitals 2. Affects a. Genital area b. Mouth c. 20% of adolescent population has this d. Twice as common in adults 20 –29 than 20 years ago 3. Symptoms a. Most people are asymptomatic 1. Can still spread disease b. Blister like sores on genital area c. Cold or flu like symptoms d. Appearance 1. Periodically 2. Outbreaks are worse in initial stages of disease 4. Treatment a. Only to control symptoms b. Once you have it you have it for life F. Syphilis 1. Bacterium – spirochete 2. Affects a. Initially genitals b. Later many parts of the body 3. Symptoms a. Sore on genitals 1. Heals on own b. If left untreated 1. Infection moves to blood stream 2. Travels to other parts of the body a. Internal organs 3. Causes a. Blindness b. Convulsions c. Heart disease G. Other Common STD’s 1. Chancroid a. Bacteria b. Symptoms 1. Sores or bumps on the genitals c. Affects 1. Sores 2. Infection in Lymph glands in groin area d. Treatment 1. 2. Antibiotics 2. Hepatitis B (HBV) a. Virus b. Symptoms 1. 90% asymptomatic 2. Jaundice 3. Vomiting, nausea 4. Loss of appetite c. Affects 1. Cirrhosis of Liver 2. Cancer of Liver d. Treatment/Prevention 1. Antiviral drugs but no cure 2. Vaccine 3. Bacterial Vaginosis a. Bacteria b. Symptoms 1. Abnormal a. Discharge b. Odor c. Itching 2. Pain during urination c. Affects 1. Can lead to PID d. Treatment 1. Antibiotics 4. Hepatitis C (HCV) a. Virus b. Symptoms 1. Often asymptomatic c. Affects 1. Liver Disease d. Treatment 1. Antiviral drugs but no cure 5. LGV a. Bacteria b. Symptoms 1. Male/Female 2. Small painless ulcers on the genitals 3. Swelling of the genitals 4. Anal bleeding/pus, painful bowel movements and swollen lymph nodes c. Affects 1. Development of strictures (narrowing or tightening of a body passage) in the rectum or vagina. d. Treatment 1. Antibiotics 6. Scabies a. Parasite/Protozoan b. Symptoms 1. Severe, persistent itching, Pimple-like rash 2. Symptoms may not show for 2-6 weeks after infection c. Affects 1. d. Prevalence is estimated at 300 million people infected worldwide annually, 1 million people in the US alone e. Scabies can be spread thru sexual contact, clothes, towels, bedding, any fabric, prolonged skin contact. f. Treatment 1. ‘Scabicide’ lotion or cream 2. Wash all bedding, clothing, or fabric (scabies can only live 2-3 days without a human host) 3. Infected sores from itching may need to be treated with antibiotics 7. Pubic Lice a. Protozoan Parasite b. Symptoms 1. Itching and irritation in the genital area c. Treatment 1. Prescription or over-the-counter shampoo 2. Seeking Treatment A. Important personal responsibility 1. Regular Check-ups 2. If you think you have been exposed seek treatment B. Social obligation 1. Notifying partners