Preparation of Mn(acac)
... Manganese is a first row transition metal that has a tremendous variety of oxidation states that appear in its compounds. The oxidation numbers range from Mn(–III) in compounds like Mn(NO)3CO to Mn(VII) in KMnO4. Compounds of manganese range in oxidation number between theses two extremes. This expe ...
... Manganese is a first row transition metal that has a tremendous variety of oxidation states that appear in its compounds. The oxidation numbers range from Mn(–III) in compounds like Mn(NO)3CO to Mn(VII) in KMnO4. Compounds of manganese range in oxidation number between theses two extremes. This expe ...
Determination of the Copper Content in a Copper Clad Penny 2
... Complex ions are ions formed by the bonding of a metal atom or ion to two or more ligands by coordinate covalent bonds. A ligand is a negative ion or neutral molecule attached to the central metal ion in a complex ion. Many of these species are highly colored due to their ability to absorb light in ...
... Complex ions are ions formed by the bonding of a metal atom or ion to two or more ligands by coordinate covalent bonds. A ligand is a negative ion or neutral molecule attached to the central metal ion in a complex ion. Many of these species are highly colored due to their ability to absorb light in ...
revised
... Using the TMHMM program, a total of 21473 TMs for the mesophilic set of proteins and 13340 for the thermophilic organims were predicted. The average length of the predicted TMs was 22 for both sets of proteins (thermophilic and mesophilic), which is in good agreement with the average length of TMs p ...
... Using the TMHMM program, a total of 21473 TMs for the mesophilic set of proteins and 13340 for the thermophilic organims were predicted. The average length of the predicted TMs was 22 for both sets of proteins (thermophilic and mesophilic), which is in good agreement with the average length of TMs p ...
NIH Public Access
... These findings show that phylogenetically unbiased consensus design can lead to substantial stabilization of secondary structural motifs in mesostable proteins. Analogous experiments with a chorismate mutase from Methanococcus jannaschii (MjCM),26 an EcCM homolog, suggest that this strategy is gener ...
... These findings show that phylogenetically unbiased consensus design can lead to substantial stabilization of secondary structural motifs in mesostable proteins. Analogous experiments with a chorismate mutase from Methanococcus jannaschii (MjCM),26 an EcCM homolog, suggest that this strategy is gener ...
Water soluble Vit. Vit C: (Ascorbic Acid)
... 2- VitC is essential for the activity of enzyme proline hydroxylase which catalyze the conversion of proline to hydroxyproline. hydroxyproline is amino acid vital or important in the formation of collagen 3- Vit C involved in biologic oxidation. 4- It is required for the metabolism of tyrosine. 5- I ...
... 2- VitC is essential for the activity of enzyme proline hydroxylase which catalyze the conversion of proline to hydroxyproline. hydroxyproline is amino acid vital or important in the formation of collagen 3- Vit C involved in biologic oxidation. 4- It is required for the metabolism of tyrosine. 5- I ...
Fe superoxide dismutase - Chemistry
... is believed to access each active site is lined with residues from both monomers.45 Thus, SOD displays a theme common among metalloenzymes, of metal binding at the interface between domains or subunits. This device may allow protein domains to fold around individual hydrophobic cores before coordina ...
... is believed to access each active site is lined with residues from both monomers.45 Thus, SOD displays a theme common among metalloenzymes, of metal binding at the interface between domains or subunits. This device may allow protein domains to fold around individual hydrophobic cores before coordina ...
Chapter 3 Chemical Compounds
... (a) The ions present are the calcium ion (Ca2+) and the phosphate ion (PO43–), so this is calcium phosphate. Remember that the Greek prefixes are not used in ionic compounds, only molecular compounds. (b) The ions present are the chromium(III) ion (Cr3+) and the nitride ion (the ‘-ide’ ending tells ...
... (a) The ions present are the calcium ion (Ca2+) and the phosphate ion (PO43–), so this is calcium phosphate. Remember that the Greek prefixes are not used in ionic compounds, only molecular compounds. (b) The ions present are the chromium(III) ion (Cr3+) and the nitride ion (the ‘-ide’ ending tells ...
ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN, OXIDATIVE
... Catabolism provides the energy needed for useful work, Energy is used mainly as Adenosine Tri-phosphate (ATP), ATP links Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions, ATP: Adenosine and Ribose bonded to 3-Phosphate groups via Phosphate Ester bonds, • Two bonds in ATP are High-energy bonds ...
... Catabolism provides the energy needed for useful work, Energy is used mainly as Adenosine Tri-phosphate (ATP), ATP links Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions, ATP: Adenosine and Ribose bonded to 3-Phosphate groups via Phosphate Ester bonds, • Two bonds in ATP are High-energy bonds ...
A Statistical Analysis of the Linear Interaction Energy Method
... Models of Protein-Ligand Binding • This paper classifies protein-protein binding in terms of these models • Induced fit assumed if there is no experimental evidence for a pre-existing equilibrium of multiple conformations • Note that strictly this is an artificial distinction – Statistical mechanic ...
... Models of Protein-Ligand Binding • This paper classifies protein-protein binding in terms of these models • Induced fit assumed if there is no experimental evidence for a pre-existing equilibrium of multiple conformations • Note that strictly this is an artificial distinction – Statistical mechanic ...
Organic and Bio Chemistry 16
... 1. Amino acids are the monomeric units of proteins & have the following general formula: R – CH (NH2) – COOH a. Naturally occurring amino acids are mostly L, -amino acids. Proteins are made up of the 20 different amino acids, which differ in the side chain (R) attached to the -carbon. The 20 diffe ...
... 1. Amino acids are the monomeric units of proteins & have the following general formula: R – CH (NH2) – COOH a. Naturally occurring amino acids are mostly L, -amino acids. Proteins are made up of the 20 different amino acids, which differ in the side chain (R) attached to the -carbon. The 20 diffe ...
15.Flexible_Protein_Docking_Jonathan
... Models of Protein-Ligand Binding • This paper classifies protein-protein binding in terms of these models • Induced fit assumed if there is no experimental evidence for a pre-existing equilibrium of multiple conformations • Note that strictly this is an artificial distinction – Statistical mechanic ...
... Models of Protein-Ligand Binding • This paper classifies protein-protein binding in terms of these models • Induced fit assumed if there is no experimental evidence for a pre-existing equilibrium of multiple conformations • Note that strictly this is an artificial distinction – Statistical mechanic ...
answers to part a of the canadian chemistry
... The people involved in preparing the CCC very much appreciate all the comments and feedback that we get from teachers. We have tried to incorporate some of these comments in with the solutions. We have also tried to indicate how students did in particular questions, although, unfortunately, we have ...
... The people involved in preparing the CCC very much appreciate all the comments and feedback that we get from teachers. We have tried to incorporate some of these comments in with the solutions. We have also tried to indicate how students did in particular questions, although, unfortunately, we have ...
Lecture 27
... N-acetylglutamate is synthesized from glutamate and acetylCoA by N-acetylglutamate synthase, it is hydrolyzed by a specific hydrolase. Rate of urea production is dependent on [N-acetylglutamate]. When aa breakdown rates increase, excess nitrogen must be excreted. This results in increase in Glu thro ...
... N-acetylglutamate is synthesized from glutamate and acetylCoA by N-acetylglutamate synthase, it is hydrolyzed by a specific hydrolase. Rate of urea production is dependent on [N-acetylglutamate]. When aa breakdown rates increase, excess nitrogen must be excreted. This results in increase in Glu thro ...
Biomimetic oxidation of catechol employing complexes formed in
... research on the chemistry and toxicology of these compounds has taken place [7-10]. The two most common types of quinones are ortho- and para-quinones. Ortho-quinones are the products of catechols oxidation. This oxidation is often performed to metalloproteins containing copper, like catechol oxidas ...
... research on the chemistry and toxicology of these compounds has taken place [7-10]. The two most common types of quinones are ortho- and para-quinones. Ortho-quinones are the products of catechols oxidation. This oxidation is often performed to metalloproteins containing copper, like catechol oxidas ...
IGCSE® Chemistry - Hodder Plus Home
... 2 (a) Gas particles from the coffee are moving randomly, from the coffee shop, colliding with other particles in the air until they reach you. They are diffusing. [2] (b) When the temperature rises, the steel tracks will expand. The gaps allow the tracks to expand without buckling the railway line ...
... 2 (a) Gas particles from the coffee are moving randomly, from the coffee shop, colliding with other particles in the air until they reach you. They are diffusing. [2] (b) When the temperature rises, the steel tracks will expand. The gaps allow the tracks to expand without buckling the railway line ...
Introductory Microbiology Chap. 5 Outlines Microbial Metabolism I
... 1) Bonding of a phosphate group to ADP to form ATP. 2) The energy required to bond the phosphate to ADP (and that is then stored in the resulting bond) is provided by the movement of protons back into the cell during chemiosmosis. 3) When the protons rush back into the cell (due to the gradient), en ...
... 1) Bonding of a phosphate group to ADP to form ATP. 2) The energy required to bond the phosphate to ADP (and that is then stored in the resulting bond) is provided by the movement of protons back into the cell during chemiosmosis. 3) When the protons rush back into the cell (due to the gradient), en ...
Enzymes
... Of enzyme protein on the surface of waterinsoluble carriers. Advantages : no reagents and only a minimum of activation steps are required Disadvantages : the adsorbed enzyme may leak from the carrier during use due to a weak binding force between the enzyme and the carrier. Moreover, the adsorption ...
... Of enzyme protein on the surface of waterinsoluble carriers. Advantages : no reagents and only a minimum of activation steps are required Disadvantages : the adsorbed enzyme may leak from the carrier during use due to a weak binding force between the enzyme and the carrier. Moreover, the adsorption ...
Physical Science Chapter 7 Chemical Reactions Section 7.1
... Oxidation For a long time, people have known that metals react with oxygen. Calcium reacts with oxygen and forms calcium oxide (CaO). _________________________________ __________________________________________________________________. These types of synthesis _______________________________________ ...
... Oxidation For a long time, people have known that metals react with oxygen. Calcium reacts with oxygen and forms calcium oxide (CaO). _________________________________ __________________________________________________________________. These types of synthesis _______________________________________ ...
cellular respiration
... • Cellular respiration can produce up to 38 ATP molecules for each glucose molecule consumed. • During cellular respiration, hydrogen and its bonding electrons change partners. – Hydrogen and its electrons go from sugar to oxygen, forming water. – This hydrogen transfer is why oxygen is so vital to ...
... • Cellular respiration can produce up to 38 ATP molecules for each glucose molecule consumed. • During cellular respiration, hydrogen and its bonding electrons change partners. – Hydrogen and its electrons go from sugar to oxygen, forming water. – This hydrogen transfer is why oxygen is so vital to ...
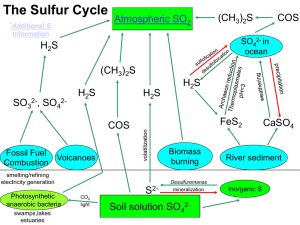
Sulfur - SOIL 5813
... synthesis of other metabolites, including CoA, biotin, thiamine, and glutathione; main function in proteins is the formation of disulfide bonds between polypeptide chains; component of other S-containing substances, including S-adenosylmethionine, formylmethionine, lipoic acid, and sulfolipid; about ...
... synthesis of other metabolites, including CoA, biotin, thiamine, and glutathione; main function in proteins is the formation of disulfide bonds between polypeptide chains; component of other S-containing substances, including S-adenosylmethionine, formylmethionine, lipoic acid, and sulfolipid; about ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.