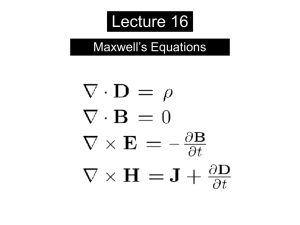
Lecture 16 - The Local Group
... •a changing magnetic field creates an induced electric field (Faraday’s Law) •a changing electric field also creates a magnetic field With the generalized version of Ampere’s Law, including displacement currents due to a changing electric field, Maxwell was able to unify the laws of electricity and ...
... •a changing magnetic field creates an induced electric field (Faraday’s Law) •a changing electric field also creates a magnetic field With the generalized version of Ampere’s Law, including displacement currents due to a changing electric field, Maxwell was able to unify the laws of electricity and ...
10-1 GLOSSARY TO TERMS A - Abbreviation for ampere. Absolute
... Circular Mil - An area equal to that of a circle with a diameter of .001 inch. It is used for measuring the cross section of wires. Coil - An inductive device created by looping turns of wire around a core. Collector - The element in a transistor which collects the current carriers. Commutator - Th ...
... Circular Mil - An area equal to that of a circle with a diameter of .001 inch. It is used for measuring the cross section of wires. Coil - An inductive device created by looping turns of wire around a core. Collector - The element in a transistor which collects the current carriers. Commutator - Th ...
Alternating Current (AC) Circuits
... Transformer is device used to increase or decrease the AC voltage in a circuit Typical device consists of two coils of wire primary and secondary wound around an iron core Primary coil with ...
... Transformer is device used to increase or decrease the AC voltage in a circuit Typical device consists of two coils of wire primary and secondary wound around an iron core Primary coil with ...
A lamp rated at 12 V 60 W is connected to the secondary coil
... The majority of candidates gained maximum marks in both parts (a)(i) and (a)(ii), but a few candidates, who scored reasonably well elsewhere, lost marks in part (ii) as a result of attempting unnecessarily complicated solutions involving expressions for loss of potential energy and gain of kinetic e ...
... The majority of candidates gained maximum marks in both parts (a)(i) and (a)(ii), but a few candidates, who scored reasonably well elsewhere, lost marks in part (ii) as a result of attempting unnecessarily complicated solutions involving expressions for loss of potential energy and gain of kinetic e ...
EI Measurements amp Instrumentation Two Marks QampA Unit I
... What are the constructional parts of current transformer Primary winding Secondary winding Magnetic core. Name the methods used for low resistance measurement. . What is the range of medium resistance Resistance of kilo ohms and above are usually termed as high resistance. . Define megger. How the p ...
... What are the constructional parts of current transformer Primary winding Secondary winding Magnetic core. Name the methods used for low resistance measurement. . What is the range of medium resistance Resistance of kilo ohms and above are usually termed as high resistance. . Define megger. How the p ...
CS5171BSTEVB CS5171/3 3.3 V to 5.0 V/ 400 mA Boost Regulator
... The CS5171 incorporates a current mode control scheme, in which the PWM ramp signal is derived from the power switch current. This ramp signal is compared to the output of the error amplifier to control the on-time of the power switch. The oscillator is only used here as a fixed frequency clock to e ...
... The CS5171 incorporates a current mode control scheme, in which the PWM ramp signal is derived from the power switch current. This ramp signal is compared to the output of the error amplifier to control the on-time of the power switch. The oscillator is only used here as a fixed frequency clock to e ...
dc generator - 123SeminarsOnly.com
... unsaturated condition the flux produced will be proportional to the field current. In order to implement shunt connection, the field winding is connected in parallel with the armature. It will be shown that subject to fulfillment of certain conditions, the machine may have sufficient field current d ...
... unsaturated condition the flux produced will be proportional to the field current. In order to implement shunt connection, the field winding is connected in parallel with the armature. It will be shown that subject to fulfillment of certain conditions, the machine may have sufficient field current d ...
Inductor

An inductor, also called a coil or reactor, is a passive two-terminal electrical component which resists changes in electric current passing through it. It consists of a conductor such as a wire, usually wound into a coil. When a current flows through it, energy is stored temporarily in a magnetic field in the coil. When the current flowing through an inductor changes, the time-varying magnetic field induces a voltage in the conductor, according to Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, According to Lenz's law the direction of induced e.m.f is always such that it opposes the change in current that created it. As a result, inductors always oppose a change in current, in the same way that a flywheel oppose a change in rotational velocity. Care should be taken not to confuse this with the resistance provided by a resistor.An inductor is characterized by its inductance, the ratio of the voltage to the rate of change of current, which has units of henries (H). Inductors have values that typically range from 1 µH (10−6H) to 1 H. Many inductors have a magnetic core made of iron or ferrite inside the coil, which serves to increase the magnetic field and thus the inductance. Along with capacitors and resistors, inductors are one of the three passive linear circuit elements that make up electric circuits. Inductors are widely used in alternating current (AC) electronic equipment, particularly in radio equipment. They are used to block AC while allowing DC to pass; inductors designed for this purpose are called chokes. They are also used in electronic filters to separate signals of different frequencies, and in combination with capacitors to make tuned circuits, used to tune radio and TV receivers.























