File - Principles of Biology 103
... A. They both utilize electron transfer chains B. They both begin with glycolysis C. They both yield the same amount of ATP D. They both rely on oxygen E. The both utilize the Kreb’s cycle 31. In alcoholic fermentation, the electrons and hydrogen are transferred from NADH to acetaldehyde forming: A. ...
... A. They both utilize electron transfer chains B. They both begin with glycolysis C. They both yield the same amount of ATP D. They both rely on oxygen E. The both utilize the Kreb’s cycle 31. In alcoholic fermentation, the electrons and hydrogen are transferred from NADH to acetaldehyde forming: A. ...
Preview Sample 2
... Global LO: G2 7) Water is both a hydrogen bond donor and acceptor. Answer: TRUE Objective: 2.3 Global LO: G2 8) Amphipathic molecules are not able to interact via van der Waals forces. Answer: FALSE Objective: 2.3 Global LO: G2 9) Ionic compounds can be readily dissolved in water because the high di ...
... Global LO: G2 7) Water is both a hydrogen bond donor and acceptor. Answer: TRUE Objective: 2.3 Global LO: G2 8) Amphipathic molecules are not able to interact via van der Waals forces. Answer: FALSE Objective: 2.3 Global LO: G2 9) Ionic compounds can be readily dissolved in water because the high di ...
Transition Metals and Coordination Chemistry
... Zn2+ => [Ar]3d10 => since all of the d orbitals are filled the d electrons if excited would have to absorb an energy outside of the visible spectrum => if the compound doesn’t absorb visible light it will be colorless (with the exception of black which is absorbing ...
... Zn2+ => [Ar]3d10 => since all of the d orbitals are filled the d electrons if excited would have to absorb an energy outside of the visible spectrum => if the compound doesn’t absorb visible light it will be colorless (with the exception of black which is absorbing ...
4.2 Respiration – Page 1 S. Preston 1 From the
... One glucose molecule is converted into _____________________ molecules. ___ ATP molecules are used per glucose molecule but ____ are produced so there is a net yield of___ ATP molecules. ___ NAD+ are converted into two ______ + ______. If oxygen is present the pyruvate will diffuse into the matrix o ...
... One glucose molecule is converted into _____________________ molecules. ___ ATP molecules are used per glucose molecule but ____ are produced so there is a net yield of___ ATP molecules. ___ NAD+ are converted into two ______ + ______. If oxygen is present the pyruvate will diffuse into the matrix o ...
Introduction to: Cellular Respiration
... Organisms cannot use glucose directly, it must be broken down into smaller units…… ATP This process in living things begins with glycolysis. If oxygen is present, glycolysis is followed by the Krebs Cycle and electron transport chain – This is called Cellular Respiration ...
... Organisms cannot use glucose directly, it must be broken down into smaller units…… ATP This process in living things begins with glycolysis. If oxygen is present, glycolysis is followed by the Krebs Cycle and electron transport chain – This is called Cellular Respiration ...
Transition Metals and Coordination Chemistry
... Zn2+ => [Ar]3d10 => since all of the d orbitals are filled the d electrons if excited would have to absorb an energy outside of the visible spectrum => if the compound doesn’t absorb visible light it will be colorless (with the exception of black which is absorbing ...
... Zn2+ => [Ar]3d10 => since all of the d orbitals are filled the d electrons if excited would have to absorb an energy outside of the visible spectrum => if the compound doesn’t absorb visible light it will be colorless (with the exception of black which is absorbing ...
8.5DF: Chemical Formulas and Equations
... reacting with water to produce carbon dioxide gas. This gas produces the “holes” in the cake that give the cake its light, fluffy texture. A similar type of reaction occurs when baking soda is mixed with vinegar. Work with your child to investigate, either online or via textbook, the chemical formul ...
... reacting with water to produce carbon dioxide gas. This gas produces the “holes” in the cake that give the cake its light, fluffy texture. A similar type of reaction occurs when baking soda is mixed with vinegar. Work with your child to investigate, either online or via textbook, the chemical formul ...
Document
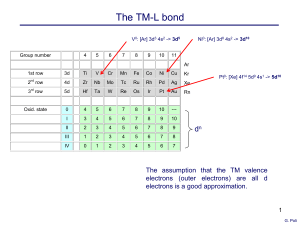
... Difference between the d configuration of the metal at zero oxidation state and the formal oxidation state of the complex Coordination Number (CN): The number of ligands directly bonded to the metal atom. Coordinative Unsaturation: Empty coordination sites where another ligand can be accommodated. I ...
... Difference between the d configuration of the metal at zero oxidation state and the formal oxidation state of the complex Coordination Number (CN): The number of ligands directly bonded to the metal atom. Coordinative Unsaturation: Empty coordination sites where another ligand can be accommodated. I ...
EF-G-GTP
... EF-Ts induces EF-Tu to release bound GDP & bind GTP. EF-Ts dissociates from EF-Tu when EF-Tu changes its conformation, upon binding GTP. ...
... EF-Ts induces EF-Tu to release bound GDP & bind GTP. EF-Ts dissociates from EF-Tu when EF-Tu changes its conformation, upon binding GTP. ...
Role of Pro-297 in the catalytic mechanism of sheep liver... hydroxymethyltransferase
... are either homodimers or homotetramers with subunit molecular masses ranging from 45 to 54 kDa. The availability of the X-ray structures of human liver cytosolic SHMT (hcSHMT) [3] and rabbit liver cytosolic SHMT [4], coupled with site-directed mutagenesis studies on Escherichia coli SHMT (eSHMT) and ...
... are either homodimers or homotetramers with subunit molecular masses ranging from 45 to 54 kDa. The availability of the X-ray structures of human liver cytosolic SHMT (hcSHMT) [3] and rabbit liver cytosolic SHMT [4], coupled with site-directed mutagenesis studies on Escherichia coli SHMT (eSHMT) and ...
glucose, faKy acids, amino acids
... • PhosphorylaDon is the process of adding a phosphate group to an organic molecule (oNen a protein) to acDvate or inacDvate the molecule. • ATP is oNen a source of phosphate groups for these rea ...
... • PhosphorylaDon is the process of adding a phosphate group to an organic molecule (oNen a protein) to acDvate or inacDvate the molecule. • ATP is oNen a source of phosphate groups for these rea ...
bio II ch 8 brookings guided pp
... • Prevents energy release in 1 explosive step • Allows energy to be released slowly in steps and captured as ATP • Electron route: food → NADH → ETC → oxygen (to make H2O) ...
... • Prevents energy release in 1 explosive step • Allows energy to be released slowly in steps and captured as ATP • Electron route: food → NADH → ETC → oxygen (to make H2O) ...
Physical Setting/Chemistry Examination
... Record the number of your choice for each Part A and Part B–1 multiple-choice question on your separate answer sheet. Write your answers to the Part B–2 and Part C questions in your answer booklet. All work should be written in pen, except for graphs and drawings, which should be done in pencil. You ...
... Record the number of your choice for each Part A and Part B–1 multiple-choice question on your separate answer sheet. Write your answers to the Part B–2 and Part C questions in your answer booklet. All work should be written in pen, except for graphs and drawings, which should be done in pencil. You ...
www.XtremePapers.com
... Permission to reproduce items where third-party owned material protected by copyright is included has been sought and cleared where possible. Every reasonable effort has been made by the publisher (UCLES) to trace copyright holders, but if any items requiring clearance have unwittingly been included ...
... Permission to reproduce items where third-party owned material protected by copyright is included has been sought and cleared where possible. Every reasonable effort has been made by the publisher (UCLES) to trace copyright holders, but if any items requiring clearance have unwittingly been included ...
Exam 2 Review Sheet - Iowa State University
... What type of fermentation occurs in animal cells in the absence of oxygen? Lactic acid (lactate) fermentation Alcoholic fermentation Galactic fermentation None of these; fermentation can only occur in yeast cells. ...
... What type of fermentation occurs in animal cells in the absence of oxygen? Lactic acid (lactate) fermentation Alcoholic fermentation Galactic fermentation None of these; fermentation can only occur in yeast cells. ...
An Introduction to Metabolism by Dr. Ty C.M. Hoffman
... not capable of cellular respiration), glycolysis must still be allowed to occur to produce ATP using energy from glucose. However, because glycolysis involves the reduction of NAD+ into NADH+H+, glycolysis re ...
... not capable of cellular respiration), glycolysis must still be allowed to occur to produce ATP using energy from glucose. However, because glycolysis involves the reduction of NAD+ into NADH+H+, glycolysis re ...
Chapter 20
... • An enzyme is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst. • Enzymes are incredibly selective for specific molecules. • An enzyme can speed up a biochemical reaction so that the rate is a million times faster than it would be in the absence of the enzyme. • Many reactions catalyzed by enzymes woul ...
... • An enzyme is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst. • Enzymes are incredibly selective for specific molecules. • An enzyme can speed up a biochemical reaction so that the rate is a million times faster than it would be in the absence of the enzyme. • Many reactions catalyzed by enzymes woul ...
Document
... • These are enzymes that use two or more substrates but catalyze reactions that are strictly ordered in the sequence in which substrates bind and products are released (Figure U2-3.3a). • Lineweaver-Burk plots of the velocity against one substrate concentration at a series of fixed concentrations of ...
... • These are enzymes that use two or more substrates but catalyze reactions that are strictly ordered in the sequence in which substrates bind and products are released (Figure U2-3.3a). • Lineweaver-Burk plots of the velocity against one substrate concentration at a series of fixed concentrations of ...
The P5 protein from bacteriophage phi
... Our analysis of sequence similarity searches and Cystovirus phage genomes suggests that the P5 protein from bacteriophage phi-6, as the only member of peptidase family U40, is homologous to the lytic transglycosylases and has a lysozyme-like fold. This prediction is consistent with the lytic functio ...
... Our analysis of sequence similarity searches and Cystovirus phage genomes suggests that the P5 protein from bacteriophage phi-6, as the only member of peptidase family U40, is homologous to the lytic transglycosylases and has a lysozyme-like fold. This prediction is consistent with the lytic functio ...
Fermentation
... electron acceptor in its electron transport chain. There are many environments or instances, however, where oxygen is not available to cells or organisms. Consider, for example, the muddy bottom of a bog, or even your muscles when they are rapidly overworked. In both of these instances, oxygen suppl ...
... electron acceptor in its electron transport chain. There are many environments or instances, however, where oxygen is not available to cells or organisms. Consider, for example, the muddy bottom of a bog, or even your muscles when they are rapidly overworked. In both of these instances, oxygen suppl ...
Protein and Lipid Catabolism
... • NADH oxidized back to NAD+ • Uses organic compound as terminal electron acceptor – Typically pyruvate or derivative • NO oxidative phosphorylation so ATP yield is low ...
... • NADH oxidized back to NAD+ • Uses organic compound as terminal electron acceptor – Typically pyruvate or derivative • NO oxidative phosphorylation so ATP yield is low ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.