LS50 Section 02 Slides
... Linear sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain: the amino acids are joined together by covalent peptide bonds Peptide bond ...
... Linear sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain: the amino acids are joined together by covalent peptide bonds Peptide bond ...
Groups 2 and 7
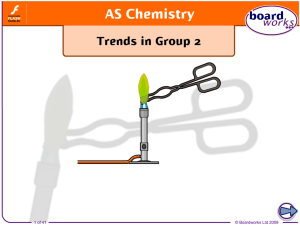
... When heated, the group 2 metal carbonates decompose to form the metal oxide and carbon dioxide gas. Splitting compounds using heat is called thermal decomposition. MCO3(s) MO(s) + CO2(g) ...
... When heated, the group 2 metal carbonates decompose to form the metal oxide and carbon dioxide gas. Splitting compounds using heat is called thermal decomposition. MCO3(s) MO(s) + CO2(g) ...
Connections of Carbohydrate, Protein, and Lipid
... muscle. The glycogen will be hydrolyzed into glucose monomers (G-1-P) if blood sugar levels drop. The presence of glycogen as a source of glucose allows ATP to be produced for a longer period of time during exercise. Glycogen is broken down into G-1-P and converted into G-6-P in both muscle and live ...
... muscle. The glycogen will be hydrolyzed into glucose monomers (G-1-P) if blood sugar levels drop. The presence of glycogen as a source of glucose allows ATP to be produced for a longer period of time during exercise. Glycogen is broken down into G-1-P and converted into G-6-P in both muscle and live ...
WEEK 11
... shown by some proteases, which split any peptide linkage. The activity of other proteases is dependent on the amino acid side chains attached to the peptide bonds. Chymotrypsin splits only those peptide bonds next to aromatic amino acids. This enzyme is said to be LINKAGE- SPECIFIC. Specificity of a ...
... shown by some proteases, which split any peptide linkage. The activity of other proteases is dependent on the amino acid side chains attached to the peptide bonds. Chymotrypsin splits only those peptide bonds next to aromatic amino acids. This enzyme is said to be LINKAGE- SPECIFIC. Specificity of a ...
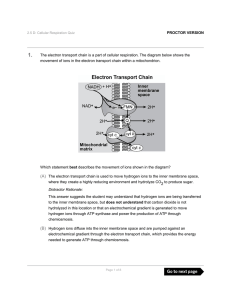
The electron transport chain is a part of cellular respiration. The
... (D) The root cutting is undergoing photolysis in the light-dependent reactions because oxygen is being split and combined with carbon to form carbon dioxide. Distractor Rationale: This answer suggests the student may understand that photolysis occurs during the lightdependent reactions in photosynth ...
... (D) The root cutting is undergoing photolysis in the light-dependent reactions because oxygen is being split and combined with carbon to form carbon dioxide. Distractor Rationale: This answer suggests the student may understand that photolysis occurs during the lightdependent reactions in photosynth ...
Amino Acid Metabolism - Breakdown Other metabolic
... 1. By flux of nitrogen through cycle - depends on diet lots protein in diet = carbon skeletons used for fuel, lots of urea starvation = breakdown muscle protein for energy, lots of urea All enzymes (CPS-I and 4 in cycle) synthesized at higher rates in starving animals and animals on high protein die ...
... 1. By flux of nitrogen through cycle - depends on diet lots protein in diet = carbon skeletons used for fuel, lots of urea starvation = breakdown muscle protein for energy, lots of urea All enzymes (CPS-I and 4 in cycle) synthesized at higher rates in starving animals and animals on high protein die ...
Chapter 8- An Introduction to Microbial Metabolism
... Cofactors: Supporting the Work of Enzymes Cofactors – metallic cofactors, such as iron, copper and zinc, they help to bring the active site and substrates together. Coenzymes – remove functional groups from one substrate molecule and add it to another substrate; i.e. they serve as transient carriers ...
... Cofactors: Supporting the Work of Enzymes Cofactors – metallic cofactors, such as iron, copper and zinc, they help to bring the active site and substrates together. Coenzymes – remove functional groups from one substrate molecule and add it to another substrate; i.e. they serve as transient carriers ...
Protein Tyrosine Nitration
... Specific proteins modified by nitration have been detected in more than 50 human disorders Associated with oxidative stress, most of the nitrating agents require the formation of reactive nitrogen and oxygen species Localized at site(s) of injury and in selective cell types Only a selective numb ...
... Specific proteins modified by nitration have been detected in more than 50 human disorders Associated with oxidative stress, most of the nitrating agents require the formation of reactive nitrogen and oxygen species Localized at site(s) of injury and in selective cell types Only a selective numb ...
1 Introduction
... paediatric patients are involved. The multiple practical advantages associated with the use of stable isotopes should also be appreciated. For instance, the non-radioactive character of the tracer allows for the simultaneous and repeated administration in one subject. Again, in paediatric investigat ...
... paediatric patients are involved. The multiple practical advantages associated with the use of stable isotopes should also be appreciated. For instance, the non-radioactive character of the tracer allows for the simultaneous and repeated administration in one subject. Again, in paediatric investigat ...
3 - Moodle NTOU
... Concept 5.3: Lipids are a diverse group of hydrophobic molecules • Lipids are the one class of large biological molecules that do not form polymers. • The unifying feature of lipids is having little or no affinity for water. • Lipids are hydrophobic becausethey consist mostly of hydrocarbons, whic ...
... Concept 5.3: Lipids are a diverse group of hydrophobic molecules • Lipids are the one class of large biological molecules that do not form polymers. • The unifying feature of lipids is having little or no affinity for water. • Lipids are hydrophobic becausethey consist mostly of hydrocarbons, whic ...
Enzymes
... an enzyme in saliva that breaks down starch into simpler sugars. This reaction occurs up to a million times faster with amylase than without it. Enzymes are also an important part of your immune system, as shown in figure 5.2. Almost all enzymes are proteins. These enzymes, like other proteins, ar ...
... an enzyme in saliva that breaks down starch into simpler sugars. This reaction occurs up to a million times faster with amylase than without it. Enzymes are also an important part of your immune system, as shown in figure 5.2. Almost all enzymes are proteins. These enzymes, like other proteins, ar ...
Coordination number 4 - INTEC Chemistry Blog
... The reason why the top line is better is because you are much less likely to spend less time with trying to write the correct number of ligands and resulting charge. And less likely to make a mistake. If however the question said something like: aq. Cu 2+ ions have a small amount of dil NH3 added to ...
... The reason why the top line is better is because you are much less likely to spend less time with trying to write the correct number of ligands and resulting charge. And less likely to make a mistake. If however the question said something like: aq. Cu 2+ ions have a small amount of dil NH3 added to ...
Electron transport via metalloporphyrins C.
... Figure 2 follows the changes in the absorption The shape of the cyclic voltammograms varied significantly according to the supporting electrolyte spectra of Ni(II)TPP during electrolysis at 1.24 V to used. Figure I shows cyclic voltammograms of give the green one-electron oxidation product. The Ni(I ...
... Figure 2 follows the changes in the absorption The shape of the cyclic voltammograms varied significantly according to the supporting electrolyte spectra of Ni(II)TPP during electrolysis at 1.24 V to used. Figure I shows cyclic voltammograms of give the green one-electron oxidation product. The Ni(I ...
CYP74C3 and CYP74A1, plant cytochrome P450 enzymes whose
... detergent micelles and that the protein was entirely watersoluble. In the same work, however, it was reported that the specific activity of the enzyme was enhanced 2–3-fold by detergent, but the molecular mechanism responsible for this activation is unknown. The molecular mechanisms and primary dete ...
... detergent micelles and that the protein was entirely watersoluble. In the same work, however, it was reported that the specific activity of the enzyme was enhanced 2–3-fold by detergent, but the molecular mechanism responsible for this activation is unknown. The molecular mechanisms and primary dete ...
Unique plant respiration
... • Electrons move from higher energy level to lower energy level, releasing energy in the process • O2 is final electron acceptor ...
... • Electrons move from higher energy level to lower energy level, releasing energy in the process • O2 is final electron acceptor ...
ATP-binding site as a further application of neural network
... residues in catalytic sites of E. coli ATP synthase was shown to improve the catalytic activity by ten times [4,] while negatively charged residues were found to abrogate the Pi binding in the same catalytic site [7, 8]. Knowledge of specific amino acids involved in ATP binding plays crucial role in ...
... residues in catalytic sites of E. coli ATP synthase was shown to improve the catalytic activity by ten times [4,] while negatively charged residues were found to abrogate the Pi binding in the same catalytic site [7, 8]. Knowledge of specific amino acids involved in ATP binding plays crucial role in ...
Chemistry 1 to 4 - Dominican
... It turns out that there are many different types of atom (over 100 in fact), and some substances are made from just one type of atom, while other substances are made from combinations of different types of atom. Elements The different types of atom are arranged in terms of their size in a table call ...
... It turns out that there are many different types of atom (over 100 in fact), and some substances are made from just one type of atom, while other substances are made from combinations of different types of atom. Elements The different types of atom are arranged in terms of their size in a table call ...
LECT23 Enz1
... 1. Enzyme: A protein or RNA molecule that has the property of a catalyst, sometimes called a biocatalyst. 2. Substrate: The target of the enzyme’s action. The molecule that will undergo chemical change as a result of the enzyme 3. Enzyme activity: A measure of the enzymes catalytic effectiveness as ...
... 1. Enzyme: A protein or RNA molecule that has the property of a catalyst, sometimes called a biocatalyst. 2. Substrate: The target of the enzyme’s action. The molecule that will undergo chemical change as a result of the enzyme 3. Enzyme activity: A measure of the enzymes catalytic effectiveness as ...
descriptive transition metal chemistry
... Oxidation State of +4 is the most pronounced, which indicates covalent character (a +4 ion would be unstable). It can have lower oxidation states though, but these are readily oxidised. Ti has a high affinity for Oxygen (sulphide ores are rare, unlike other TM’s). Ti-O bonds are short and strong, wh ...
... Oxidation State of +4 is the most pronounced, which indicates covalent character (a +4 ion would be unstable). It can have lower oxidation states though, but these are readily oxidised. Ti has a high affinity for Oxygen (sulphide ores are rare, unlike other TM’s). Ti-O bonds are short and strong, wh ...
B. Electron Deficient (less than an octet)
... Ex. Ni2+ compounds Ni has 10 valence electrons - it needs 4 bonds to reach 18 valence electrons. - Ni(CO)4 is a compound that illustrates this point. CO valence electrons :C ≡ O: (unsaturated) ...
... Ex. Ni2+ compounds Ni has 10 valence electrons - it needs 4 bonds to reach 18 valence electrons. - Ni(CO)4 is a compound that illustrates this point. CO valence electrons :C ≡ O: (unsaturated) ...
Protein structure prediction
... proteins, whose parameters are obtained by fitting experimental data on small molecules and/or from quantum mechanical calculations (Halgren, 1995 ; Moult, 1997 ; Lazaridis and Karplus, 2000 ). They present the incontestable advantage of corresponding to well-defined interactions, with a clear physi ...
... proteins, whose parameters are obtained by fitting experimental data on small molecules and/or from quantum mechanical calculations (Halgren, 1995 ; Moult, 1997 ; Lazaridis and Karplus, 2000 ). They present the incontestable advantage of corresponding to well-defined interactions, with a clear physi ...
Peer-reviewed Article PDF
... total dose can be reduced significantly if combined with other drugs [15,16]. However, drug toxicity level is high and effective only in late stage trypanosomiasis. Hence, alternative drug targets identification is indispensable. Hence, ZINC database can be used for virtual screening (VS) experiment ...
... total dose can be reduced significantly if combined with other drugs [15,16]. However, drug toxicity level is high and effective only in late stage trypanosomiasis. Hence, alternative drug targets identification is indispensable. Hence, ZINC database can be used for virtual screening (VS) experiment ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.