Engineering subunit association of multisubunit proteins
... soluble dimeric streptavidin in the presence of biotin. There are many examples of the successful production of individual subunits of multisubunit proteins using recombinant DNA technology. However, in most of these successful cases, each subunit functions independently of the other subunits in its ...
... soluble dimeric streptavidin in the presence of biotin. There are many examples of the successful production of individual subunits of multisubunit proteins using recombinant DNA technology. However, in most of these successful cases, each subunit functions independently of the other subunits in its ...
Structural and Biochemical Characterization of a Bifunctional
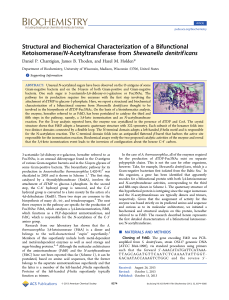
... structure shows that FdtD adopts a hexameric quaternary structure with 322 symmetry. Each subunit of the hexamer folds into two distinct domains connected by a flexible loop. The N-terminal domain adopts a left-handed β-helix motif and is responsible for the N-acetylation reaction. The C-terminal dom ...
... structure shows that FdtD adopts a hexameric quaternary structure with 322 symmetry. Each subunit of the hexamer folds into two distinct domains connected by a flexible loop. The N-terminal domain adopts a left-handed β-helix motif and is responsible for the N-acetylation reaction. The C-terminal dom ...
Multiple Lines of Evidence Localize Signaling
... Using GFP tagging, mitochondria have been visualized to undergo fusion, fission, and rapid movements, suggesting a dynamic interaction with components of the cytoskeleton (Sheahan et al., 2004, 2005; Logan, 2010). However, many of the specific proteins that mediate such processes remain unknown. Whi ...
... Using GFP tagging, mitochondria have been visualized to undergo fusion, fission, and rapid movements, suggesting a dynamic interaction with components of the cytoskeleton (Sheahan et al., 2004, 2005; Logan, 2010). However, many of the specific proteins that mediate such processes remain unknown. Whi ...
The green fluorescent protein: discovery
... the chemotactic swimming responses of bacteria (Kalir et al., 2001). By expressing full-length GFP-tagged proteins from their endogenous chromosomal locations at natural levels, it has become feasible to monitor the intracellular location and concentration spectrum of the whole proteasome of differe ...
... the chemotactic swimming responses of bacteria (Kalir et al., 2001). By expressing full-length GFP-tagged proteins from their endogenous chromosomal locations at natural levels, it has become feasible to monitor the intracellular location and concentration spectrum of the whole proteasome of differe ...
MODified™ Protein Domain Binding Kit Manual
... residues, phosphorylation of serine or threonine residues, citrullination and ubiquitination. These epigenetic marks play a role in the regulation of gene expression and chromatin state1-4. These histone modifications are recognized and bound by specific proteins that are coined ‘writers’ ‘readers’ ...
... residues, phosphorylation of serine or threonine residues, citrullination and ubiquitination. These epigenetic marks play a role in the regulation of gene expression and chromatin state1-4. These histone modifications are recognized and bound by specific proteins that are coined ‘writers’ ‘readers’ ...
The Cleavage and Polyadenylation Specificity Factor in Xenopus
... polyadenylation site (10, 47, 48). CPSF binds directly to this sequence and is required for both reactions (22, 29). In mammalian somatic cells, purified CPSF consists of four subunits, with molecular masses of 160, 100, 73, and 30 kDa (6, 18, 29). The 160-kDa subunit interacts with the AAUAAA seque ...
... polyadenylation site (10, 47, 48). CPSF binds directly to this sequence and is required for both reactions (22, 29). In mammalian somatic cells, purified CPSF consists of four subunits, with molecular masses of 160, 100, 73, and 30 kDa (6, 18, 29). The 160-kDa subunit interacts with the AAUAAA seque ...
Hydrolysis of a Series of Synthetic Peptide Substrates by the Human
... respective plasmids and the details of the purification protocol were as described previously (Knott et at., 1989). Briefly, the 3C proteins were purified from the soluble extract of induced cells using a two-stage high pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) procedure on a cation-exchange column (TSK ...
... respective plasmids and the details of the purification protocol were as described previously (Knott et at., 1989). Briefly, the 3C proteins were purified from the soluble extract of induced cells using a two-stage high pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) procedure on a cation-exchange column (TSK ...
A Diurnal Component to the Variation in Sieve Tube Amino Acid
... isoleucine (Leu/Ile), arginine, asparagine, glutamine, tyrosine (Tyr), and lysine (Lys) across the ST samples. These could not be explained by plant-to-plant variation. Statistical analyses revealed five analytes (Tyr, Lys, Phe, His/Val, and Leu/Ile) that showed striking covariation in their concent ...
... isoleucine (Leu/Ile), arginine, asparagine, glutamine, tyrosine (Tyr), and lysine (Lys) across the ST samples. These could not be explained by plant-to-plant variation. Statistical analyses revealed five analytes (Tyr, Lys, Phe, His/Val, and Leu/Ile) that showed striking covariation in their concent ...
Structure and function of the eukaryotic ADP
... extensively tested by 31P-NMR, where the enzyme proved to be highly specific for Dglucose. Residues important for catalysis have been modified by site-directed mutagenesis and the variants of H. sapiens ADPGK were purified and kinetic parameters determined. A single crystal was obtained from a trunc ...
... extensively tested by 31P-NMR, where the enzyme proved to be highly specific for Dglucose. Residues important for catalysis have been modified by site-directed mutagenesis and the variants of H. sapiens ADPGK were purified and kinetic parameters determined. A single crystal was obtained from a trunc ...
Nucleic Acids - Farmasi Unand
... sites for many ligands. Two other forms of DNA, the A and Z forms, have also been identified but it is not certain if these forms occur naturally in living ...
... sites for many ligands. Two other forms of DNA, the A and Z forms, have also been identified but it is not certain if these forms occur naturally in living ...
Protein metabolism in exercising human with special reference to
... If the body is in positive nitrogen balance, then protein is retained as new tissue is being synthesized. This is often observed in children, during pregnancy, in recovery from illness, and during resistance exercise training where protein synthesis occurs in muscle cells. A greater output of nitrog ...
... If the body is in positive nitrogen balance, then protein is retained as new tissue is being synthesized. This is often observed in children, during pregnancy, in recovery from illness, and during resistance exercise training where protein synthesis occurs in muscle cells. A greater output of nitrog ...
Abstract Background The present study aimed to compare the
... medicine [1], [2] and [3]. Wild ginseng is grown in wild environments without artificial intervention, while the growth conditions of cultivated ginseng are artificially controlled. The medicinal components of ginseng reach stable levels only when the ginseng has matured. Because of their different ...
... medicine [1], [2] and [3]. Wild ginseng is grown in wild environments without artificial intervention, while the growth conditions of cultivated ginseng are artificially controlled. The medicinal components of ginseng reach stable levels only when the ginseng has matured. Because of their different ...
A defined subset of adenylyl cyclases is regulated by bicarbonate ion.
... Spirulina cyaC and that this subgroup of class III ACs was distinct from the HCO3- nonresponsive mammalian tmACs2. A CLUSTALW alignment of the catalytic domains from a number of prokaryotic and eukaryotic ACs showed that the active site amino acids involved in divalent metal ion coordination (D650; ...
... Spirulina cyaC and that this subgroup of class III ACs was distinct from the HCO3- nonresponsive mammalian tmACs2. A CLUSTALW alignment of the catalytic domains from a number of prokaryotic and eukaryotic ACs showed that the active site amino acids involved in divalent metal ion coordination (D650; ...
Combining docking and molecular dynamic simulations in drug design
... The three dimensional (3-D) structure of both ligand and protein are necessary for the application of docking techniques. While the manifold of conformational structures of small molecules may be relatively easy to predict, the lowest energy conformation obtained may not correspond to that of the bo ...
... The three dimensional (3-D) structure of both ligand and protein are necessary for the application of docking techniques. While the manifold of conformational structures of small molecules may be relatively easy to predict, the lowest energy conformation obtained may not correspond to that of the bo ...
ref. #28 of the TIBS article
... Lys-series, with local maxima around positions ÿ1, 3 and 7 and minima around position 2, 5 and 10. Our interpretation of these results is based on the so-called snorkel model (Segrest et al., 1990), which has also been invoked to explain the membrane burial of the Ca of Lys40 in the M13 coat protein ...
... Lys-series, with local maxima around positions ÿ1, 3 and 7 and minima around position 2, 5 and 10. Our interpretation of these results is based on the so-called snorkel model (Segrest et al., 1990), which has also been invoked to explain the membrane burial of the Ca of Lys40 in the M13 coat protein ...
Rab Proteins and the Organization of Organelle Membrane Domains
... Phosphoinositide metabolism and Rab GTPase function are tightly interconnected and Rab proteins can directly bind PI kinases and phosphatases to generate lipid domains enriched in specific PIs (Jean and Kiger 2012). This is exemplified by the interaction of Rab5 with two PI3 kinases and two PI phosp ...
... Phosphoinositide metabolism and Rab GTPase function are tightly interconnected and Rab proteins can directly bind PI kinases and phosphatases to generate lipid domains enriched in specific PIs (Jean and Kiger 2012). This is exemplified by the interaction of Rab5 with two PI3 kinases and two PI phosp ...
Bacillus cereus
... Habitat; symbiosis; contributions to the environment. Pathology Considered non-pathogenic ...
... Habitat; symbiosis; contributions to the environment. Pathology Considered non-pathogenic ...
The final publication is available at Copyright - RiuNet
... domestic process, almost boiling water for a short time. ...
... domestic process, almost boiling water for a short time. ...
Formate Dehydrogenase, Molecular Modeling and Docking with
... Swiss. As shown in Fig. 2, the Formate dehydrogenase from O. parapolymorpha DL-1 was modeled into dimer structure. As shown in Fig. 3A, the Ramachandran plot for FDH suggested 87.1%, 12.6%, 0.3% and 0.0% for residues in most favoured regions, additional allowed regions, generously allowed regions an ...
... Swiss. As shown in Fig. 2, the Formate dehydrogenase from O. parapolymorpha DL-1 was modeled into dimer structure. As shown in Fig. 3A, the Ramachandran plot for FDH suggested 87.1%, 12.6%, 0.3% and 0.0% for residues in most favoured regions, additional allowed regions, generously allowed regions an ...
Lactobacillus plantarum - UEF Electronic Publications
... Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) are a heterogeneous group of organisms found in a wide range of environmental niches due to their large adaptation capacity. They are responsible for the fermentation of many fermented food and feed products because they can transform sugars into organic acids and decrease ...
... Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) are a heterogeneous group of organisms found in a wide range of environmental niches due to their large adaptation capacity. They are responsible for the fermentation of many fermented food and feed products because they can transform sugars into organic acids and decrease ...
functional and structural complexity of signal transduction via g
... of the ultimate goal of co-crystalizing activated heptahelical receptors and Gprotein heterotrimers. Several segments in the Gα molecule undergo structural changes upon GTP hydrolysis and are designated switch regions (Lambright et al 1994, Mixon et al 1995). The most dramatic changes occur in the s ...
... of the ultimate goal of co-crystalizing activated heptahelical receptors and Gprotein heterotrimers. Several segments in the Gα molecule undergo structural changes upon GTP hydrolysis and are designated switch regions (Lambright et al 1994, Mixon et al 1995). The most dramatic changes occur in the s ...
Amino Acid Interrelationships in Cysteine Toxicity in
... The existence of complex inter-relationships between amino acids in the growth and nutrition of micro-organisms and animals is well known. In several instances such antagonisms involve amino acids which possess structural similarities or are connected by interlinked metabolic pathways. The toxicity ...
... The existence of complex inter-relationships between amino acids in the growth and nutrition of micro-organisms and animals is well known. In several instances such antagonisms involve amino acids which possess structural similarities or are connected by interlinked metabolic pathways. The toxicity ...
Selected reaction monitoring applied to proteomics
... fragmentation pattern and the ability of the search engine to reliably assign the amino acid sequence. In contrast, peptides with fewer fragments, e.g. short amino acid sequences or the presence of proline residues often yield fewer but more intense signals. Such peptides may not be reported in disc ...
... fragmentation pattern and the ability of the search engine to reliably assign the amino acid sequence. In contrast, peptides with fewer fragments, e.g. short amino acid sequences or the presence of proline residues often yield fewer but more intense signals. Such peptides may not be reported in disc ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.