Lecture 7: Life`s Information Molecule II
... • Most eukaryotic genes have long noncoding stretches of nucleotides that lie between coding regions • These noncoding regions are called intervening sequences, or introns • The other regions are called exons because they are eventually expressed, usually translated into amino acid sequences • RNA ...
... • Most eukaryotic genes have long noncoding stretches of nucleotides that lie between coding regions • These noncoding regions are called intervening sequences, or introns • The other regions are called exons because they are eventually expressed, usually translated into amino acid sequences • RNA ...
Department of Health Informatics Telephone: [973] 972
... oligogenic traits. Careful consideration needs to be given to the design aspects of such studies in order to maximize their potential for detecting disease-causing variants. These include subject ascertainment and DNA marker map selection, as well as their effects on the statistical analysis of the ...
... oligogenic traits. Careful consideration needs to be given to the design aspects of such studies in order to maximize their potential for detecting disease-causing variants. These include subject ascertainment and DNA marker map selection, as well as their effects on the statistical analysis of the ...
Understanding DNA
... A. mRNA enters the ribosome B. 3 mRNA nucleotides (codons) pair up with 3 tRNA nucleotides (anticodons) C. amino acids are added until the “stop” message is reached ...
... A. mRNA enters the ribosome B. 3 mRNA nucleotides (codons) pair up with 3 tRNA nucleotides (anticodons) C. amino acids are added until the “stop” message is reached ...
gene regulation
... amino acid tryptophan. All 5 genes are transcribed together as a unit called an operon, which produces a single long piece of mRNA for all the genes. Operon is a segment of DNA that includes a specific gene sequence and the promotor/operator region for that gene. RNA polymerase binds to a promoter l ...
... amino acid tryptophan. All 5 genes are transcribed together as a unit called an operon, which produces a single long piece of mRNA for all the genes. Operon is a segment of DNA that includes a specific gene sequence and the promotor/operator region for that gene. RNA polymerase binds to a promoter l ...
Slide 1
... – Local minimum problem. If an error is introduced early in the alignment process, it is impossible to correct this later in the procedure. – Arbitrary alignment. ...
... – Local minimum problem. If an error is introduced early in the alignment process, it is impossible to correct this later in the procedure. – Arbitrary alignment. ...
No Slide Title
... bioluminescence in the firefly. This is one of the few examples of a bioluminescent reaction that only requires enzyme, substrate and ATP. Rapid and simple biochemical assay. Read in minutes Two phases to the reaction, flash and glow. These can be used to design different types of assays. • Addition ...
... bioluminescence in the firefly. This is one of the few examples of a bioluminescent reaction that only requires enzyme, substrate and ATP. Rapid and simple biochemical assay. Read in minutes Two phases to the reaction, flash and glow. These can be used to design different types of assays. • Addition ...
File S4 (DOC) - cloudfront.net
... All the results of simulating estrogen receptor bound to DNA generated data which were remarkably different from the results obtained for the dimer unbound to DNA. However, as stated in the text, we cannot predict which residues are going to recognize precisely interaction with its respective ligand ...
... All the results of simulating estrogen receptor bound to DNA generated data which were remarkably different from the results obtained for the dimer unbound to DNA. However, as stated in the text, we cannot predict which residues are going to recognize precisely interaction with its respective ligand ...
Transcription - Winston Knoll Collegiate
... The enzyme RNA polymerase finds the beginning of a protein recipe called the promotor - promotor = a series of nucleotides that indicate the start of a protein recipe The RNA polymerase opens the DNA molecule at the promotor ...
... The enzyme RNA polymerase finds the beginning of a protein recipe called the promotor - promotor = a series of nucleotides that indicate the start of a protein recipe The RNA polymerase opens the DNA molecule at the promotor ...
Chipster What is it?
... Pathway analysis RNA-seq: quantitation and detection of novel splice variants Integration with target gene expression ...
... Pathway analysis RNA-seq: quantitation and detection of novel splice variants Integration with target gene expression ...
"Amino Acid Substitutions: Effects on Protein Stability". In
... The easiest way to construct random mutations throughout the whole gene is to do PCR with a low-fidelity polymerase, which makes random mistakes during DNA replication. Such ‘error-prone PCR’ can be combined with DNA shuffling (Figure 4) so that diverse sequences can be rapidly generated and selected. ...
... The easiest way to construct random mutations throughout the whole gene is to do PCR with a low-fidelity polymerase, which makes random mistakes during DNA replication. Such ‘error-prone PCR’ can be combined with DNA shuffling (Figure 4) so that diverse sequences can be rapidly generated and selected. ...
A bioinformatika elméleti alapjai 4
... Examples for aggregation in bioinformatics Single proteins, genes: constructing protein/gene similarity from local similarities (BLAST) Inferring homolgy. Proteomics: Constructing protein similarities from peptide fragment similarities. Inferring protein presence. Genomics1: Aggregating a lon ...
... Examples for aggregation in bioinformatics Single proteins, genes: constructing protein/gene similarity from local similarities (BLAST) Inferring homolgy. Proteomics: Constructing protein similarities from peptide fragment similarities. Inferring protein presence. Genomics1: Aggregating a lon ...
Open Reading Frames and Codon Bias in Streptomyces coelicolor
... over thirty members of the heat shock protein 70 (HSP-70) family that have sense antisense open reading frames (SAS ORFs) (manuscript in preparation). In an attempt to identify other families of proteins having a similar bias in gene composition and to further explore the possible implications of th ...
... over thirty members of the heat shock protein 70 (HSP-70) family that have sense antisense open reading frames (SAS ORFs) (manuscript in preparation). In an attempt to identify other families of proteins having a similar bias in gene composition and to further explore the possible implications of th ...
DNA2016 - saddlespace.org
... EX: Reading strand from 5’ to 3’ left top down is the same as right bottom up. AP Biology ...
... EX: Reading strand from 5’ to 3’ left top down is the same as right bottom up. AP Biology ...
Document
... producing reproducible patterns of fragments). This step produces a huge number of DNA fragments that are short enough to be separated by gel electrophoresis. After running the gel the DNA fragments are transferred to a nylon or nitrocellulose membrane to which the DNA sticks in the same pattern as ...
... producing reproducible patterns of fragments). This step produces a huge number of DNA fragments that are short enough to be separated by gel electrophoresis. After running the gel the DNA fragments are transferred to a nylon or nitrocellulose membrane to which the DNA sticks in the same pattern as ...
No Slide Title
... How does RNA polymerase work and what does it make? How does it know where to start and stop? How does a ribosome work and what does it make? How does it know where to start and stop? If the DNA in every cell in your body is the ...
... How does RNA polymerase work and what does it make? How does it know where to start and stop? How does a ribosome work and what does it make? How does it know where to start and stop? If the DNA in every cell in your body is the ...
Slide 1
... The dimer is constructed such that it has bifold symmetry allowing the recognition helix of the second protein sub-unit to make the same groove binding interactions as the first. The distance between the recognition helices is 34 angstroms which corresponds to one turn of the B-DNA double helix. Th ...
... The dimer is constructed such that it has bifold symmetry allowing the recognition helix of the second protein sub-unit to make the same groove binding interactions as the first. The distance between the recognition helices is 34 angstroms which corresponds to one turn of the B-DNA double helix. Th ...
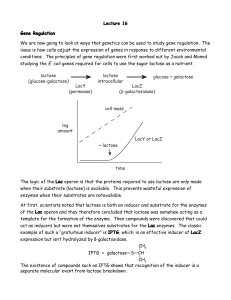
Lecture 16 Gene Regulation
... We are now going to look at ways that genetics can be used to study gene regulation. The issue is how cells adjust the expression of genes in response to different environmental conditions. The principles of gene regulation were first worked out by Jacob and Monod studying the E. coli genes required ...
... We are now going to look at ways that genetics can be used to study gene regulation. The issue is how cells adjust the expression of genes in response to different environmental conditions. The principles of gene regulation were first worked out by Jacob and Monod studying the E. coli genes required ...
DNA and Gene Expression - Zanichelli online per la scuola
... purines is the same as the amount of pyrimidines. ...
... purines is the same as the amount of pyrimidines. ...
Introduction to Biotechnology Gel Electrophoresis and DNA Analysis
... Standard with known amount/mass (create standard curve), helps to check if cyber green will stain DNA, determine mass or amount of DNA for unknown samples by comparing with the standard (AKA Ladder DNA). ...
... Standard with known amount/mass (create standard curve), helps to check if cyber green will stain DNA, determine mass or amount of DNA for unknown samples by comparing with the standard (AKA Ladder DNA). ...
Introduction to Protein Structure
... 3. Why were N, O, P, S used? Unpaired electrons are critical to Hydrogen bonding, which is critical for proteins, DNA and RNA to ...
... 3. Why were N, O, P, S used? Unpaired electrons are critical to Hydrogen bonding, which is critical for proteins, DNA and RNA to ...


![Department of Health Informatics Telephone: [973] 972](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/004679878_1-03eb978d1f17f67290cf7a537be7e13d-300x300.png)