Evolution of the genetic code. Emergence of DNA
... Deamination first leads to the formation of uracil in the enol form. Then it must be transformed into the keto form, which is more stable in solution. However, when uracil is gripped in the backbone of the RNA double helix, the enol form is more advantageous for it. Uracil in the enol form can mak ...
... Deamination first leads to the formation of uracil in the enol form. Then it must be transformed into the keto form, which is more stable in solution. However, when uracil is gripped in the backbone of the RNA double helix, the enol form is more advantageous for it. Uracil in the enol form can mak ...
Clinical and Molecular Aspects of Diseases of Mitochondrial DNA
... mitochondrial genome is 16,569 base pairs (Fig. 1). Despite its small size, mtDNA encodes 22 transfer RNAs, 2 ribosomal RNAs and 13 polypeptides which are required for OXPHOS. Although the number 1000 is widely quoted as the mtDNA complement of a typical cell, there is in fact considerable variation ...
... mitochondrial genome is 16,569 base pairs (Fig. 1). Despite its small size, mtDNA encodes 22 transfer RNAs, 2 ribosomal RNAs and 13 polypeptides which are required for OXPHOS. Although the number 1000 is widely quoted as the mtDNA complement of a typical cell, there is in fact considerable variation ...
Bio11U_Ch 6_approvedcopyedit_100817
... therapy has been successful and where it has failed • recognize that the manipulation of genomes has far-reaching consequences for society and the ...
... therapy has been successful and where it has failed • recognize that the manipulation of genomes has far-reaching consequences for society and the ...
Prevention of DNA Rereplication Through a Meiotic Recombination
... segregation. As during the mitotic cell cycle, meiotic DNA replication is tightly regulated so that initiation occurs at precisely the correct time and only once during the process (Strich 2004); in the absence of appropriate controls, errors such as DNA rereplication can occur that are typically ...
... segregation. As during the mitotic cell cycle, meiotic DNA replication is tightly regulated so that initiation occurs at precisely the correct time and only once during the process (Strich 2004); in the absence of appropriate controls, errors such as DNA rereplication can occur that are typically ...
Single-stranded heteroduplex intermediates in l Red homologous
... [31,32,45], the host cells contained only Redb. In parallel as a positive control, we performed a recombination reaction with single-stranded oligonucleotides to repair a mutation in the kanamycin resistance gene (neo) and so restore kanamycin resistance. As expected from previous observations, the ...
... [31,32,45], the host cells contained only Redb. In parallel as a positive control, we performed a recombination reaction with single-stranded oligonucleotides to repair a mutation in the kanamycin resistance gene (neo) and so restore kanamycin resistance. As expected from previous observations, the ...
Slide 1
... antibodies by fusing the specific antibodyproducing plasma cells with a tumor cell Made way for a very effective diagnostic and therapeutic tool ...
... antibodies by fusing the specific antibodyproducing plasma cells with a tumor cell Made way for a very effective diagnostic and therapeutic tool ...
Genome Rearrangements Caused by Depletion of Essential DNA
... cycle following gene-product depletion by promoter shut off (Yu et al. 2006). Spontaneous DNA damage was measured by the relocalization of the DNA damage checkpoint protein Ddc2 from a diffuse nuclear pattern to discrete subnuclear foci (Figure 1A) (Melo et al. 2001; Lisby et al. 2004). Following gr ...
... cycle following gene-product depletion by promoter shut off (Yu et al. 2006). Spontaneous DNA damage was measured by the relocalization of the DNA damage checkpoint protein Ddc2 from a diffuse nuclear pattern to discrete subnuclear foci (Figure 1A) (Melo et al. 2001; Lisby et al. 2004). Following gr ...
Structure and function of the GINS complex, a key component of the
... in replication initiation [22]. Similar results were seen when the phosphomimicking Sld2 mutant was combined with cells expressing the Cdc45-JET protein and overproducing Dpb11 [21]. Dpb11, therefore, bridges phosphorylated Sld2 and Sld3, but to what end? Although yet to be described in detail, Sld2 ...
... in replication initiation [22]. Similar results were seen when the phosphomimicking Sld2 mutant was combined with cells expressing the Cdc45-JET protein and overproducing Dpb11 [21]. Dpb11, therefore, bridges phosphorylated Sld2 and Sld3, but to what end? Although yet to be described in detail, Sld2 ...
Modular Stitching To Image Single
... Movie S1 in the Supporting Information makes the pattern plain: one end of a chain tends to stretch out and pulls slack from the still-quiescent remainder of the chain until the other ...
... Movie S1 in the Supporting Information makes the pattern plain: one end of a chain tends to stretch out and pulls slack from the still-quiescent remainder of the chain until the other ...
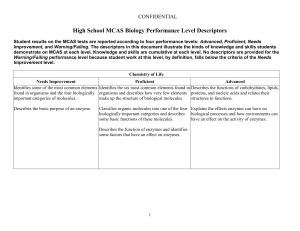
Biology Performance Level Descriptors
... Identifies the basic structure (double helix, Describes the basic structure of DNA and its sugar/phosphate backbone, linked by function in genetic inheritance, and describes the complementary nucleotide pairs) of DNA and semi-conservative nature of DNA replication. describes DNA as a carrier of gene ...
... Identifies the basic structure (double helix, Describes the basic structure of DNA and its sugar/phosphate backbone, linked by function in genetic inheritance, and describes the complementary nucleotide pairs) of DNA and semi-conservative nature of DNA replication. describes DNA as a carrier of gene ...
The percentage of bacterial genes on leading versus
... It has been observed that bacterial genomes have a large variation in terms of the percentage of their leading-strand genes, ranging from ~45% to ~90%. We have provided our explanation for the observed strand-biases and the large variation of the biases, which extends the previous proposed explanati ...
... It has been observed that bacterial genomes have a large variation in terms of the percentage of their leading-strand genes, ranging from ~45% to ~90%. We have provided our explanation for the observed strand-biases and the large variation of the biases, which extends the previous proposed explanati ...
Tertiary base pair interactions in slipped loop-DNA
... sequences can assume 'unusual' forms, such as Z-, H-forms, cruciforms, etc. (1,2). As a rule, such forms do not constitute the ground state (lowest energy) conformation, but they can be stabilized either by an appropriate solution environment (high ionic strength or low pH) or superhelical stress in ...
... sequences can assume 'unusual' forms, such as Z-, H-forms, cruciforms, etc. (1,2). As a rule, such forms do not constitute the ground state (lowest energy) conformation, but they can be stabilized either by an appropriate solution environment (high ionic strength or low pH) or superhelical stress in ...
A new FISH protocol with increased sensitivity for
... labelling and hybridization conditions. The optimization of the technique was made possible because, under nonoptimal conditions, few spots were detectable and their number and intensity increased slightly when the individual steps were improved. This allowed better experimental conditions to be cho ...
... labelling and hybridization conditions. The optimization of the technique was made possible because, under nonoptimal conditions, few spots were detectable and their number and intensity increased slightly when the individual steps were improved. This allowed better experimental conditions to be cho ...
... injected must match the mature “trimmed” mRNA sequence for the gene and the interference could not be elicited by intron sequences. This implies that interference takes place after transcription, probably in the cytoplasm rather than in the cell nucleus (4) The mRNA was revealed to be targeted with ...
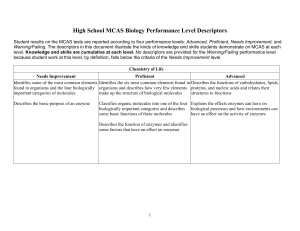
High School Biology MCAS Performance Level Descriptors
... Identifies the basic structure (double helix, Describes the basic structure of DNA and its sugar/phosphate backbone, linked by function in genetic inheritance, and describes the complementary nucleotide pairs) of DNA and semi-conservative nature of DNA replication; describes DNA as a carrier of gene ...
... Identifies the basic structure (double helix, Describes the basic structure of DNA and its sugar/phosphate backbone, linked by function in genetic inheritance, and describes the complementary nucleotide pairs) of DNA and semi-conservative nature of DNA replication; describes DNA as a carrier of gene ...
Lectures prepared by Christine L. Case Chapter 8 Microbial Genetics
... Genomics (基因體學): The molecular study of genomes Genotype (基因型): The genes of an organism Phenotype (外表型): Expression of the genes In microbes, most proteins are either enzymatic or structural. ...
... Genomics (基因體學): The molecular study of genomes Genotype (基因型): The genes of an organism Phenotype (外表型): Expression of the genes In microbes, most proteins are either enzymatic or structural. ...
JOIN2004 Universidade do Minho
... Regular expressions permit you to find and alter many patterns with relative ease. The excellent regular expressions in Perl are a major reason for Perl's success as a bioinformatics programming language. ...
... Regular expressions permit you to find and alter many patterns with relative ease. The excellent regular expressions in Perl are a major reason for Perl's success as a bioinformatics programming language. ...
Studies on Polynucleotides
... Sequence Encoded in the tRNA Gene-The 3’-terminal sequence, C-C-A, is encoded in the tRNA gene. A direct proof that the terminal C-C-A sequence is coded for by the tRNA gene was obtained by using DNA III, a 19.nucleotide-unit-long polynucleotide which lacks the C-C-A sequence, as the primer, and @Op ...
... Sequence Encoded in the tRNA Gene-The 3’-terminal sequence, C-C-A, is encoded in the tRNA gene. A direct proof that the terminal C-C-A sequence is coded for by the tRNA gene was obtained by using DNA III, a 19.nucleotide-unit-long polynucleotide which lacks the C-C-A sequence, as the primer, and @Op ...
Replisome
The replisome is a complex molecular machine that carries out replication of DNA. The replisome first unwinds double stranded DNA into two single strands. For each of the resulting single strands, a new complementary sequence of DNA is synthesized. The net result is formation of two new double stranded DNA sequences that are exact copies of the original double stranded DNA sequence.In terms of structure, the replisome is composed of two replicative polymerase complexes, one of which synthesizes the leading strand, while the other synthesizes the lagging strand. The replisome is composed of a number of proteins including helicase, RFC, PCNA, gyrase/topoisomerase, SSB/RPA, primase, DNA polymerase I, RNAse H, and ligase.