Cellular Respiration PPT
... Occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell. Glycolysis is the process in which one molecule of glucose(6C) is broken in half, producing two molecules of pyruvic acid(3C) Requires 2 ATP molecules to get it started, but produces 4 ATP molecules and 2 NADH molecules in return ...
... Occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell. Glycolysis is the process in which one molecule of glucose(6C) is broken in half, producing two molecules of pyruvic acid(3C) Requires 2 ATP molecules to get it started, but produces 4 ATP molecules and 2 NADH molecules in return ...
Unit 03 Chapter 3 Notes
... 1. Chemical equation2. Bonds break and re-form3. All atoms that are present as reactants must 4. Balancing chemical equations- ...
... 1. Chemical equation2. Bonds break and re-form3. All atoms that are present as reactants must 4. Balancing chemical equations- ...
Summer Assignment
... temperature is constant during a phase change, but the potential energy continues to increase (heating) or decrease (cooling) ...
... temperature is constant during a phase change, but the potential energy continues to increase (heating) or decrease (cooling) ...
Introduction 1
... Lk = linking number: Number of times one edge of ribbon linked around other – topological property cannot change w/o cutting. (calculate by Lk = Tw+Wr) Twist = winding of Watson around Crick – integrated angle of twist/2p along length, not an integer, necessarily (calculate by Tw = (number of base ...
... Lk = linking number: Number of times one edge of ribbon linked around other – topological property cannot change w/o cutting. (calculate by Lk = Tw+Wr) Twist = winding of Watson around Crick – integrated angle of twist/2p along length, not an integer, necessarily (calculate by Tw = (number of base ...
Chapter 5: Microbial Metabolism
... 1. ___________ PHOSPHORYLATION- the transfer of a high-energy PO4- to ADP. 2. _________ - energy released from the transfer(loss) of electrons (oxidation) from one compound to another (reduction) is used to generate a proton gradient which is then used to make ATP 3. PHOTOPHOSPHORYLATION – sunlight ...
... 1. ___________ PHOSPHORYLATION- the transfer of a high-energy PO4- to ADP. 2. _________ - energy released from the transfer(loss) of electrons (oxidation) from one compound to another (reduction) is used to generate a proton gradient which is then used to make ATP 3. PHOTOPHOSPHORYLATION – sunlight ...
CHAPTER 1: ENZYME KINETICS AND APPLICATIONS (Part 1a
... a) they act as CATALYSTS (they are not consumed in a reaction and are regenerated to their starting state) a) they INCREASE the rate of a reaction towards equilibrium (ratio of substrate to product), but they do not determine the overall equilibrium of a reaction. [email protected] ...
... a) they act as CATALYSTS (they are not consumed in a reaction and are regenerated to their starting state) a) they INCREASE the rate of a reaction towards equilibrium (ratio of substrate to product), but they do not determine the overall equilibrium of a reaction. [email protected] ...
물리화학 소개
... These short strands served as "bio-bar codes" for identifying the protein--in this case PSA--to which the nanoparticles bound. For their experiments, Mirkin and his students added both sets of nanoparticles to solutions containing PSA proteins. Both the monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies bound to ...
... These short strands served as "bio-bar codes" for identifying the protein--in this case PSA--to which the nanoparticles bound. For their experiments, Mirkin and his students added both sets of nanoparticles to solutions containing PSA proteins. Both the monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies bound to ...
formation of chemical bonds. -
... with other atoms. The valence electrons 2. Explain the difference between the only involve in bond formation. valence electrons and the covalency of 5. Explain the formation of sodium an element. chloride and calcium oxide on the A. Valence electrons:The electrons present basis of the concept of ele ...
... with other atoms. The valence electrons 2. Explain the difference between the only involve in bond formation. valence electrons and the covalency of 5. Explain the formation of sodium an element. chloride and calcium oxide on the A. Valence electrons:The electrons present basis of the concept of ele ...
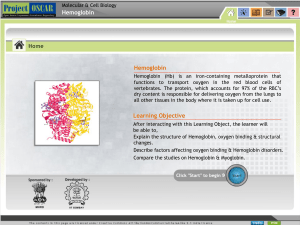
Hemoglobin Learning Objective Hemoglobin
... deoxyHb, the -His 146 forms a salt bridge with a lysine residue in the subunit. This interaction is however not possible when the His residue is deprotonated, which occurs at high pH. Upon lowering the pH, protonation of the His residue ...
... deoxyHb, the -His 146 forms a salt bridge with a lysine residue in the subunit. This interaction is however not possible when the His residue is deprotonated, which occurs at high pH. Upon lowering the pH, protonation of the His residue ...
Study Guide
... be solved empirically, a “homology model” is often constructed, based on the solved structure of another similar protein. By aligning the amino acid sequences of the two proteins, the approximate shape of the new protein can be deduced. Behavioral assay. The experiments shown in Figure 4 offered h ...
... be solved empirically, a “homology model” is often constructed, based on the solved structure of another similar protein. By aligning the amino acid sequences of the two proteins, the approximate shape of the new protein can be deduced. Behavioral assay. The experiments shown in Figure 4 offered h ...
molecule building organic
... activity. This is the way that starch is formed from glucose molecules and proteins are formed from amino acids. The monomers are linked together by the REMOVAL of a water molecule from the site of the new bond. This process is called dehydration synthesis (dehydration=removal of water, synthesis=jo ...
... activity. This is the way that starch is formed from glucose molecules and proteins are formed from amino acids. The monomers are linked together by the REMOVAL of a water molecule from the site of the new bond. This process is called dehydration synthesis (dehydration=removal of water, synthesis=jo ...
Organic Compounds
... hydrogen and oxygen. The oceans also contain salt, made up of sodium and chlorine. The atmosphere is mostly made up of the element nitrogen, existing in diatomic form (N2). It also includes oxygen, carbon (in carbon dioxide) and a small amount of other elements. Even though most of the other element ...
... hydrogen and oxygen. The oceans also contain salt, made up of sodium and chlorine. The atmosphere is mostly made up of the element nitrogen, existing in diatomic form (N2). It also includes oxygen, carbon (in carbon dioxide) and a small amount of other elements. Even though most of the other element ...
AP Review to Share - Wappingers Central School District
... Exceptions: Oxygen in peroxides is -1 Ex. H2O2 Na2O2 Then, assign hydrogen. The oxidation number of hydrogen is usually +1, but may be –1 when combined with a metal. For example: H in hydrides is -1 Ex. NaH For compounds in which both atoms cannot have the oxidation number which is equal to the char ...
... Exceptions: Oxygen in peroxides is -1 Ex. H2O2 Na2O2 Then, assign hydrogen. The oxidation number of hydrogen is usually +1, but may be –1 when combined with a metal. For example: H in hydrides is -1 Ex. NaH For compounds in which both atoms cannot have the oxidation number which is equal to the char ...
Protein 1 File
... the SAME blue colored product. This reaction is performed post-column, after Ion Exchange Chromatography separation of a mixture of amino acids. The area of each peak in the chromatogram is proportional to the relative molar amount of the amino acid of that retention time. ...
... the SAME blue colored product. This reaction is performed post-column, after Ion Exchange Chromatography separation of a mixture of amino acids. The area of each peak in the chromatogram is proportional to the relative molar amount of the amino acid of that retention time. ...
Balancing Chemical Equations Guided Inquiry (CC)
... destroyed. In fact, matter can never be created or destroyed. This is one of the basic principles in chemistry known as the Law of Conservation of Mass. Matter cannot be created or destroyed, but we can change its form. In order for the equation to make sense, we need to balance the equation. This c ...
... destroyed. In fact, matter can never be created or destroyed. This is one of the basic principles in chemistry known as the Law of Conservation of Mass. Matter cannot be created or destroyed, but we can change its form. In order for the equation to make sense, we need to balance the equation. This c ...
Enzymes
... •Each enzyme binds to a single type of substrate > both have complementary structure •substrate overall shape and charge distribution allow it to enter and interact with the enzymes active site. E + S > ES > E+ P ...
... •Each enzyme binds to a single type of substrate > both have complementary structure •substrate overall shape and charge distribution allow it to enter and interact with the enzymes active site. E + S > ES > E+ P ...
Practice exam #1 review
... 18.) What of the following is/ are the product(s) of the citric acid cyclea. CO2 b. NAPH and FAPH2 c. ATP d. H2O e. all the above Modified True or False Write T or F at each question and if false correct then make it true. 1. ATP is an energy intermediate T F 2. ATP releases energy when the bond un ...
... 18.) What of the following is/ are the product(s) of the citric acid cyclea. CO2 b. NAPH and FAPH2 c. ATP d. H2O e. all the above Modified True or False Write T or F at each question and if false correct then make it true. 1. ATP is an energy intermediate T F 2. ATP releases energy when the bond un ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.