ligands - SRM University
... It forms complexes with metals like iron,copper and zinc. Three molecules of 1,10phenanthroline dissolve easily in solutions of ferrous salts and combine with one ferrous ion to give the 1,10-phecanthroline-ferrous complex known as ferroin which is intensely red in colour. It has the following struc ...
... It forms complexes with metals like iron,copper and zinc. Three molecules of 1,10phenanthroline dissolve easily in solutions of ferrous salts and combine with one ferrous ion to give the 1,10-phecanthroline-ferrous complex known as ferroin which is intensely red in colour. It has the following struc ...
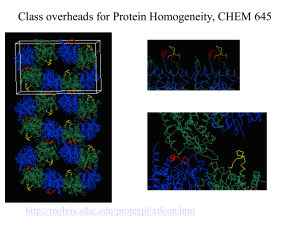
6. 3-D structure of proteins
... • The spatial arrangement of atoms in a protein is called its conformation. • Proteins in any of their functional folded conformations are called native proteins. • Stability can be defined as the tendency to ...
... • The spatial arrangement of atoms in a protein is called its conformation. • Proteins in any of their functional folded conformations are called native proteins. • Stability can be defined as the tendency to ...
Examples
... ▫ 2. Active site - the small region on the enzyme that is involved in the chemical action ▫ 3. Enzyme-substrate complex substrates are the materials that are acted on by the enzyme - when the enzyme and substrate combine they form an enzyme-substrate ...
... ▫ 2. Active site - the small region on the enzyme that is involved in the chemical action ▫ 3. Enzyme-substrate complex substrates are the materials that are acted on by the enzyme - when the enzyme and substrate combine they form an enzyme-substrate ...
The Chemical Basis of Life
... rates of chemical reactions, but are not consumed (used up) in the reaction. Enzymes are biological catalysts (proteins). ...
... rates of chemical reactions, but are not consumed (used up) in the reaction. Enzymes are biological catalysts (proteins). ...
Stoichiometry
... 1) A mass of 75 grams of sodium reacts with water to produce how many grams of sodium hydroxide? Sodium + water sodium hydroxide + hydrogen 2) 50 grams of copper II combines with ...
... 1) A mass of 75 grams of sodium reacts with water to produce how many grams of sodium hydroxide? Sodium + water sodium hydroxide + hydrogen 2) 50 grams of copper II combines with ...
DNA Strand Breakage and Fragmentation Induced by Low
... The effect of ionizing radiations upon biological material continues to evoke great scientific interest. It is well known that such radiations can cause undesirable biological consequences, particularly via damage to DNA. Recent studies [1] have shown that low energy electrons (1-20 eV) are capable ...
... The effect of ionizing radiations upon biological material continues to evoke great scientific interest. It is well known that such radiations can cause undesirable biological consequences, particularly via damage to DNA. Recent studies [1] have shown that low energy electrons (1-20 eV) are capable ...
A.P. Chemistry
... Problem: What volume of 16 M sulfuric acid must be used to prepare 1.5 L of a 0.10 M H2SO4 solution? ...
... Problem: What volume of 16 M sulfuric acid must be used to prepare 1.5 L of a 0.10 M H2SO4 solution? ...
Chapter 2: Chemical Principles
... • __________ - when a molecule is split into smaller molecules, ions, or atoms. ...
... • __________ - when a molecule is split into smaller molecules, ions, or atoms. ...
Chapter 2 Notes: The Chemistry of Life
... saturated fat, unsaturated fat, nucleic acids, nucleotides, proteins, amino acids, chemical reaction, reactants, products, activation energy, catalyst, enzymes, substrates, dehydration synthesis, hydrolysis, active site, lock‐and‐key model, organic The Nature of Matter Atom: The smallest _______ ...
... saturated fat, unsaturated fat, nucleic acids, nucleotides, proteins, amino acids, chemical reaction, reactants, products, activation energy, catalyst, enzymes, substrates, dehydration synthesis, hydrolysis, active site, lock‐and‐key model, organic The Nature of Matter Atom: The smallest _______ ...
Chem 464 Biochemistry
... C. Predict the pI of this amino acid From A we know is +1 initial So at first equivalence point it will be zero First equivalence point is (2+2.3)/2 = 2.15 10. (10 points) Histones are proteins found in eukariotic cell nuclei, tightly bound to DNA which has many negatively charged phosphate groups. ...
... C. Predict the pI of this amino acid From A we know is +1 initial So at first equivalence point it will be zero First equivalence point is (2+2.3)/2 = 2.15 10. (10 points) Histones are proteins found in eukariotic cell nuclei, tightly bound to DNA which has many negatively charged phosphate groups. ...
2. Chemistry of Living Things Outline
... catalyze. In organisms, _____________ allow the chemical reactions of ______________ to take place more efficiently than they otherwise would at body temperature. For example, amino acids are produced from protein digestion. The enzymes needed for this reaction are not changed but must be present fo ...
... catalyze. In organisms, _____________ allow the chemical reactions of ______________ to take place more efficiently than they otherwise would at body temperature. For example, amino acids are produced from protein digestion. The enzymes needed for this reaction are not changed but must be present fo ...
Affinity Chromatography using fusion proteins
... Yellow - polar http://binfo.ym.edu.tw/bioflash/emboss/iep/iep.htm ...
... Yellow - polar http://binfo.ym.edu.tw/bioflash/emboss/iep/iep.htm ...
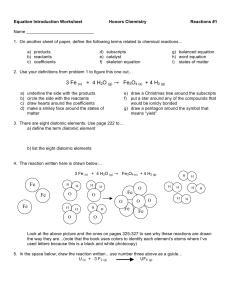
Equation Intro Worksheet 1213
... c) potassium iodide + lead (II) nitrate → lead (II) iodide + potassium nitrate ...
... c) potassium iodide + lead (II) nitrate → lead (II) iodide + potassium nitrate ...
Units 3 and 4 Revision
... outer energy level – this gives them similar properties. Q10. Chlorine atoms exists as two different isotopes 35Cl and ...
... outer energy level – this gives them similar properties. Q10. Chlorine atoms exists as two different isotopes 35Cl and ...
Reading guide - Chemistry Courses: About
... 2. Describe the major structural features of myoglobin and how they are similar to/different than hemoglobin. 3. Draw a simple schematic of the ligands that bind to the iron ion found in myoglobin. What does His F8 do, and why is it called that? What additional amino acid residue binds to molecular ...
... 2. Describe the major structural features of myoglobin and how they are similar to/different than hemoglobin. 3. Draw a simple schematic of the ligands that bind to the iron ion found in myoglobin. What does His F8 do, and why is it called that? What additional amino acid residue binds to molecular ...
Chapter 5 Test Review Notes
... The nucleus of an atom does not contain electrons, but has protons and neutrons. Atoms that have gained or lost an electron are called ions. The smallest part of an element that has all the properties of that element is called an atom. Lead has an electron configuration of 2,8,18,32, 18,4. How many ...
... The nucleus of an atom does not contain electrons, but has protons and neutrons. Atoms that have gained or lost an electron are called ions. The smallest part of an element that has all the properties of that element is called an atom. Lead has an electron configuration of 2,8,18,32, 18,4. How many ...
Modeling Biological Molecules
... will make models to see how atoms are arranged and rearranged in biological systems. Because we are investigating a part of the world that we can’t directly see, using models helps us to actually see and make sense of what happens in a chemical reaction. The atoms in molecules are held together by c ...
... will make models to see how atoms are arranged and rearranged in biological systems. Because we are investigating a part of the world that we can’t directly see, using models helps us to actually see and make sense of what happens in a chemical reaction. The atoms in molecules are held together by c ...
Unit 3: Basic Chemistry Content Outline: Carbon Chemistry (3.6
... II. The carbon atom has tetravalence (4 valence electrons) and can thus form four covalent bonds with other Carbon atoms or atoms of other elements. Carbon can also form multiple bonds (i.e. double and triple) with Carbon or atoms of other elements. Multiple bonds increase the “bonding strength”. II ...
... II. The carbon atom has tetravalence (4 valence electrons) and can thus form four covalent bonds with other Carbon atoms or atoms of other elements. Carbon can also form multiple bonds (i.e. double and triple) with Carbon or atoms of other elements. Multiple bonds increase the “bonding strength”. II ...
BICH 303 Exam #1 Fall 2005 1. Amphiphilic or amphipathic
... a. stability: a decrease in the surface to volume ratio and shielding of hydrophobic residues from the solvent. b genomic economy: less DNA required to code for a monomer that forms a homodimer. c. catalytic site: the monomer may not constitute a complete enzyme active site. The active site may only ...
... a. stability: a decrease in the surface to volume ratio and shielding of hydrophobic residues from the solvent. b genomic economy: less DNA required to code for a monomer that forms a homodimer. c. catalytic site: the monomer may not constitute a complete enzyme active site. The active site may only ...
Maintaining Linkage: More examples
... Both HIFα and ARNT contain an N-terminal bHLH DNA binding domain and two adjacent PAS domains, referred to as PAS-A and PAS-B. PAS domains are structural modules found in proteins from all kingdoms of life that have significant structural homology despite little conservation of amino acid sequence. ...
... Both HIFα and ARNT contain an N-terminal bHLH DNA binding domain and two adjacent PAS domains, referred to as PAS-A and PAS-B. PAS domains are structural modules found in proteins from all kingdoms of life that have significant structural homology despite little conservation of amino acid sequence. ...
Studying Transition Metal Complexes
... ligand complex. 1. For a given ligand, determine the wavelength of maximum absorbance by mixing a small amount of metal ion (5 drops) with a large amount of ligand (5 mL). Scan the region between 320 and 810nm noting the wavelength giving the maximum absorbance. Record the wavelength giving the maxi ...
... ligand complex. 1. For a given ligand, determine the wavelength of maximum absorbance by mixing a small amount of metal ion (5 drops) with a large amount of ligand (5 mL). Scan the region between 320 and 810nm noting the wavelength giving the maximum absorbance. Record the wavelength giving the maxi ...
chapter2 questions
... Nitrogen is important in all proteins and nucleic acids. Sulfur is found in many proteins. Calcium is important for nerve impulses and muscle contraction. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of covalent bonds? Covalent bonds can share their electrons equally or unequally. Covalent bonds h ...
... Nitrogen is important in all proteins and nucleic acids. Sulfur is found in many proteins. Calcium is important for nerve impulses and muscle contraction. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of covalent bonds? Covalent bonds can share their electrons equally or unequally. Covalent bonds h ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.