CHAPTER 2 OBJECTIVE EXERCISE
... riglyceride phospholipid steroid energy cell membranes Chemical messengers (hormones),cell membranes ...
... riglyceride phospholipid steroid energy cell membranes Chemical messengers (hormones),cell membranes ...
Chapter 21 - Cengage Learning
... molecule are complementary. The three hydrogen bonds between the two molecules hold cytosine and guanine together. Adenine and thymine molecules on complementary DNA strands are also held together by hydrogen bonds. Two hydrogen bonds form between adenine and thymine molecules. 17. There is evidence ...
... molecule are complementary. The three hydrogen bonds between the two molecules hold cytosine and guanine together. Adenine and thymine molecules on complementary DNA strands are also held together by hydrogen bonds. Two hydrogen bonds form between adenine and thymine molecules. 17. There is evidence ...
the chemical constituents of cells constituents include
... • for energy production which have higher energy value than carbohydrate and protein • as structural materials in cell membrane • as stored energy in oils and fats • as good heat insulator to reduce heat loss • as constituent of vitamin D and hormones • as solvent for fat soluble vitamins ...
... • for energy production which have higher energy value than carbohydrate and protein • as structural materials in cell membrane • as stored energy in oils and fats • as good heat insulator to reduce heat loss • as constituent of vitamin D and hormones • as solvent for fat soluble vitamins ...
The Chemistry of the cell
... their active conformation. However, some proteins are helped and guided in the folding process by chaperone proteins • Many proteins have sugars, phosphate groups, fatty acids, and other molecules covalently attached to certain amino acids. Most of this is done in the endoplasmic reticulum. • Many p ...
... their active conformation. However, some proteins are helped and guided in the folding process by chaperone proteins • Many proteins have sugars, phosphate groups, fatty acids, and other molecules covalently attached to certain amino acids. Most of this is done in the endoplasmic reticulum. • Many p ...
Chapter 5: What are the major types of organic molecules?
... D. roles of lipids include serving as membrane structural components, as signaling molecules, and as energy storage molecules E. major classes of lipids that you need to know are triacylglycerols (fats), phospholipids, and terpenes F. triacylglycerols contain glycerol joined to three fatty acids 1. ...
... D. roles of lipids include serving as membrane structural components, as signaling molecules, and as energy storage molecules E. major classes of lipids that you need to know are triacylglycerols (fats), phospholipids, and terpenes F. triacylglycerols contain glycerol joined to three fatty acids 1. ...
Organic Molecules
... • Each amino acid unique due to the functional group located at the R position attached to the central carbon atom ...
... • Each amino acid unique due to the functional group located at the R position attached to the central carbon atom ...
Organic Molecules
... • Each amino acid unique due to the functional group located at the R position attached to the central carbon atom ...
... • Each amino acid unique due to the functional group located at the R position attached to the central carbon atom ...
Chapter 2 Review Sheet Name:_______________________
... 20. An ___enzyme__________ is made of proteins and catalyzes reactions 21. Monomers are linked together by the process of _____polymerization/dehydration synthesis____. 22. Polymers are broken apart by the process of ___hydrolysis________________. 23. The monomer of a nucleic acid is called a ____nu ...
... 20. An ___enzyme__________ is made of proteins and catalyzes reactions 21. Monomers are linked together by the process of _____polymerization/dehydration synthesis____. 22. Polymers are broken apart by the process of ___hydrolysis________________. 23. The monomer of a nucleic acid is called a ____nu ...
ERT320 BIOSEPARATION ENGINEERING
... Ribonucleotide acid (RNA) – polynucleotide containing only ribose sugar while deoxyribose (DNA) contains only deoxyriboses (DNA) (lacking a hydroxyl group at the 2’ position) The use of DNA in tiny quantities; large-scale purification – never been ...
... Ribonucleotide acid (RNA) – polynucleotide containing only ribose sugar while deoxyribose (DNA) contains only deoxyriboses (DNA) (lacking a hydroxyl group at the 2’ position) The use of DNA in tiny quantities; large-scale purification – never been ...
Amino Acid Catabolism
... Nitrogen Metabolism I (Ch 18) Amino Acid Oxidation and the Production of Urea ...
... Nitrogen Metabolism I (Ch 18) Amino Acid Oxidation and the Production of Urea ...
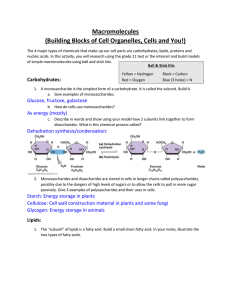
Macromolecules
... 3. Fatty acids can be attached (through dehydration synthesis) to different chemicals to perform different functions in the cell. Find two different types of lipids and record their function and the chemical that the fatty acids are attached to. ...
... 3. Fatty acids can be attached (through dehydration synthesis) to different chemicals to perform different functions in the cell. Find two different types of lipids and record their function and the chemical that the fatty acids are attached to. ...
Lab Protein and Amino Acids
... are not able to synthesize proteins in this way, so proteinaceous material must be obtained in the diet. Most protein in the body is used in body building and repair. The principal component of all enzymes is protein. While lipids and, to a lesser extent, carbohydrates are stored in the body ads an ...
... are not able to synthesize proteins in this way, so proteinaceous material must be obtained in the diet. Most protein in the body is used in body building and repair. The principal component of all enzymes is protein. While lipids and, to a lesser extent, carbohydrates are stored in the body ads an ...
CHEM 214 Elementary Biochemistry
... Any changes to the topics to be covered will be announced prior to the change. You are responsible for ALL the material covered in class and stated in the assigned chapters unless explicitly stated otherwise. There are no make-up quizzes or exams. An hourly exam missed for a valid reason (first disc ...
... Any changes to the topics to be covered will be announced prior to the change. You are responsible for ALL the material covered in class and stated in the assigned chapters unless explicitly stated otherwise. There are no make-up quizzes or exams. An hourly exam missed for a valid reason (first disc ...
Document
... All amino acids are identical in the amino and carboxyl groups. Any amino acid can be joined to any other amino acid by a peptide bond formed between these amino and carboxyl groups. Amino acids differ from each other in a side chain called the R-groups, which have a range of different properties. M ...
... All amino acids are identical in the amino and carboxyl groups. Any amino acid can be joined to any other amino acid by a peptide bond formed between these amino and carboxyl groups. Amino acids differ from each other in a side chain called the R-groups, which have a range of different properties. M ...
Sample%20Exam%20Protein%20ANSWERS
... Anfinson experiment described in class. The fact that the peptides react with this reducing agent tells you that the cysteines have indeed oxidized to form a C1-C6 disulfide, which creates a cyclic peptide of six amino acids 4. Use the Chou and Fassman rules to calculate the probabilities for this n ...
... Anfinson experiment described in class. The fact that the peptides react with this reducing agent tells you that the cysteines have indeed oxidized to form a C1-C6 disulfide, which creates a cyclic peptide of six amino acids 4. Use the Chou and Fassman rules to calculate the probabilities for this n ...
The citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle, tricarboxylic acid cycle)
... The citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle, tricarboxylic acid cycle) The citric acid cycle is a series of reactions in mitochondria that oxidize acetyl residues (as acetyl-CoA) and reduce coenzymes that upon reoxidation are linked to the formation of ATP. The citric acid cycle is the final common pathway f ...
... The citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle, tricarboxylic acid cycle) The citric acid cycle is a series of reactions in mitochondria that oxidize acetyl residues (as acetyl-CoA) and reduce coenzymes that upon reoxidation are linked to the formation of ATP. The citric acid cycle is the final common pathway f ...
Protein Structure HW Key
... increase of entropy of surroundings when water of hydration is displaced from nonpolar amino acids when they are brought together. 7. Give two ways amino acid sequences are determined. 1. from the DNA sequence. 2. from purification and enzymatic cleavage followed by sequential Edman degradation 8. A ...
... increase of entropy of surroundings when water of hydration is displaced from nonpolar amino acids when they are brought together. 7. Give two ways amino acid sequences are determined. 1. from the DNA sequence. 2. from purification and enzymatic cleavage followed by sequential Edman degradation 8. A ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS AND PROCESSING Protein biosynthesis is
... precursor is produced. A proprotein is an inactive protein containing one or more inhibitory peptides that can be activated when the inhibitory sequence is removed byproteolysis during posttranslational modification. A preprotein is a form that contains a signal sequence (an N-terminal signal peptid ...
... precursor is produced. A proprotein is an inactive protein containing one or more inhibitory peptides that can be activated when the inhibitory sequence is removed byproteolysis during posttranslational modification. A preprotein is a form that contains a signal sequence (an N-terminal signal peptid ...
Slide 1
... sequential loss of acetyl groups from carbon chain of fatty acid) – Energy yield depends on length of carbon chain (ex. 16C palmitic acid results in 129 ATPs, ~3.5x more than glucose) – Ketoacidosis: results if oxaloacetate in short supply; acetyl-CoA converted into ketones, which are weak acids; ca ...
... sequential loss of acetyl groups from carbon chain of fatty acid) – Energy yield depends on length of carbon chain (ex. 16C palmitic acid results in 129 ATPs, ~3.5x more than glucose) – Ketoacidosis: results if oxaloacetate in short supply; acetyl-CoA converted into ketones, which are weak acids; ca ...
SLIB biochemistry homework
... 23) Describe two dietary factors that are thought to increase levels of LDL cholesterol in the blood and explain why this might be dangerous to the individual. 24) Describe the difference in structure between linoleic and linolenic acid and explain why it is important in include these two acids in ...
... 23) Describe two dietary factors that are thought to increase levels of LDL cholesterol in the blood and explain why this might be dangerous to the individual. 24) Describe the difference in structure between linoleic and linolenic acid and explain why it is important in include these two acids in ...
Amino Acids as Acids, Bases and Buffers
... o Can be very short to very long § Dipeptide = two amino acids linked § Tripeptide = three amino acids linked Amino acids sometimes called RESIDUES Identity and function of a protein or peptide is determined by o Amino acid composition o Order of amino acids in the chain o Enormous variety of poss ...
... o Can be very short to very long § Dipeptide = two amino acids linked § Tripeptide = three amino acids linked Amino acids sometimes called RESIDUES Identity and function of a protein or peptide is determined by o Amino acid composition o Order of amino acids in the chain o Enormous variety of poss ...