Selected chapters from enzymology, membrane biochemistry and
... phosphorylates D-glucose but not L-glucose) and bond specificity that is ability of some enzymes to cleave or create specific bond (e.g. α-amylase that catalyses hydrolysis of α-Oglycosidic bond in starch but not β-O-glycosidic bond in cellulose). Enzyme specificity was explained by the fact that bo ...
... phosphorylates D-glucose but not L-glucose) and bond specificity that is ability of some enzymes to cleave or create specific bond (e.g. α-amylase that catalyses hydrolysis of α-Oglycosidic bond in starch but not β-O-glycosidic bond in cellulose). Enzyme specificity was explained by the fact that bo ...
AP Biology Name Colony Transformation Lab Answer these
... For this part of the lab, follow the instructions indicated to calculate transformation efficiency. Your next task is to learn how to determine the extent to which you genetically transformed E. coli cells. This quantitative measurement is referred to as the transformation efficiency. What is the im ...
... For this part of the lab, follow the instructions indicated to calculate transformation efficiency. Your next task is to learn how to determine the extent to which you genetically transformed E. coli cells. This quantitative measurement is referred to as the transformation efficiency. What is the im ...
Chapter 11 Lecture PowerPoint - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... • TAFs are not universally required for transcription of class II genes • Even TBP is not universally required • Some promoters in higher eukaryotes respond to an alternative protein such as TRF1 (TBPrelated factor 1) ...
... • TAFs are not universally required for transcription of class II genes • Even TBP is not universally required • Some promoters in higher eukaryotes respond to an alternative protein such as TRF1 (TBPrelated factor 1) ...
iGenetics: A Molecular Approach, 3e (Russell/Bose)
... 32) Cloning vectors generally possess unique restriction sites and dominant selectable markers. Answer: TRUE Skill: Factual recall 33) A linear strand of DNA with two restriction enzyme cut sites will yield three fragments on digestion. Answer: TRUE Skill: Problem-solving 34) A circular DNA molecule ...
... 32) Cloning vectors generally possess unique restriction sites and dominant selectable markers. Answer: TRUE Skill: Factual recall 33) A linear strand of DNA with two restriction enzyme cut sites will yield three fragments on digestion. Answer: TRUE Skill: Problem-solving 34) A circular DNA molecule ...
08_chapter 1
... of the similar abundance values of complementary nucleotides. But Szybalski and his collegues (1966) had already described that purine richness predominated in the coding strand and pyrimidine richness predominated in the non-coding strand. In support of this, Smithies et al (1981) reported strand c ...
... of the similar abundance values of complementary nucleotides. But Szybalski and his collegues (1966) had already described that purine richness predominated in the coding strand and pyrimidine richness predominated in the non-coding strand. In support of this, Smithies et al (1981) reported strand c ...
Mechanical opening of DNA by micromanipulation and force
... vector DNA (7280 bp) is linearized by double digestion. One extremity is ligated to the PCR product, the other extremity is ligated to a short synthetic DNA fragment formed by hybridisation of two partial complementary oligonucleotides. This way we create two different types of linker arm molecules ...
... vector DNA (7280 bp) is linearized by double digestion. One extremity is ligated to the PCR product, the other extremity is ligated to a short synthetic DNA fragment formed by hybridisation of two partial complementary oligonucleotides. This way we create two different types of linker arm molecules ...
LNA-PNA Comparison4
... Applications of peptide nucleic acid probes 1) PNA fluorescent insitu hybridisationThe PNA-FISH technique was first developed for quantitative telomere analysis. Using a unique fluorescein-labelled PNA probe thus one can map the sequence onto a chromosome. In FISH applications PNA probes have severa ...
... Applications of peptide nucleic acid probes 1) PNA fluorescent insitu hybridisationThe PNA-FISH technique was first developed for quantitative telomere analysis. Using a unique fluorescein-labelled PNA probe thus one can map the sequence onto a chromosome. In FISH applications PNA probes have severa ...
Review for Final
... 74) What are treatments to prevent viral infection (more than 1)? Chap 19 75) Briefly describe the role of the different histone proteins in chromatin packaging. 76) Briefly describe the difference between heterochromatin and euchromatin. 77) What is differential gene expression? 78) Define the func ...
... 74) What are treatments to prevent viral infection (more than 1)? Chap 19 75) Briefly describe the role of the different histone proteins in chromatin packaging. 76) Briefly describe the difference between heterochromatin and euchromatin. 77) What is differential gene expression? 78) Define the func ...
Leukaemia Section t(11;19)(q23;p13.1) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... Phenotype / cell stem origin M4/M5 most often; M1/M2 at times; therapy related AL; however, clonal rearrangements of IgH gene have been found, demonstrating a biphenotypic nature. Epidemiology Children and, most often, adults (7 days to 83 yrs); congenital cases are rare, in contrast with the t(11;1 ...
... Phenotype / cell stem origin M4/M5 most often; M1/M2 at times; therapy related AL; however, clonal rearrangements of IgH gene have been found, demonstrating a biphenotypic nature. Epidemiology Children and, most often, adults (7 days to 83 yrs); congenital cases are rare, in contrast with the t(11;1 ...
nuclear morphology and the ultra
... The complexities of the technique of electron-microscope autoradiography make it feasible to analyse only a relatively small number of labelled cells and the conclusions which can be drawn are limited by this fact. Nevertheless it seems probable that the nuclear membrane is an important locus of DNA ...
... The complexities of the technique of electron-microscope autoradiography make it feasible to analyse only a relatively small number of labelled cells and the conclusions which can be drawn are limited by this fact. Nevertheless it seems probable that the nuclear membrane is an important locus of DNA ...
Protein_Synthesis_and_Words
... protein, with the sequence of these nucleotides determining which protein it is. The sequence of these nucleotides are used to create amino acids, where chains of amino acids form to make a protein. MRNA This genetic information is found in the nucleus, though protein synthesis actually occurs in ri ...
... protein, with the sequence of these nucleotides determining which protein it is. The sequence of these nucleotides are used to create amino acids, where chains of amino acids form to make a protein. MRNA This genetic information is found in the nucleus, though protein synthesis actually occurs in ri ...
Reflection on Lloyd/Rhind Genetics Unit First and Foremost
... me students, but for myself as a Biology instructor as well. Mr. Rhind has been supportive in every way towards helping us all better grasp the genetics topics we attempted to cover. His knowledge and patience were key to making this unit work so successfully. I found that the Journaling and DNA ext ...
... me students, but for myself as a Biology instructor as well. Mr. Rhind has been supportive in every way towards helping us all better grasp the genetics topics we attempted to cover. His knowledge and patience were key to making this unit work so successfully. I found that the Journaling and DNA ext ...
Structural basis of PAM-dependent target DNA recognition by the
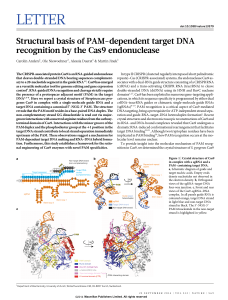
... domain active site (Fig. 1a–c). In the complex, the bound nucleic acids are enclosed by the nuclease and helical recognition lobes of Cas9 and form a four-way junction that straddles the arginine-rich bridge helix (Fig. 1b, c). The entire PAM-containing region of the target DNA (target-strand nucleo ...
... domain active site (Fig. 1a–c). In the complex, the bound nucleic acids are enclosed by the nuclease and helical recognition lobes of Cas9 and form a four-way junction that straddles the arginine-rich bridge helix (Fig. 1b, c). The entire PAM-containing region of the target DNA (target-strand nucleo ...
Remember those chromosomes?
... A sperm or egg cell (aka sex cell). The connector between chromatids. A fertilized egg. Any chromosome that is not an X or Y. In humans, they are the X & Y chromosomes. A portion of DNA that codes for a protein. A picture of chromosomes arranged by size. Chromosomes similar in size, shape, and genet ...
... A sperm or egg cell (aka sex cell). The connector between chromatids. A fertilized egg. Any chromosome that is not an X or Y. In humans, they are the X & Y chromosomes. A portion of DNA that codes for a protein. A picture of chromosomes arranged by size. Chromosomes similar in size, shape, and genet ...
AP Biology Name Colony Transformation Lab Answer these
... For this part of the lab, follow the instructions indicated to calculate transformation efficiency. Your next task is to learn how to determine the extent to which you genetically transformed E. coli cells. This quantitative measurement is referred to as the transformation efficiency. What is the im ...
... For this part of the lab, follow the instructions indicated to calculate transformation efficiency. Your next task is to learn how to determine the extent to which you genetically transformed E. coli cells. This quantitative measurement is referred to as the transformation efficiency. What is the im ...
Chapter 13 Lecture PowerPoint - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... • Eukaryotic genes do not exist naturally as naked DNA, or even as DNA molecules bound only to transcription factors • They are complexed with an equal mass of other proteins to form chromatin • Chromatin is variable and the variations play an enormous role in chromatin structure and in the control ...
... • Eukaryotic genes do not exist naturally as naked DNA, or even as DNA molecules bound only to transcription factors • They are complexed with an equal mass of other proteins to form chromatin • Chromatin is variable and the variations play an enormous role in chromatin structure and in the control ...
The Structure of Nucleic acids (DNA, RNA,Viral nucleic acids
... large nuclei; Miescher developed a method of isolating these nuclei. The minute amounts of nuclear material that he obtained were insufficient for a thorough chemical analysis, but he did establish that it contained a novel substance that turned out not to be carbohydrate, lipid, or protein. This ma ...
... large nuclei; Miescher developed a method of isolating these nuclei. The minute amounts of nuclear material that he obtained were insufficient for a thorough chemical analysis, but he did establish that it contained a novel substance that turned out not to be carbohydrate, lipid, or protein. This ma ...
Dr. Assal - World Health Organization
... • Standardization of the different steps, from sample preparation to amplification and ...
... • Standardization of the different steps, from sample preparation to amplification and ...
Full-Text PDF
... According to the soil type classification, soils consists mainly of sand, silt, and clay that are often mixed. Clay minerals are natural fine-grained phyllosilicates that might occur in soils. Thus, only soils with a high amount of clay minerals or soils with a defined small grain size are defined a ...
... According to the soil type classification, soils consists mainly of sand, silt, and clay that are often mixed. Clay minerals are natural fine-grained phyllosilicates that might occur in soils. Thus, only soils with a high amount of clay minerals or soils with a defined small grain size are defined a ...
Lab 1 genomic DNA
... phase separation, decreases the amount of material found at the aqueous and organic interface, and helps reduce foaming. Antioxidants such as 8-hydroxyquinoline or ß-mercaptoethanol are often added to phenol. During phenol extractions, the pH of the buffer is important in determining whether DNA and ...
... phase separation, decreases the amount of material found at the aqueous and organic interface, and helps reduce foaming. Antioxidants such as 8-hydroxyquinoline or ß-mercaptoethanol are often added to phenol. During phenol extractions, the pH of the buffer is important in determining whether DNA and ...
1 Chapter 5 (Nucleic Acid)/8 Quiz Multiple Choice Identify the choice
... 5. Without enzymes, the chemical reactions in the body would a. occur too slowly to support life processes. b. require a different pH. c. occur at much the same rate as they do with enzymes. ...
... 5. Without enzymes, the chemical reactions in the body would a. occur too slowly to support life processes. b. require a different pH. c. occur at much the same rate as they do with enzymes. ...
Replisome
The replisome is a complex molecular machine that carries out replication of DNA. The replisome first unwinds double stranded DNA into two single strands. For each of the resulting single strands, a new complementary sequence of DNA is synthesized. The net result is formation of two new double stranded DNA sequences that are exact copies of the original double stranded DNA sequence.In terms of structure, the replisome is composed of two replicative polymerase complexes, one of which synthesizes the leading strand, while the other synthesizes the lagging strand. The replisome is composed of a number of proteins including helicase, RFC, PCNA, gyrase/topoisomerase, SSB/RPA, primase, DNA polymerase I, RNAse H, and ligase.