
The knowledge revolution
... An extraordinary tug of war between capitalknowledge, emerging from educational sysism and socialism has dominated world politems and the cultural heritage of society. But tics and economic thinking for several it points out the fundamental difference that decades . But the issue of ownership of cap ...
... An extraordinary tug of war between capitalknowledge, emerging from educational sysism and socialism has dominated world politems and the cultural heritage of society. But tics and economic thinking for several it points out the fundamental difference that decades . But the issue of ownership of cap ...
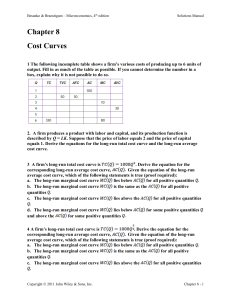
Document
... A lottery p can be depicted on a plane by taking p (z1) as the first coordinate (on the horizontal axis), and p (z2) as the second coordinate (on the vertical axis). p (z0) is 1 – p (z1) – p (z2). [See Figure 4 for the illustration.] Given any two lotteries p and q , the convex combinations ap + (1 ...
... A lottery p can be depicted on a plane by taking p (z1) as the first coordinate (on the horizontal axis), and p (z2) as the second coordinate (on the vertical axis). p (z0) is 1 – p (z1) – p (z2). [See Figure 4 for the illustration.] Given any two lotteries p and q , the convex combinations ap + (1 ...
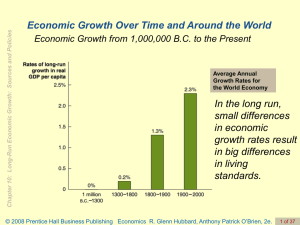
Economics R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O`Brien, 2e.
... What Determines How Fast Economies Grow? Economic growth model A model that explains growth rates in real GDP per capita over the long run. Labor productivity The quantity of goods and services that can be produced by one worker or by one hour of work. The more capital each worker has, the more prod ...
... What Determines How Fast Economies Grow? Economic growth model A model that explains growth rates in real GDP per capita over the long run. Labor productivity The quantity of goods and services that can be produced by one worker or by one hour of work. The more capital each worker has, the more prod ...
Economic growth and human capital accumulation: a discrete
... capital was an important assumption of the first neoclassical model. Probably correct because the central role of accumulation itself fifty or sixty years ago. From this years at today, growth theorists working hard over other endogenous state variables excluded from consideration by the initial neo ...
... capital was an important assumption of the first neoclassical model. Probably correct because the central role of accumulation itself fifty or sixty years ago. From this years at today, growth theorists working hard over other endogenous state variables excluded from consideration by the initial neo ...
GMU Enviromental - George Mason University
... • Deliberately address safety, efficiency, environment -- together • Reward desired behaviors; think “motivation” and “incentives” • Include human perception, interpretation, action formulation, and action. Think “human element” and the psychology of metrics. ...
... • Deliberately address safety, efficiency, environment -- together • Reward desired behaviors; think “motivation” and “incentives” • Include human perception, interpretation, action formulation, and action. Think “human element” and the psychology of metrics. ...
Peer-reviewed Article PDF - e
... tries to spread through its social solidarity institutions. But equally well an instinct is the individualism of not wanting to fool away, to be outsmarted in the bazaar. This natural marketplace rationality is what homo economicus is all about, a tractable analytically personality, seized by Neocla ...
... tries to spread through its social solidarity institutions. But equally well an instinct is the individualism of not wanting to fool away, to be outsmarted in the bazaar. This natural marketplace rationality is what homo economicus is all about, a tractable analytically personality, seized by Neocla ...
Microeconomics
Microeconomics (from Greek prefix mikro- meaning ""small"") is a branch of economics that studies the behavior of individuals and firms in making decisions regarding the allocation of limited resources. Typically, it applies to markets where goods or services are bought and sold. Microeconomics examines how these decisions and behaviors affect the supply and demand for goods and services, which determines prices, and how prices, in turn, determine the quantity supplied and quantity demanded of goods and services.This is in contrast to macroeconomics, which involves the ""sum total of economic activity, dealing with the issues of growth, inflation, and unemployment."" Microeconomics also deals with the effects of national economic policies (such as changing taxation levels) on the aforementioned aspects of the economy. Particularly in the wake of the Lucas critique, much of modern macroeconomic theory has been built upon 'microfoundations'—i.e. based upon basic assumptions about micro-level behavior.One of the goals of microeconomics is to analyze market mechanisms that establish relative prices amongst goods and services and allocation of limited resources amongst many alternative uses. Microeconomics also analyzes market failure, where markets fail to produce efficient results, and describes the theoretical conditions needed for perfect competition. Significant fields of study in microeconomics include general equilibrium, markets under asymmetric information, choice under uncertainty and economic applications of game theory. Also considered is the elasticity of products within the market system.














![Slides [pptx]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008799337_1-2f5ed078c3f1df9ce2494abb4a4233c5-300x300.png)






