LIFE SCIENCE GLEs
... Compare and contrast the processes of asexual and sexual reproduction, including the type and number of cells involved (one body cell in asexual, two sex cells in sexual) and the number of gene sets (body cell has 2 sets, sex cells have 1 set each) passed from parent(s) to offspring). Identify examp ...
... Compare and contrast the processes of asexual and sexual reproduction, including the type and number of cells involved (one body cell in asexual, two sex cells in sexual) and the number of gene sets (body cell has 2 sets, sex cells have 1 set each) passed from parent(s) to offspring). Identify examp ...
06 Life Histories 2010
... • As life history traits contribute to reproductive success, they influence evolutionary fitness. • Life histories vary consistently with environmental factors; hence may be molded by natural selection. ...
... • As life history traits contribute to reproductive success, they influence evolutionary fitness. • Life histories vary consistently with environmental factors; hence may be molded by natural selection. ...
The Repatterning of Eukaryotic Genomes by Random Genetic Drift
... to promote new adaptive mutations is reduced by linkage, as favorable (nonallelic) mutations arising on homologous chromosomes cannot be simultaneously fixed unless recombination occurs between the two sites. These interference effects from linkage are expected to increase with increasing N, as a lar ...
... to promote new adaptive mutations is reduced by linkage, as favorable (nonallelic) mutations arising on homologous chromosomes cannot be simultaneously fixed unless recombination occurs between the two sites. These interference effects from linkage are expected to increase with increasing N, as a lar ...
06 Life Histories 2009
... reproductive success, they influence evolutionary fitness. • Life histories vary consistently with environmental factors; hence may be molded by natural selection. ...
... reproductive success, they influence evolutionary fitness. • Life histories vary consistently with environmental factors; hence may be molded by natural selection. ...
GENETICS & EVOLUTION: population genetics
... remain constant from generation to generation In a given population where gametes contribute to the next generation randomly, allele frequencies will not change Mendelian inheritance preserves genetic variation in a population ...
... remain constant from generation to generation In a given population where gametes contribute to the next generation randomly, allele frequencies will not change Mendelian inheritance preserves genetic variation in a population ...
EOC Review 2011 #5
... Anatomical comparisons (comparative morphology): Comparing anatomy and finding similarities, leads scientist to believe that some organisms have a common ancestor. o Homologous structures: Structures found in organisms that have a common ancestor. They have evidence of similar structures, the fore ...
... Anatomical comparisons (comparative morphology): Comparing anatomy and finding similarities, leads scientist to believe that some organisms have a common ancestor. o Homologous structures: Structures found in organisms that have a common ancestor. They have evidence of similar structures, the fore ...
Chapter 1 Notes
... For the HW equation to work, 5 conditions must be met - large population size - no migration - no mutations - random mating - no natural selection ...
... For the HW equation to work, 5 conditions must be met - large population size - no migration - no mutations - random mating - no natural selection ...
Chapter 1 Notes - Social Circle City Schools
... For the HW equation to work, 5 conditions must be met - large population size - no migration - no mutations - random mating - no natural selection ...
... For the HW equation to work, 5 conditions must be met - large population size - no migration - no mutations - random mating - no natural selection ...
ppt - eweb.furman.edu
... When lactose is present, E. coli produce three enzymes involved in lactose metabolism. Lactose is broken into glucose and galactose, and galactose is modified into glucose, too. Glucose is then metabolized in aerobic respiration pathways to harvest energy (ATP). When lactose is absent, E. coli does ...
... When lactose is present, E. coli produce three enzymes involved in lactose metabolism. Lactose is broken into glucose and galactose, and galactose is modified into glucose, too. Glucose is then metabolized in aerobic respiration pathways to harvest energy (ATP). When lactose is absent, E. coli does ...
Theme 1: Survival - Willmar Public Schools
... evolutionary relationships among species. * Recognize that artificial selection has led to offspring through successive generations that can be very different in appearance and behavior from their distant ancestors. * Explain why genetic variation within a population is essential for evolution to oc ...
... evolutionary relationships among species. * Recognize that artificial selection has led to offspring through successive generations that can be very different in appearance and behavior from their distant ancestors. * Explain why genetic variation within a population is essential for evolution to oc ...
The evolution of Populations
... What can cause microevolution in a population? A) Genetic Drift: is the change in allele frequency of a small population, due to chance. Two events that can reduce the size of a population: 1) Bottleneck = an environmental crisis may reduce the size of the original population and the small survivin ...
... What can cause microevolution in a population? A) Genetic Drift: is the change in allele frequency of a small population, due to chance. Two events that can reduce the size of a population: 1) Bottleneck = an environmental crisis may reduce the size of the original population and the small survivin ...
Examples of Natural Selection
... For many years scientists suspected that life changes over time, but they did not understand how it worked. Charles Darwin was the first person to offer the mechanism that is still accepted as true today. He called his theory of how evolution worked natural selection. Natural selection is the theory ...
... For many years scientists suspected that life changes over time, but they did not understand how it worked. Charles Darwin was the first person to offer the mechanism that is still accepted as true today. He called his theory of how evolution worked natural selection. Natural selection is the theory ...
BB - SmartSite
... were isolated from one another, they would adapt to their new environments and become increasingly dissimilar • Eventually, the populations would diverge into different species ...
... were isolated from one another, they would adapt to their new environments and become increasingly dissimilar • Eventually, the populations would diverge into different species ...
UNIT 7 NOTES
... unnoticed due to wobble effect. Sickle cell disorder is an exception. Chromosomal mutations that delete, disrupt, or rearrange many loci are typically harmful. Duplicated genes can take on new functions by further mutation. Changes in chromosome number often result in human disorders with developmen ...
... unnoticed due to wobble effect. Sickle cell disorder is an exception. Chromosomal mutations that delete, disrupt, or rearrange many loci are typically harmful. Duplicated genes can take on new functions by further mutation. Changes in chromosome number often result in human disorders with developmen ...
Outline
... Allopatric speciation of antelope squirrels on opposite rims of the Grand Canyon. Birds and other organisms that can disperse across the Grand Canyon have not diverged into different species on opposite rims. ...
... Allopatric speciation of antelope squirrels on opposite rims of the Grand Canyon. Birds and other organisms that can disperse across the Grand Canyon have not diverged into different species on opposite rims. ...
Evolution Review
... 1. Mutations provide the raw material for new variations. All other contributions to variation, listed here, occur by rearranging existing alleles into new combinations. Mutations, however, can invent alleles that never before existed in the gene pool. a. Antibiotic and pesticide resistance alleles ...
... 1. Mutations provide the raw material for new variations. All other contributions to variation, listed here, occur by rearranging existing alleles into new combinations. Mutations, however, can invent alleles that never before existed in the gene pool. a. Antibiotic and pesticide resistance alleles ...
Chapter 1 Notes - Pikeville Independent Schools
... For the HW equation to work, 5 conditions must be met - large population size - no migration - no mutations - random mating - no natural selection ...
... For the HW equation to work, 5 conditions must be met - large population size - no migration - no mutations - random mating - no natural selection ...
Unit 1 Topic 3 - Holy Cross Collegiate
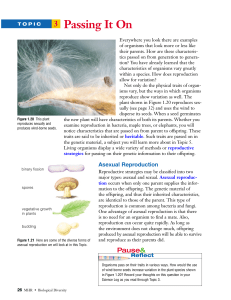
... of organisms that look more or less like their parents. How are these characteristics passed on from generation to generation? You have already learned that the characteristics of organisms vary greatly within a species. How does reproduction allow for variation? Not only do the physical traits of o ...
... of organisms that look more or less like their parents. How are these characteristics passed on from generation to generation? You have already learned that the characteristics of organisms vary greatly within a species. How does reproduction allow for variation? Not only do the physical traits of o ...
Topic 3 - Science 9 Jones
... of organisms that look more or less like their parents. How are these characteristics passed on from generation to generation? You have already learned that the characteristics of organisms vary greatly within a species. How does reproduction allow for variation? Not only do the physical traits of o ...
... of organisms that look more or less like their parents. How are these characteristics passed on from generation to generation? You have already learned that the characteristics of organisms vary greatly within a species. How does reproduction allow for variation? Not only do the physical traits of o ...
Sexual reproduction
... – Parent cell undergoes mitosis to form daughter cells – Mitosis in vegetative cells may be concurrent with budding to produce a daughter cell – May proceed through a spore form ...
... – Parent cell undergoes mitosis to form daughter cells – Mitosis in vegetative cells may be concurrent with budding to produce a daughter cell – May proceed through a spore form ...
Class 10th CBSE how do organisms Reproduction
... temperature were to be increased by global warming, most of these bacteria would die, but the few variants resistant to heat would servive and grow further, variation is thus useful for the survival of species over time. ...
... temperature were to be increased by global warming, most of these bacteria would die, but the few variants resistant to heat would servive and grow further, variation is thus useful for the survival of species over time. ...
major evolutionary transitions in flowering plant reproduction
... same position in the forest canopy are more closely related than would be expected by chance, as are species with particular pollinator syndromes (e.g., bee or bird). Transitions to generalist pollination are strongly associated with beetle and fly pollination and with position in the canopy above t ...
... same position in the forest canopy are more closely related than would be expected by chance, as are species with particular pollinator syndromes (e.g., bee or bird). Transitions to generalist pollination are strongly associated with beetle and fly pollination and with position in the canopy above t ...
AP Bio Evolution Lec Ch. 22-25
... • Mutations are changes in the nucleotide sequence of DNA • Mutations cause new genes and alleles to arise • Only mutations in cells that produce gametes can be passed to offspring ...
... • Mutations are changes in the nucleotide sequence of DNA • Mutations cause new genes and alleles to arise • Only mutations in cells that produce gametes can be passed to offspring ...
Lesson 1-AsexualInPlants
... – These organs have a store of food. Shoots grow from these organs bearing leaves and flowers. In the process, food is withdrawn from the underground storage organ which shrivels. As the leaves manufacture food, food is transported to the buds which gradually swell to become new underground stems. ...
... – These organs have a store of food. Shoots grow from these organs bearing leaves and flowers. In the process, food is withdrawn from the underground storage organ which shrivels. As the leaves manufacture food, food is transported to the buds which gradually swell to become new underground stems. ...
Evolution of sexual reproduction
.jpg?width=300)
The evolution of sexual reproduction describes how sexually reproducing animals, plants, fungi and protists evolved from a common ancestor that was a single celled eukaryotic species. There are a few species which have secondarily lost the ability to reproduce sexually, such as Bdelloidea and some parthenocarpic plants. The evolution of sex contains two related, yet distinct, themes: its origin and its maintenance. The maintenance of sexual reproduction in a highly competitive world has long been one of the major mysteries of biology given that asexual reproduction can reproduce much more quickly as 50% of offspring are not males, unable to produce offspring themselves. However, research published in 2015 indicates that sexual selection can explain the persistence of sexual reproduction.Since hypotheses for the origins of sex are difficult to test experimentally (outside of Evolutionary computation), most current work has focused on the maintenance of sexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction must offer significant fitness advantages to a species because despite the two-fold cost of sex, it dominates among multicellular forms of life, implying that the fitness of offspring produced outweighs the costs. Sexual reproduction derives from recombination, where parent genotypes are reorganized and shared with the offspring. This stands in contrast to single-parent asexual replication, where the offspring is identical to the parents. Recombination supplies two fault-tolerance mechanisms at the molecular level: recombinational DNA repair (promoted during meiosis because homologous chromosomes pair at that time) and complementation (also known as heterosis, hybrid vigor or masking of mutations). Sexual reproduction has probably contributed to the evolution of sexual dimorphism, where organisms within a species adopted different strategies of parental investment. Males adopt strategies with lower investment in individual gametes and may present a higher mutation rate, while females may invest more resources and serve to conserve better-adapted solutions.