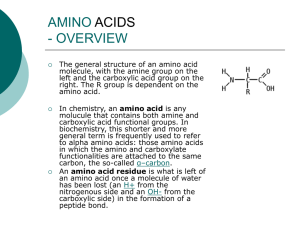
Amino Acids
... • Virtually every life process depends on proteins. • Proteins display an incredible diversity of functions, yet all share the common structural feature of being linear polymers of amino acids. • For example, enzymes and polypeptide hormones direct and regulate metabolism in the body, whereas contra ...
... • Virtually every life process depends on proteins. • Proteins display an incredible diversity of functions, yet all share the common structural feature of being linear polymers of amino acids. • For example, enzymes and polypeptide hormones direct and regulate metabolism in the body, whereas contra ...
Rapid Sample Preparation and HPLC-ESI- TOFMS Analysis of Derivatized Amino Acids Introduction
... Due to poor resolution of the isomeric pairs 1MHIS/3MHIS and LEU/ILE these compounds were reported as single peaks. In addition, THR was found to exactly coelute with GPR and so could not be automatically found. However, this compound could be detected by manual inspection of the mass spectral data ...
... Due to poor resolution of the isomeric pairs 1MHIS/3MHIS and LEU/ILE these compounds were reported as single peaks. In addition, THR was found to exactly coelute with GPR and so could not be automatically found. However, this compound could be detected by manual inspection of the mass spectral data ...
Exam III answer key - Chemistry Courses: About
... a. Uses pyruvate and aspartate for its biosynthesis lysine b. Uses two pyruvates and an acetyl CoA for its biosynthesis leucine c. Derives a methyl group via a B-12 mediated transformation methionine d. The herbicide roundup (glyphosate) targets this enzyme EPSP synthase e. Derives one of its carbon ...
... a. Uses pyruvate and aspartate for its biosynthesis lysine b. Uses two pyruvates and an acetyl CoA for its biosynthesis leucine c. Derives a methyl group via a B-12 mediated transformation methionine d. The herbicide roundup (glyphosate) targets this enzyme EPSP synthase e. Derives one of its carbon ...
British Journal of Dairy Sciences 3(2): 9-13, 2013
... phenylalanine while the non-essential amino acids detected were arginine, aspartic acid, serine, glutamic acid, proline, glycine, alanine, cysteine and tyrosine. The results show that the seventeen amino acids tested were present in all the samples in various amounts. For all the amino acids tested, ...
... phenylalanine while the non-essential amino acids detected were arginine, aspartic acid, serine, glutamic acid, proline, glycine, alanine, cysteine and tyrosine. The results show that the seventeen amino acids tested were present in all the samples in various amounts. For all the amino acids tested, ...
Peptides and proteins Chapter 36:
... acids is termed a protein. However, interleukins, cytokines, and interferon are also sometimes referred to as peptides, even though they possess a much higher molecular weight (Figure 36.2). Sometimes the distinction between the two categories relies more on the function of the molecule rather than ...
... acids is termed a protein. However, interleukins, cytokines, and interferon are also sometimes referred to as peptides, even though they possess a much higher molecular weight (Figure 36.2). Sometimes the distinction between the two categories relies more on the function of the molecule rather than ...
National Center for Biotechnology Information
... user to input a protein or DNA sequence and performing a search for structures of similar sequence. Steps for performing a protein BLAST search will be detailed, however a DNA search is very much similar. From the main page (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/), click BLAST Click Standard protein-prote ...
... user to input a protein or DNA sequence and performing a search for structures of similar sequence. Steps for performing a protein BLAST search will be detailed, however a DNA search is very much similar. From the main page (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/), click BLAST Click Standard protein-prote ...
... important residues and helix-packing interactions (11). In general, the biochemical studies correctly identified mechanistically critical residues in the LacY ligand-binding site. However, an additional important observation from the structures of LacY, GlpT, and other membrane proteins is that tran ...
No Slide Title
... One can only transfer information if the similarity is significantly high between the two sequences. Schneider (group of Sander) determined the “threshold curve” for transferring structural information from one known protein structure to another protein sequence: If the sequences are > 80 aa long, t ...
... One can only transfer information if the similarity is significantly high between the two sequences. Schneider (group of Sander) determined the “threshold curve” for transferring structural information from one known protein structure to another protein sequence: If the sequences are > 80 aa long, t ...
No Slide Title - Docenti.unina
... Water is very happy in bulk water because there it has on average 3.6 H-bonds and about six degrees of freedom. So, whenever we discuss protein structure, folding, and stability, it is all the entropy of water, and that is called the hydrophobic effect. ...
... Water is very happy in bulk water because there it has on average 3.6 H-bonds and about six degrees of freedom. So, whenever we discuss protein structure, folding, and stability, it is all the entropy of water, and that is called the hydrophobic effect. ...
Chapter 5 Macromolecules
... catalyst to speed up chemical reactions • Enzymes can perform their functions repeatedly, functioning as workhorses that carry out the processes of life ...
... catalyst to speed up chemical reactions • Enzymes can perform their functions repeatedly, functioning as workhorses that carry out the processes of life ...
amino acids - UniMAP Portal
... isomerism, because two groups on the central carbon atom are identical In cysteine, the L-S and D-R assignment is reversed to L-R and D-S. Cysteine is structured similarly (with respect to glyceraldehyde) to the other amino acids but the sulfur atom alters the interpretation of the Cahn Ingold Prelo ...
... isomerism, because two groups on the central carbon atom are identical In cysteine, the L-S and D-R assignment is reversed to L-R and D-S. Cysteine is structured similarly (with respect to glyceraldehyde) to the other amino acids but the sulfur atom alters the interpretation of the Cahn Ingold Prelo ...
Untitled
... machine made up of RNA and protein, called the ribosome. The ribosome is able to catalyze the polymerization of a protein chain at the rate of up to five amino acids per second. Small proteins of 100 – 200 amino acids are therefore made in a minute or less. ...
... machine made up of RNA and protein, called the ribosome. The ribosome is able to catalyze the polymerization of a protein chain at the rate of up to five amino acids per second. Small proteins of 100 – 200 amino acids are therefore made in a minute or less. ...
Structure of the Reovirus Membrane
... residues in two discontinuous polypeptide-chain segments (279–305 and 515–640). There are five ␣ helices (␣F–␣J) and a short  strand (25). Helices F, G, and J are an antiparallel bundle linking domains II and IV. Helices H and I and the exposed bridge between them project laterally, forming a crad ...
... residues in two discontinuous polypeptide-chain segments (279–305 and 515–640). There are five ␣ helices (␣F–␣J) and a short  strand (25). Helices F, G, and J are an antiparallel bundle linking domains II and IV. Helices H and I and the exposed bridge between them project laterally, forming a crad ...
Click Here To View Ebook
... throughout the day due to excess post exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC) thus increasin g resting metabolic rate up to 24 hours after a HIIT workout [1]. This means that you should be eating more on days you are working out in order to not only fuel your muscles pre-workout but also to aid their rep ...
... throughout the day due to excess post exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC) thus increasin g resting metabolic rate up to 24 hours after a HIIT workout [1]. This means that you should be eating more on days you are working out in order to not only fuel your muscles pre-workout but also to aid their rep ...
Characterisation and functional properties of watermelon (Citrullus
... emulsify soups and stews that provide proteins in the diet.5 The seeds are also reported to possess medicinal properties and are used to treat chronic or acute eczema.4 Watermelon seeds have been reported to contain high levels of proteins2,3,6 and lipids.7 Arginine, glutamic acid, aspartic acid and ...
... emulsify soups and stews that provide proteins in the diet.5 The seeds are also reported to possess medicinal properties and are used to treat chronic or acute eczema.4 Watermelon seeds have been reported to contain high levels of proteins2,3,6 and lipids.7 Arginine, glutamic acid, aspartic acid and ...
A Chemical Look at Proteins: Workhorses of the Cell
... RNA. These polymers are comprised of only four different building blocks each and they are highly negatively charged. DNA has a single structure -- the double helix -- and a single function that is explained by its structure. Its function is to transmit information and it does so in two ways -- thro ...
... RNA. These polymers are comprised of only four different building blocks each and they are highly negatively charged. DNA has a single structure -- the double helix -- and a single function that is explained by its structure. Its function is to transmit information and it does so in two ways -- thro ...
Review on G protein coupled receptors A Satish Chandra, M Rama
... activates a G protein, because the structure of the inactive receptor was solved, leaving open the question of the activation mechanism and the structure of the active receptor. Thus, new structural approaches are needed to address these questions. Keywords: GPCRs, ...
... activates a G protein, because the structure of the inactive receptor was solved, leaving open the question of the activation mechanism and the structure of the active receptor. Thus, new structural approaches are needed to address these questions. Keywords: GPCRs, ...
Nucleic Acids
... 1) Name the monomer of nucleic acids. 2) Draw & Label a nucleotide. 3) How are the four nitrogen bases of DNA abbreviated? RNA? 4) What does the phosphate molecule of a nucleotide bond with? 5) What do you call a section of DNA that codes for a specific protein? 6) If the DNA nitrogen bases were TAC ...
... 1) Name the monomer of nucleic acids. 2) Draw & Label a nucleotide. 3) How are the four nitrogen bases of DNA abbreviated? RNA? 4) What does the phosphate molecule of a nucleotide bond with? 5) What do you call a section of DNA that codes for a specific protein? 6) If the DNA nitrogen bases were TAC ...
Probing proteinâmembrane interactions using optical traps
... 7. Probing protein–membrane interactions using optical traps One of the proteins involved in the process of synaptic vesicle fusion in the brain are the Doc2 (double C2 domain) proteins [170]. There are three Doc2 family proteins: Doc2a,-b, and -c, of which a,b are expressed in the brain [171]. Doc ...
... 7. Probing protein–membrane interactions using optical traps One of the proteins involved in the process of synaptic vesicle fusion in the brain are the Doc2 (double C2 domain) proteins [170]. There are three Doc2 family proteins: Doc2a,-b, and -c, of which a,b are expressed in the brain [171]. Doc ...
Enzymes - Kevan Kruger
... What is the importance of enzymes in the body? Where are enzymes synthesized? What is their molecular structure and chemical make up? Where are enzymes manufactured? What is the function of enzymes in cells? How do enzymes lower the activation energy of a reaction? Give five specific examples of enz ...
... What is the importance of enzymes in the body? Where are enzymes synthesized? What is their molecular structure and chemical make up? Where are enzymes manufactured? What is the function of enzymes in cells? How do enzymes lower the activation energy of a reaction? Give five specific examples of enz ...
Protein translocation across mitochondrial membranes
... recognized both by MOM72 and MOM19. Direct interaction of precursor proteins with MOM72 and MOM 19 was demonstrated by co-immunoprecipitation of MOM72 with bound precursor or crosslinking of precursor with h.10M19(2’52Yi. A 32 kDa protein of yeast mitochondria (P32) was identified as a putative prot ...
... recognized both by MOM72 and MOM19. Direct interaction of precursor proteins with MOM72 and MOM 19 was demonstrated by co-immunoprecipitation of MOM72 with bound precursor or crosslinking of precursor with h.10M19(2’52Yi. A 32 kDa protein of yeast mitochondria (P32) was identified as a putative prot ...
Identifying proteins required for chromatin organization using a GFP
... to bypass cellular checkpoints and divide uncontrollably. Gene expression can be affected by a number of factors such as chromatin organization. When the chromatin organization is disrupted in the nucleus, this distorts the ability of DNA regulatory elements and transcriptional machinery from intera ...
... to bypass cellular checkpoints and divide uncontrollably. Gene expression can be affected by a number of factors such as chromatin organization. When the chromatin organization is disrupted in the nucleus, this distorts the ability of DNA regulatory elements and transcriptional machinery from intera ...
Chapter 7 (Nov 12-13)
... membrane that is selective for a particular solute. (right) Other transport proteins shuttle a substance from one side to the other by changing shape. Some of these proteins hydrolyze ATP as an energy source to actively pump substances across the membrane. ATP (b) Enzymatic activity. A protein built ...
... membrane that is selective for a particular solute. (right) Other transport proteins shuttle a substance from one side to the other by changing shape. Some of these proteins hydrolyze ATP as an energy source to actively pump substances across the membrane. ATP (b) Enzymatic activity. A protein built ...
structure-helix-text
... Interactions (electrostatic or hydrophobic) between R groups situated 3 to 4 amino acid residues away (stabilizes) ...
... Interactions (electrostatic or hydrophobic) between R groups situated 3 to 4 amino acid residues away (stabilizes) ...
Untitled
... machine made up of RNA and protein, called the ribosome. The ribosome is able to catalyze the polymerization of a protein chain at the rate of up to five amino acids per second. Small proteins of 100 – 200 amino acids are therefore made in a minute or less. ...
... machine made up of RNA and protein, called the ribosome. The ribosome is able to catalyze the polymerization of a protein chain at the rate of up to five amino acids per second. Small proteins of 100 – 200 amino acids are therefore made in a minute or less. ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.