Chapter 7: Proteins
... Amino acids are used to synthesize new body proteins If not used to synthesize new proteins – Deamination: liver removes amino group – Nitrogen is converted to urea – Kidneys flush nitrogen from the body ...
... Amino acids are used to synthesize new body proteins If not used to synthesize new proteins – Deamination: liver removes amino group – Nitrogen is converted to urea – Kidneys flush nitrogen from the body ...
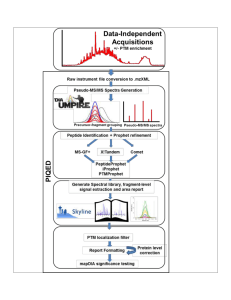
Supplementary Figure 1 Details of PIQED Automated Qualitative
... Modified peptides enriched from biological samples or peptides from proteome digestion without modification enrichment are analyzed by data-independent acquisition. PIQED supports data from SCIEX or Thermo instruments. PIQED automates all data analysis steps st arting from instrument .wiff or .raw f ...
... Modified peptides enriched from biological samples or peptides from proteome digestion without modification enrichment are analyzed by data-independent acquisition. PIQED supports data from SCIEX or Thermo instruments. PIQED automates all data analysis steps st arting from instrument .wiff or .raw f ...
AP Midterm Study Guide
... **You must be able to recognize the structures of these compounds – study the pictures! 1. CARBOHYDRATES Used by the cells of the body - in energy-producing reactions - as structural materials Classified into 3 groups according to the number of sugar (saccharide) molecules: 1) Monsaccharide: “si ...
... **You must be able to recognize the structures of these compounds – study the pictures! 1. CARBOHYDRATES Used by the cells of the body - in energy-producing reactions - as structural materials Classified into 3 groups according to the number of sugar (saccharide) molecules: 1) Monsaccharide: “si ...
Properties of Metals
... metals. When we describe something as being metallic it is often because it is hard, heavy, lustrous and strong enough to be made into huge variety of tools, machines and structures. This is true for many metals but there are exceptions to these basic properties. Humans first used metals about 8000 ...
... metals. When we describe something as being metallic it is often because it is hard, heavy, lustrous and strong enough to be made into huge variety of tools, machines and structures. This is true for many metals but there are exceptions to these basic properties. Humans first used metals about 8000 ...
DNA Day Project 1) Definitions: Drugs
... DNA Day Project 1) Definitions: Drugs- Substance, natural or artificial that alters function of the body. Genome- total DNA in each cell nucleus of an organism. Gene- functional unit controls inherited trait expression that is passed on from one generation to another generation. Nucleotides- ...
... DNA Day Project 1) Definitions: Drugs- Substance, natural or artificial that alters function of the body. Genome- total DNA in each cell nucleus of an organism. Gene- functional unit controls inherited trait expression that is passed on from one generation to another generation. Nucleotides- ...
Inorganic concepts relevant to metal binding, activity
... ligands, L - , approach the positively-charged metal ion, M 2 + , in the gas phase (Fig. 1), the five-fold degenerate d-orbitals become differentiated in the presence of the electrostatic field of the ligands. Orbitals oriented in the direction of the incoming ligands (dz2, dx2_y2) are preferentiall ...
... ligands, L - , approach the positively-charged metal ion, M 2 + , in the gas phase (Fig. 1), the five-fold degenerate d-orbitals become differentiated in the presence of the electrostatic field of the ligands. Orbitals oriented in the direction of the incoming ligands (dz2, dx2_y2) are preferentiall ...
nomenclature review
... If 7.40g of calcium hydroxide reacts with excess nitric acid, how many grams of calcium nitrate are formed?(16.4grams) ...
... If 7.40g of calcium hydroxide reacts with excess nitric acid, how many grams of calcium nitrate are formed?(16.4grams) ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment
... 1. A quiz on the most common polyatomic ions after the firstclass meeting and frequent quizzes on nomenclature and netionic equations every Monday thereafter. Correctly writing chemical equations is an essential part of learning chemistry and should be a focus of study early in the course. It ...
... 1. A quiz on the most common polyatomic ions after the firstclass meeting and frequent quizzes on nomenclature and netionic equations every Monday thereafter. Correctly writing chemical equations is an essential part of learning chemistry and should be a focus of study early in the course. It ...
complex ion
... [Co(NH3)5Cl]Br(aq) + AgNO3(aq) [Co(NH3)5Cl]NO3(aq) + AgBr(s) [Co(NH3)5Br]Cl(aq) + AgNO3(aq) [Co(NH3)5Br]NO3(aq) + AgCl(aq) ...
... [Co(NH3)5Cl]Br(aq) + AgNO3(aq) [Co(NH3)5Cl]NO3(aq) + AgBr(s) [Co(NH3)5Br]Cl(aq) + AgNO3(aq) [Co(NH3)5Br]NO3(aq) + AgCl(aq) ...
PP133 Impact of free fatty acids binding to nsLTP on their tertiary
... study indicates that Pru p 3 displays some binding specificity as compared to Cor a 8 and Jug r 3. It prefers to bind unsaturated versus saturated fatty acids and short carbon chains ligands (C12 vs C18). Moreover, certain ligands can influence tertiary structure of protein. Interestingly, the regio ...
... study indicates that Pru p 3 displays some binding specificity as compared to Cor a 8 and Jug r 3. It prefers to bind unsaturated versus saturated fatty acids and short carbon chains ligands (C12 vs C18). Moreover, certain ligands can influence tertiary structure of protein. Interestingly, the regio ...
01. Inorganic chemistry and medicine. Complex compounds and
... A saturated solution is one that is in equilibrium with excess undissolved solute, or would be in equilibrium if excess solute were present. The term saturated denotes the highest concentration of solute which a solution can have and be in equilibrium with any undissolved solute with which it is pla ...
... A saturated solution is one that is in equilibrium with excess undissolved solute, or would be in equilibrium if excess solute were present. The term saturated denotes the highest concentration of solute which a solution can have and be in equilibrium with any undissolved solute with which it is pla ...
chem A exercise package C
... electron into this overlapping region or into an electron "pool." By doing this, each atom appears to gain an electron within its original boundary. For every overlapping region an atom appears to gain one electron. Two overlapping regions, such as for oxygen, will result in the gain of two electron ...
... electron into this overlapping region or into an electron "pool." By doing this, each atom appears to gain an electron within its original boundary. For every overlapping region an atom appears to gain one electron. Two overlapping regions, such as for oxygen, will result in the gain of two electron ...
Biochemistry Note
... Biochemistry Organic Chemistry – The study of compounds containing carbon (C) atoms bound to other elements such as hydrogen (H), oxygen (O) and nitrogen (N). The human body is 96% organic compounds. Note: Not all compounds that contain carbon are organic e.g. carbon dioxide (CO2), carbon monoxide ( ...
... Biochemistry Organic Chemistry – The study of compounds containing carbon (C) atoms bound to other elements such as hydrogen (H), oxygen (O) and nitrogen (N). The human body is 96% organic compounds. Note: Not all compounds that contain carbon are organic e.g. carbon dioxide (CO2), carbon monoxide ( ...
Name: Block: Date: Biology 12 - Biologically Important Molecules
... atom and H from the other breaking a bond between two atoms by adding OH to one atom and H to the other biological catalysts, composed of protein, that speed up chemical reactions ATP - the molecule that carries energy in the cell any molecule with the molecular formula Cn(H2O)n an important compone ...
... atom and H from the other breaking a bond between two atoms by adding OH to one atom and H to the other biological catalysts, composed of protein, that speed up chemical reactions ATP - the molecule that carries energy in the cell any molecule with the molecular formula Cn(H2O)n an important compone ...
Glossary of Key Terms in Chapter Two
... allosteric enzymes (19.9) enzymes that have an effector binding site as well as an active site; effector binding changes the shape of the active site, rendering it either active or inactive. apoenzyme (19.7) the protein portion of an enzyme that requires a cofactor in order to function in catalysis. ...
... allosteric enzymes (19.9) enzymes that have an effector binding site as well as an active site; effector binding changes the shape of the active site, rendering it either active or inactive. apoenzyme (19.7) the protein portion of an enzyme that requires a cofactor in order to function in catalysis. ...
Chapter 6.2 Notes
... - What do atoms joined by covalent bonds share? - What gives metals their distinctive properties? - How are polyatomic ions similar to other ions? ...
... - What do atoms joined by covalent bonds share? - What gives metals their distinctive properties? - How are polyatomic ions similar to other ions? ...
Document
... In spite of the huge size of the problem (because each side chain influences its neighbours) there are quite succesful algorithms to this problem. ...
... In spite of the huge size of the problem (because each side chain influences its neighbours) there are quite succesful algorithms to this problem. ...
A cofactor is a non-protein chemical compound that is
... substrate for a set of enzymes that produce it and a set of enzymes that consume it. An example of this is the dehydrogenases that use nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) as a cofactor. Here, hundreds of separate types of enzymes remove electrons from their substrates and reduce NAD+ to NADH. T ...
... substrate for a set of enzymes that produce it and a set of enzymes that consume it. An example of this is the dehydrogenases that use nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) as a cofactor. Here, hundreds of separate types of enzymes remove electrons from their substrates and reduce NAD+ to NADH. T ...
Enzymes
... • Enzymes act upon a substance called its substrate • Each reaction requires a specific enzyme • Enzymes must be made of something that can take ...
... • Enzymes act upon a substance called its substrate • Each reaction requires a specific enzyme • Enzymes must be made of something that can take ...
DYMATIZE
... You expect only the best from yourself and your nutrition. DYMATIZE ISO•100® is one of the most advanced and effective proteins available and was developed to give you 100% of what you need to support muscle growth and achieve your ambitions. The Fastest-Acting Protein. ISO•100 provides 25 grams of ...
... You expect only the best from yourself and your nutrition. DYMATIZE ISO•100® is one of the most advanced and effective proteins available and was developed to give you 100% of what you need to support muscle growth and achieve your ambitions. The Fastest-Acting Protein. ISO•100 provides 25 grams of ...
A physical palette for ion-beam cancer therapy
... shown in Fig. 4a divided by a factor of 5. e probabiliComplexity of the ties of DSB’s due to different geometry of dNA in electrons are shown in Fig. different states may be 4b, again for parallel and overcome, because the normal cases. Once again we geometrical differences see that the dependence o ...
... shown in Fig. 4a divided by a factor of 5. e probabiliComplexity of the ties of DSB’s due to different geometry of dNA in electrons are shown in Fig. different states may be 4b, again for parallel and overcome, because the normal cases. Once again we geometrical differences see that the dependence o ...
Spectroscopy
... macromolecules, because of their enormous number of vibrational modes. • Biological macromolecules exhibit an intrinsic order of repeating units: • the peptide bond in the protein backbone, • the phosphate ester bond • IR spectra of biological macromolecules are simpler than at first expected • line ...
... macromolecules, because of their enormous number of vibrational modes. • Biological macromolecules exhibit an intrinsic order of repeating units: • the peptide bond in the protein backbone, • the phosphate ester bond • IR spectra of biological macromolecules are simpler than at first expected • line ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.