Disease/Disorder Matching Review List
... Chronic pain in muscles and soft tissues surrounding joints. Chronic pulmonary disease characterized by increase in the size of the alveolar clusters. Chronic, organic mental disorder, a form of pre-senile dementia due to atrophy of frontal neuron. Completely unexpected and unexplained death of an a ...
... Chronic pain in muscles and soft tissues surrounding joints. Chronic pulmonary disease characterized by increase in the size of the alveolar clusters. Chronic, organic mental disorder, a form of pre-senile dementia due to atrophy of frontal neuron. Completely unexpected and unexplained death of an a ...
Notes
... types enter through breaks in the skin or direct openings into the body including mucus membranes such as the nose, eyes, teats, and vaginal area ...
... types enter through breaks in the skin or direct openings into the body including mucus membranes such as the nose, eyes, teats, and vaginal area ...
Session 13 - Teaching Slides
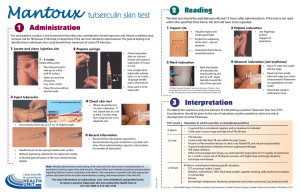
... Vietnam is among the 22 high burden countries that account for about 80% of new TB cases per year In 2010, in the general population (including HIV positives): • The incidence is 180/100,000 • The prevalence is 334/100,000 ...
... Vietnam is among the 22 high burden countries that account for about 80% of new TB cases per year In 2010, in the general population (including HIV positives): • The incidence is 180/100,000 • The prevalence is 334/100,000 ...
Chapter 19, Section 1 Infectious Disease
... and identify the kinds of organisms that cause disease. • Describe the methods in which pathogens enter the body. ...
... and identify the kinds of organisms that cause disease. • Describe the methods in which pathogens enter the body. ...
JHCC/GBEB-AR - Communicable Diseases
... The school administrator may, when he/she has reasonable cause to believe the student has a school restrictable disease, exclude that student from attendance until a physician, public health nurse or school nurse certifies that the student is not infectious to others; ...
... The school administrator may, when he/she has reasonable cause to believe the student has a school restrictable disease, exclude that student from attendance until a physician, public health nurse or school nurse certifies that the student is not infectious to others; ...
Pulmonary Infectious Diseases: Review Questions
... transbronchial biopsy, and open lung biopsy can aid in the diagnosis of TPE, they are not necessary to make the diagnosis1; they would be reasonable if results of the work-up for TPE were negative. Stool for ova and parasites are usually negative in TPE unless the patient is coinfected with another ...
... transbronchial biopsy, and open lung biopsy can aid in the diagnosis of TPE, they are not necessary to make the diagnosis1; they would be reasonable if results of the work-up for TPE were negative. Stool for ova and parasites are usually negative in TPE unless the patient is coinfected with another ...
1% (if treated)
... David W. Haas, M.D. Division of Infectious Diseases Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Nashville, Tennessee ...
... David W. Haas, M.D. Division of Infectious Diseases Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Nashville, Tennessee ...
Synopsis - Web Adventures
... of Germany. He earned his MD degree in 1866. Dr. Koch made numerous contributions to early microbiology, working on the human diseases anthrax, tuberculosis, cholera, and malaria. He also studied tropical disease in cattle. In 1905, he received the Noble Prize for his work on tuberculosis. His major ...
... of Germany. He earned his MD degree in 1866. Dr. Koch made numerous contributions to early microbiology, working on the human diseases anthrax, tuberculosis, cholera, and malaria. He also studied tropical disease in cattle. In 1905, he received the Noble Prize for his work on tuberculosis. His major ...
Chapter 7
... are three types (Figure 7.1). Mutualism is a condition in which both species benefit (for example, lichens represent a mutualistic relationship between a fungus and an alga; Figure 7.3). In commensalism, one species benefits but the other neither benefits nor is harmed (the human normal flora receive ...
... are three types (Figure 7.1). Mutualism is a condition in which both species benefit (for example, lichens represent a mutualistic relationship between a fungus and an alga; Figure 7.3). In commensalism, one species benefits but the other neither benefits nor is harmed (the human normal flora receive ...
L6- InfectionChain.Prevention.share.KSA.2015
... pattern of any infectious disease among that community • The level of susceptibility increases as new infants are born, an epidemic will develop after accumulation of susceptible • It could be produced artificially by immunization, or naturally after infection ...
... pattern of any infectious disease among that community • The level of susceptibility increases as new infants are born, an epidemic will develop after accumulation of susceptible • It could be produced artificially by immunization, or naturally after infection ...
Chapter 14 The Hematopoietic and Lymphatic Systems
... Diffuse marrow hyperplasia of unknown cause. Overproduction of white cells, platelets, and red cells. Some cases evolve into granulocytic leukemia. COMPLICATIONS As a result of increased blood viscosity. Increased tendency to thromboses. TREATMENT Primary polycythemia treated by drugs that suppress ...
... Diffuse marrow hyperplasia of unknown cause. Overproduction of white cells, platelets, and red cells. Some cases evolve into granulocytic leukemia. COMPLICATIONS As a result of increased blood viscosity. Increased tendency to thromboses. TREATMENT Primary polycythemia treated by drugs that suppress ...
TRAVEL - Cromwell Vets
... diseases that aren’t present in the UK. British animals appear to be more susceptible to these diseases, as unlike their foreign counterparts, they have not developed any kind of natural resistance in the population. Rabies - This extremely dangerous virus is transmitted though a bite from an infect ...
... diseases that aren’t present in the UK. British animals appear to be more susceptible to these diseases, as unlike their foreign counterparts, they have not developed any kind of natural resistance in the population. Rabies - This extremely dangerous virus is transmitted though a bite from an infect ...
Feline Infectious Peritonitis (FIP)
... Early signs include loss of appetite, high fever, and labored breathing. These early signs are very vague and can mimic other diseases. As the disease progresses signs may include difficulty breathing, distended abdomen, and weight loss. Death will eventually occur. There are two forms the dis ...
... Early signs include loss of appetite, high fever, and labored breathing. These early signs are very vague and can mimic other diseases. As the disease progresses signs may include difficulty breathing, distended abdomen, and weight loss. Death will eventually occur. There are two forms the dis ...
Fever of Unknown Origin (FUO)
... PPD pos. < 50% of pts with TB and FUO, sputum samples pos. ¼ of patients Abscesses usually in abdomen or pelvis with some pre-disposing cause (e.g. recent surgery, diab., biliary tract disease, etc.) other infections: osteomyelitis, endocarditis (e.g. in pts with recent antibiotic use) Mal ...
... PPD pos. < 50% of pts with TB and FUO, sputum samples pos. ¼ of patients Abscesses usually in abdomen or pelvis with some pre-disposing cause (e.g. recent surgery, diab., biliary tract disease, etc.) other infections: osteomyelitis, endocarditis (e.g. in pts with recent antibiotic use) Mal ...
Life course epidemiology and infectious diseases
... through the immune system. This system is clearly the critical one when considering infections. Thus much of the interest in infectious disease lifecourse epidemiology will revolve around influences on the integrity and functionality of immunity. The natural history of immune responses is still rela ...
... through the immune system. This system is clearly the critical one when considering infections. Thus much of the interest in infectious disease lifecourse epidemiology will revolve around influences on the integrity and functionality of immunity. The natural history of immune responses is still rela ...
Immune System Presentation
... and working properly? To keep the immune system working properly you need to eat healthy to build up a good immune function. Immunisation can also prevent diseases by the immune system fighting germs. When you go on a holiday overseas you need to get an inoculation which protects the body from forei ...
... and working properly? To keep the immune system working properly you need to eat healthy to build up a good immune function. Immunisation can also prevent diseases by the immune system fighting germs. When you go on a holiday overseas you need to get an inoculation which protects the body from forei ...
Chapter 23: Cardiovascular, Lymphatic, and Systemic Infectious
... • Parasites invade RBCs, causing – anemia – headache – occasionally meningitis • The Trypanosoma Parasites Can Cause Life-Threatening Systemic Diseases • Trypanosomiasis is the name for 2 diseases caused by species of Trypanosoma • Human African sleeping sickness is caused by T. brucei • It is trans ...
... • Parasites invade RBCs, causing – anemia – headache – occasionally meningitis • The Trypanosoma Parasites Can Cause Life-Threatening Systemic Diseases • Trypanosomiasis is the name for 2 diseases caused by species of Trypanosoma • Human African sleeping sickness is caused by T. brucei • It is trans ...
Read questions first Scan for important nouns and verbs
... poorly cooked seafood taken from contaminated waters. The disease is especially prevalent after a natural disaster or other destruction that results in a lack of fresh water. When sewer systems fail so that waste travels into the rivers or streams and 10 piped water is not available so that people m ...
... poorly cooked seafood taken from contaminated waters. The disease is especially prevalent after a natural disaster or other destruction that results in a lack of fresh water. When sewer systems fail so that waste travels into the rivers or streams and 10 piped water is not available so that people m ...
Protists and Human Disease
... Members of the genus Trypanosoma are flagellate protozoa that cause sleeping sickness, which is common in Africa. They also cause Chagas disease, which is common in South America. The parasites are spread by insect vectors. The vector for Chagas disease is shown in Figure 1.1. Trypanosoma parasites ...
... Members of the genus Trypanosoma are flagellate protozoa that cause sleeping sickness, which is common in Africa. They also cause Chagas disease, which is common in South America. The parasites are spread by insect vectors. The vector for Chagas disease is shown in Figure 1.1. Trypanosoma parasites ...
Management Of Newly Introduced Sheep
... for 4 weeks. This includes purchased animals but also those returning from away grazing. Any lameness, illness or deaths should be investigated to prevent the spread of infectious disease outwith the group. Diseases such as salmonellosis or pasteurellosis could flare up after the stress of sales, mi ...
... for 4 weeks. This includes purchased animals but also those returning from away grazing. Any lameness, illness or deaths should be investigated to prevent the spread of infectious disease outwith the group. Diseases such as salmonellosis or pasteurellosis could flare up after the stress of sales, mi ...
Visceral leishmaniasis

Visceral leishmaniasis (VL), also known as kala-azar, black fever, and Dumdum fever, is the most severe form of leishmaniasis. Leishmaniasis is a disease caused by protozoan parasites of the Leishmania genus. This disease is the second-largest parasitic killer in the world (after malaria), responsible for an estimated 200,000 to 400,000 infections each year worldwide. The parasite migrates to the internal organs such as the liver, spleen (hence ""visceral""), and bone marrow, and, if left untreated, will almost always result in the death of the host. Signs and symptoms include fever, weight loss, fatigue, anemia, and substantial swelling of the liver and spleen. Of particular concern, according to the World Health Organization (WHO), is the emerging problem of HIV/VL co-infection.