Science.7 Circulatory System Homework Due on
... Blood is a substance that is always flowing through our bodies. Your blood is pumped by your heart. It travels through thousands of miles of blood vessels right within your own body. Your blood carries nutrients, water, oxygen and waste products to and from your body cells. A young person has about ...
... Blood is a substance that is always flowing through our bodies. Your blood is pumped by your heart. It travels through thousands of miles of blood vessels right within your own body. Your blood carries nutrients, water, oxygen and waste products to and from your body cells. A young person has about ...
File
... Movements of the ribs, rib muscles and diaphragm allow air into and out of the lungs: this is called breathing or ventilation – when we breathe in, we inhale and when we breathe out, we exhale ...
... Movements of the ribs, rib muscles and diaphragm allow air into and out of the lungs: this is called breathing or ventilation – when we breathe in, we inhale and when we breathe out, we exhale ...
Cells and Systems Pbl2
... was later named after him. AD is most commonly noticed in the elderly aged 65 and above. By 2050, AD will have affected 1 in 85 people globally. Sometimes the early symptoms are commonly mistaken for age-related problems that most elderly experience. At first difficulty of movement occurs and later ...
... was later named after him. AD is most commonly noticed in the elderly aged 65 and above. By 2050, AD will have affected 1 in 85 people globally. Sometimes the early symptoms are commonly mistaken for age-related problems that most elderly experience. At first difficulty of movement occurs and later ...
Blood Last modified January 9, 2017 at 5:21 am
... A) is the most common blood protein. B) is secreted by the kidney. C) stimulates the red bone marrow to generate red blood cells. D) is an enzyme that functions in blood clotting. E) increases the ability of plasma to transport carbon dioxide. Question # 4 When the oxygen level in the tissues is low ...
... A) is the most common blood protein. B) is secreted by the kidney. C) stimulates the red bone marrow to generate red blood cells. D) is an enzyme that functions in blood clotting. E) increases the ability of plasma to transport carbon dioxide. Question # 4 When the oxygen level in the tissues is low ...
Biology Lesson 1 Keeping Healthy Learning Objectives: In this
... Heart - Position and structure, Cardiac cycle, Control of heart rate, Cardiac output, Blood pressure, Blood supply to the heart Double circulation - Pulmonary and systemic circulation Blood vessels - Artery, veins and capillary, Exchange of materials between blood and body cells Blood - Composition ...
... Heart - Position and structure, Cardiac cycle, Control of heart rate, Cardiac output, Blood pressure, Blood supply to the heart Double circulation - Pulmonary and systemic circulation Blood vessels - Artery, veins and capillary, Exchange of materials between blood and body cells Blood - Composition ...
Lecture 14 - UC Davis Statistics
... the second sample is 7.1 with a standard deviation 1.5. Is the new product better than the old product by one unit? Test at 0.05 level of ...
... the second sample is 7.1 with a standard deviation 1.5. Is the new product better than the old product by one unit? Test at 0.05 level of ...
OrganizationofBodyBodySystems
... •Consists of : •Heart •Blood vessels •Arteries •Arterioles •Capillaries •Venules •Veins •Function •Pumps blood to all body tissue •Blood transports oxygen and nutrients to the tissue •Blood returns waste products from the tissue to the kidneys and Co2 to the lungs •Plays an important part in the imm ...
... •Consists of : •Heart •Blood vessels •Arteries •Arterioles •Capillaries •Venules •Veins •Function •Pumps blood to all body tissue •Blood transports oxygen and nutrients to the tissue •Blood returns waste products from the tissue to the kidneys and Co2 to the lungs •Plays an important part in the imm ...
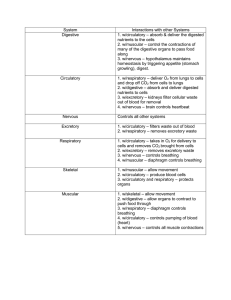
Interactions between the Nervous System and…
... used by the body's cells and tissues. The food is broken apart through chewing and stomach churning, but also chemically -- through the stomach's acid-loving enzymes, and on to the small intestine, which receives pancreatic enzymes and juices specially tailored to dissolve and digest proteins, carbo ...
... used by the body's cells and tissues. The food is broken apart through chewing and stomach churning, but also chemically -- through the stomach's acid-loving enzymes, and on to the small intestine, which receives pancreatic enzymes and juices specially tailored to dissolve and digest proteins, carbo ...
Human Body Introduction
... Different tissue types work together within organs: Muscle tissue (most abundant): controls internal movements of materials (ex: blood, food) Epithelial tissue: closely packed cells covering the surface of the body and line internal organs (ex: inside chambers of heart, glands) Connective t ...
... Different tissue types work together within organs: Muscle tissue (most abundant): controls internal movements of materials (ex: blood, food) Epithelial tissue: closely packed cells covering the surface of the body and line internal organs (ex: inside chambers of heart, glands) Connective t ...
Human Body Systems
... and your blood. • This system controls how your muscles move your bones by carrying electrical signals from your brain, to your spinal cord, to your muscles. • This system is a transportation system that carries food and oxygen to each cell and then takes away cells’ wastes. • This system supports t ...
... and your blood. • This system controls how your muscles move your bones by carrying electrical signals from your brain, to your spinal cord, to your muscles. • This system is a transportation system that carries food and oxygen to each cell and then takes away cells’ wastes. • This system supports t ...
Circulation lesson 2 vertebrate circulation systemic circulation
... 2. Anatomy of the C. S. The main organs are: • The Heart. It is a muscular organ that pumps blood and fluids trough an elaborate system of vessels. • Blood: liquid tissue that transports nutrients, waste and hormones. contains 3 different types of cells (Red, white, and platelets) and ...
... 2. Anatomy of the C. S. The main organs are: • The Heart. It is a muscular organ that pumps blood and fluids trough an elaborate system of vessels. • Blood: liquid tissue that transports nutrients, waste and hormones. contains 3 different types of cells (Red, white, and platelets) and ...
Blood - Dr Magrann
... CIRCULATORY SYSTEM FUNCTIONS: 1. Transports oxygen and nutrients to cells 2. Removes carbon dioxide and wastes from cells 3. Immunity (protects from disease) 4. Temperature regulation (cold, constricts; hot, dilates) 5. Helps prevent loss of blood by clotting 6. Transports hormones 7. Erection of th ...
... CIRCULATORY SYSTEM FUNCTIONS: 1. Transports oxygen and nutrients to cells 2. Removes carbon dioxide and wastes from cells 3. Immunity (protects from disease) 4. Temperature regulation (cold, constricts; hot, dilates) 5. Helps prevent loss of blood by clotting 6. Transports hormones 7. Erection of th ...
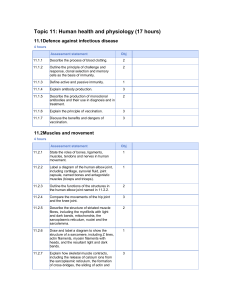
Topic 11: Human health and physiology (17 hours)
... Draw and label a diagram to show the structure of a sarcomere, including Z lines, actin filaments, myosin filaments with heads, and the resultant light and dark ...
... Draw and label a diagram to show the structure of a sarcomere, including Z lines, actin filaments, myosin filaments with heads, and the resultant light and dark ...
Biology 2154 Study Guide #2 Chapter 20: 1. List structural
... 3. Identify the major classification of epithelial, connective muscle and nervous tissue discussed in class. 4. Prepare to give an example of one location where each type of epithelial tissue is found 5. Identify the 6 types of connective tissue. 6. What are the characteristics of each type of muscl ...
... 3. Identify the major classification of epithelial, connective muscle and nervous tissue discussed in class. 4. Prepare to give an example of one location where each type of epithelial tissue is found 5. Identify the 6 types of connective tissue. 6. What are the characteristics of each type of muscl ...
A. The Respiratory Cycle
... 3. Air moves via this route: nasal cavities >>> pharynx >>> larynx >>> vocal cords (space between is glottis) >>> trachea >>> bronchi >>> bronchioles respiratory bronchioles >>> alveoli. a) The trachea leads from the larynx downward to branch into two bronchi, which are lined with cilia and mucus to ...
... 3. Air moves via this route: nasal cavities >>> pharynx >>> larynx >>> vocal cords (space between is glottis) >>> trachea >>> bronchi >>> bronchioles respiratory bronchioles >>> alveoli. a) The trachea leads from the larynx downward to branch into two bronchi, which are lined with cilia and mucus to ...
Elementary Science 5E+ Lesson Plan Cycle
... activity begins. Provide each group of students with stopwatches or a clock with a second-hand. Challenge students to hypothesize what effect exercise will have on their heart rates. Have them first count the heart beats for thirty seconds. Have them record the number of beats for thirty seconds at ...
... activity begins. Provide each group of students with stopwatches or a clock with a second-hand. Challenge students to hypothesize what effect exercise will have on their heart rates. Have them first count the heart beats for thirty seconds. Have them record the number of beats for thirty seconds at ...
The Egyptian language school Science department Model answer of
... Question (7):1- By using lubricants and oils. They decrease the friction force between the objects so it is used in engines. 2- By using ball bearings. Because ball bearing decrease the friction area, so the friction force decrease ...
... Question (7):1- By using lubricants and oils. They decrease the friction force between the objects so it is used in engines. 2- By using ball bearings. Because ball bearing decrease the friction area, so the friction force decrease ...
How Does Your Body Take In Oxygen?
... • Many nutrients are simple kinds of sugar. • Cells use oxygen to break the sugar down into carbon dioxide and water. This releases energy. Sugar + Oxygen energy ...
... • Many nutrients are simple kinds of sugar. • Cells use oxygen to break the sugar down into carbon dioxide and water. This releases energy. Sugar + Oxygen energy ...
Chapter 50
... Characteristics of Blood Vessels • Capillaries – Every cell in the body is within 100 micrometers (μm) of a capillary – Although each capillary is very narrow, so many of them exist that the capillaries have the greatest total cross-sectional area of any other type of vessel • Slows blood flow to a ...
... Characteristics of Blood Vessels • Capillaries – Every cell in the body is within 100 micrometers (μm) of a capillary – Although each capillary is very narrow, so many of them exist that the capillaries have the greatest total cross-sectional area of any other type of vessel • Slows blood flow to a ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.