Course Title - Positive Networking
... The growth percentage (Magic number) How to increase prices for your business ...
... The growth percentage (Magic number) How to increase prices for your business ...
Economic Simulation
... Cartograms are maps in which country size is dependent on a particular variable. They are used as an efficient method to communicate information on relative country data In this project a rectangular cartogram scaled to GDP will be used. ...
... Cartograms are maps in which country size is dependent on a particular variable. They are used as an efficient method to communicate information on relative country data In this project a rectangular cartogram scaled to GDP will be used. ...
Human_Capital_and_Capital_Goods
... Entrepreneurship – innovators (creating new products) – The entrepreneur is the driving force behind production. – Entrepreneurs introduce new products and new techniques – Risk takers- the people who take chances. They do this because they anticipate that they will make profits. But they may also s ...
... Entrepreneurship – innovators (creating new products) – The entrepreneur is the driving force behind production. – Entrepreneurs introduce new products and new techniques – Risk takers- the people who take chances. They do this because they anticipate that they will make profits. But they may also s ...
The Factors of Production - Danville
... Entrepreneur, a risk-taker in search of profits who does something new with existing resources. Some people are special because they are the innovators responsible for much of the change in our economy. • They provide the initiative that combines the resources of land, labor, and capital into new pr ...
... Entrepreneur, a risk-taker in search of profits who does something new with existing resources. Some people are special because they are the innovators responsible for much of the change in our economy. • They provide the initiative that combines the resources of land, labor, and capital into new pr ...
Karl Marx
... material process of private property, as this occurs in reality, in general and abstract formulas which then serve it as laws. It does not comprehend these laws…” “…in other words, what should be explained is assumed.” (656) “The only motive forces which political economy recognizes are avarice and ...
... material process of private property, as this occurs in reality, in general and abstract formulas which then serve it as laws. It does not comprehend these laws…” “…in other words, what should be explained is assumed.” (656) “The only motive forces which political economy recognizes are avarice and ...
Critics of Friedman
... companies ought to maximize profit above all else. • Companies pay what the market determines is a fair price for the materials and labor needed for production of goods and services. • Customers pay what the goods and services are worth to them. • Profit therefore represents the net contribution the ...
... companies ought to maximize profit above all else. • Companies pay what the market determines is a fair price for the materials and labor needed for production of goods and services. • Customers pay what the goods and services are worth to them. • Profit therefore represents the net contribution the ...
Economics Notes Chapter One Scarcity – the
... [stocks, bonds, and money] Can’t produce anything directly with these ...
... [stocks, bonds, and money] Can’t produce anything directly with these ...
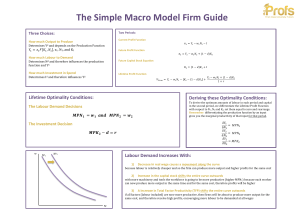
The Simple Macro Model Firm Guide
... if all factors (capital included) are going to be more productive in the future, then firms will be about to produce more output for the same cost, and therefore receive high profits, encouraging mo ...
... if all factors (capital included) are going to be more productive in the future, then firms will be about to produce more output for the same cost, and therefore receive high profits, encouraging mo ...
IS CAPITALISM GOOD FOR THE ECONOMY?
... ‘utilitarian’ framework that capital accumulation plays an instrumental role in the process of optimizing ‘real capitalist wealth’. The reason for this is straightforward - if we assume that capitalists maximize their individual ...
... ‘utilitarian’ framework that capital accumulation plays an instrumental role in the process of optimizing ‘real capitalist wealth’. The reason for this is straightforward - if we assume that capitalists maximize their individual ...
Ch - OnCourse
... The money used to buy the tools and equipment needed for production is known as financial capital Actions in one part of country or world that have an economic impact on what happens else where are examples of economic interdependence Microeconomics ...
... The money used to buy the tools and equipment needed for production is known as financial capital Actions in one part of country or world that have an economic impact on what happens else where are examples of economic interdependence Microeconomics ...
Ch1
... ◦ The situation where some necessities, such as water, have little monetary value, whereas some non-necessities, such as diamonds have a much higher value ...
... ◦ The situation where some necessities, such as water, have little monetary value, whereas some non-necessities, such as diamonds have a much higher value ...
The `Marginal Revolution` in Economics against the Labour Theory
... Distribution, 1889”] (cf. Marx’s “falling rate of profit”) has to be countered. Employers do it through the absolute and relative lengthening of the working day and constant technological development, constant centralization with big capitals swallowing the smaller ones, and concentration via measu ...
... Distribution, 1889”] (cf. Marx’s “falling rate of profit”) has to be countered. Employers do it through the absolute and relative lengthening of the working day and constant technological development, constant centralization with big capitals swallowing the smaller ones, and concentration via measu ...
Theories - TPP-PED
... -free market would tend towards an equilibrium e.g. supply and demand PARETO OPTIMALITY-free exchange will always achieve the best outcome NECESSARY CONDITIONS FOR ASSUMPTIONS TO WORK 1. Perfect competition (with a monopoly can set the price) 2. Perfect knowledge for all market participation e.g. kn ...
... -free market would tend towards an equilibrium e.g. supply and demand PARETO OPTIMALITY-free exchange will always achieve the best outcome NECESSARY CONDITIONS FOR ASSUMPTIONS TO WORK 1. Perfect competition (with a monopoly can set the price) 2. Perfect knowledge for all market participation e.g. kn ...
Tugan-Baranovsky, Mikhail Ivanovich (1865–1919)
... His major contribution to economic theory was Osnovy politicheskoi ekonomii (1917), which went through many editions, and represented an attempt at a synthesis between Marxist political economy (the labour theory of value) and subjective value theory. He considered that the marginalists ignored ‘the ...
... His major contribution to economic theory was Osnovy politicheskoi ekonomii (1917), which went through many editions, and represented an attempt at a synthesis between Marxist political economy (the labour theory of value) and subjective value theory. He considered that the marginalists ignored ‘the ...
Social Action Theory, Feminism and The New Right
... To understand social change we need to understand social interaction Critical of Marx’s view that social change is linked to social class. Felt Marx over emphasised importance of class. Similarly to Marx looked at differences in power in society. Recognised that very charismatic individuals can chan ...
... To understand social change we need to understand social interaction Critical of Marx’s view that social change is linked to social class. Felt Marx over emphasised importance of class. Similarly to Marx looked at differences in power in society. Recognised that very charismatic individuals can chan ...
Week 5 - Monday - Université d`Ottawa
... surplus value, but that surplus value must always find a market. ...
... surplus value, but that surplus value must always find a market. ...
John Milios
... (‘B’). The value of the latter cannot be expressed; it does not exist in the world of tangible reality. The relation of general exchangeability of commodities is expressed only in an indirect, mediated sense, i.e. through money, which functions as general equivalent. The essential feature of the ‘ma ...
... (‘B’). The value of the latter cannot be expressed; it does not exist in the world of tangible reality. The relation of general exchangeability of commodities is expressed only in an indirect, mediated sense, i.e. through money, which functions as general equivalent. The essential feature of the ‘ma ...
Marxist economics MARXISM IS COMPLICATED by the fact that
... Conditions for capitalism Today, modern production is concentrated in the hands of giant companies. Unilever, ICI, Fords, British Petroleum, are some examples of the firms which dominate our lives. Although it is true that small businesses do exist, they really represent the production of the past ...
... Conditions for capitalism Today, modern production is concentrated in the hands of giant companies. Unilever, ICI, Fords, British Petroleum, are some examples of the firms which dominate our lives. Although it is true that small businesses do exist, they really represent the production of the past ...
Chapter 7 - Karl Marx
... is necessary to discover the essential and particular features of the mode The failure to make this discovery, according to Marx, led the Classicals to two “confusions” The first confusion was the belief that capital was a universal element in all production processes The second was that all economi ...
... is necessary to discover the essential and particular features of the mode The failure to make this discovery, according to Marx, led the Classicals to two “confusions” The first confusion was the belief that capital was a universal element in all production processes The second was that all economi ...
1st Quarter, Unit 2: Economics Fundamentals (Ch
... capital (factories, machines, tools) resource opportunity cost good capital significance of scarcity in econ importance of choice consumption allocation productivity costs and benefits Pig Principle law of diminishing returns profit invest currency capital investment why people trade ...
... capital (factories, machines, tools) resource opportunity cost good capital significance of scarcity in econ importance of choice consumption allocation productivity costs and benefits Pig Principle law of diminishing returns profit invest currency capital investment why people trade ...
Surplus value

Surplus value is a central concept in Karl Marx's critique of political economy. Marx did not himself invent the term, he developed the concept. ""Surplus value"" is a translation of the German word ""Mehrwert"", which simply means value added (sales revenue less the cost of materials used up). Conventionally, value-added is equal to the sum of gross wage income and gross profit income. However, Marx's use of this concept is different, because for Marx, the Mehrwert refers to the yield, profit or return on production capital invested, i.e. the amount of the increase in the value of capital. Hence, Marx's use of Mehrwert has always been translated as ""surplus value"", distinguishing it from ""value-added"". According to Marx's theory, surplus value is equal to the new value created by workers in excess of their own labour-cost, which is appropriated by the capitalist as profit when products are sold.Marx thought that the gigantic increase in wealth and population from the 19th century onwards was mainly due to the competitive striving to obtain maximum surplus-value from the employment of labor, resulting in an equally gigantic increase of productivity and capital resources. To the extent that increasingly the economic surplus is convertible into money and expressed in money, the amassment of wealth is possible on a larger and larger scale (see capital accumulation and surplus product).