October 15 AP Biology - John D. O`Bryant School of Math & Science
... changes in pH adds or remove H+ disrupts bonds, disrupts 3D shape disrupts attractions between charged amino acids affect 2° & 3° structure denatures protein (end 10/11) ...
... changes in pH adds or remove H+ disrupts bonds, disrupts 3D shape disrupts attractions between charged amino acids affect 2° & 3° structure denatures protein (end 10/11) ...
Document
... b. a specific t-RNA molecule, with a complementary UAC anti-codon sequence, binds to the m-RNA/ribosome complex. c. A second t-RNA-AA binds to the second site ...
... b. a specific t-RNA molecule, with a complementary UAC anti-codon sequence, binds to the m-RNA/ribosome complex. c. A second t-RNA-AA binds to the second site ...
Novel Amycolatopsis balhimycina biochemical abilities
... intact proteins and nanoLC-ESI-LIT-MS/MS analysis of their tryptic digests was carried out. With this procedure, 206 additional new proteins such as very basic, hydrophobic or large species were identified. This analysis revealed either components whose expression was previously only inferred by gro ...
... intact proteins and nanoLC-ESI-LIT-MS/MS analysis of their tryptic digests was carried out. With this procedure, 206 additional new proteins such as very basic, hydrophobic or large species were identified. This analysis revealed either components whose expression was previously only inferred by gro ...
Transition Metals
... When atomic orbitals merge into molecular orbitals to form a bond, the atomic orbitals have to overlap one-another. Only wavefunction lobes of the same sign can overlap in this way (otherwise, if lobes of opposite sign overlap then an antibonding molecular orbital forms). (The wavefunction sign has ...
... When atomic orbitals merge into molecular orbitals to form a bond, the atomic orbitals have to overlap one-another. Only wavefunction lobes of the same sign can overlap in this way (otherwise, if lobes of opposite sign overlap then an antibonding molecular orbital forms). (The wavefunction sign has ...
RESPIRATION: SYNTHESIS OF ATP
... NADH, FADH2; citric acid cycle stops. ! Without air, some cells regenerate NAD+ (from glycolysis only) by passing e- (+ H+) to pyruvic acid ! Result: continued glycolysis, forming 2 ATP per ...
... NADH, FADH2; citric acid cycle stops. ! Without air, some cells regenerate NAD+ (from glycolysis only) by passing e- (+ H+) to pyruvic acid ! Result: continued glycolysis, forming 2 ATP per ...
Cellular Respiration Chapter 9
... Just like glycolysis!! Fermentation A series of reactions that convert NADH (from glycolysis) back into NAD allowing glycolysis to keep producing a small amount of ATP ...
... Just like glycolysis!! Fermentation A series of reactions that convert NADH (from glycolysis) back into NAD allowing glycolysis to keep producing a small amount of ATP ...
Summer Study Assignment – Honors Chem 2/AP Chemistry
... 104. An essential amino acid which cannot be made (synthesized) by the body and must be obtained in the diet is methionine. What is the percentage of carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur in this amino acid if the formula of methionine is CH3SCH2CH2CHNH2COOH? 105. Ammonia is produced by the reaction of nitr ...
... 104. An essential amino acid which cannot be made (synthesized) by the body and must be obtained in the diet is methionine. What is the percentage of carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur in this amino acid if the formula of methionine is CH3SCH2CH2CHNH2COOH? 105. Ammonia is produced by the reaction of nitr ...
A chemist has discovered a drug that blocks
... respiration when all of the cell’s NAD has been converted to NADH? 5. If the Krebs cycle does not require oxygen, why does cellular respiration stop after glycolysis when no oxygen is present? 6. Why can’t cells store large quantities of ATP? (Hint: Consider both the chemical stability of the molec ...
... respiration when all of the cell’s NAD has been converted to NADH? 5. If the Krebs cycle does not require oxygen, why does cellular respiration stop after glycolysis when no oxygen is present? 6. Why can’t cells store large quantities of ATP? (Hint: Consider both the chemical stability of the molec ...
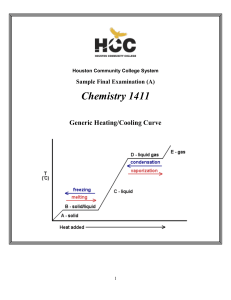
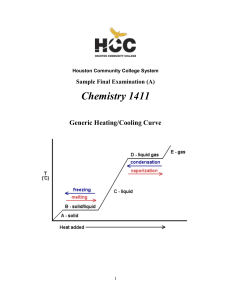
1411FINALSAMPLE+KEY - Houston Community College
... sulfur atom in the first structure is therefore sp3. However, the sulfur is not simply sp3 hybridized in the second structure, which has an “expanded octet” around the sulfur atom. Hybridizations that allow more than an octet of electrons around an atom are sp3d (10 electrons) and sp3d2 (12 electron ...
... sulfur atom in the first structure is therefore sp3. However, the sulfur is not simply sp3 hybridized in the second structure, which has an “expanded octet” around the sulfur atom. Hybridizations that allow more than an octet of electrons around an atom are sp3d (10 electrons) and sp3d2 (12 electron ...
Coordination Chemistry III: Tanabe
... Jahn-Teller Effect in Spectroscopy Frontier MO diagram eg CuII, d9 t2g There should only be one d–d transition, why is there a split in the absorption band at 900 nm? ...
... Jahn-Teller Effect in Spectroscopy Frontier MO diagram eg CuII, d9 t2g There should only be one d–d transition, why is there a split in the absorption band at 900 nm? ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC) e-ISSN: 2278-5736.
... simplest and most economical methods for the preparation of α-amino acids [2,3] for both laboratory and industrial scales [4]. The synthesis of Nitrogen-containing heterocyclic is important such as thienopyrimidine derivatives which have antibacterial and antifungal activities higher than the corres ...
... simplest and most economical methods for the preparation of α-amino acids [2,3] for both laboratory and industrial scales [4]. The synthesis of Nitrogen-containing heterocyclic is important such as thienopyrimidine derivatives which have antibacterial and antifungal activities higher than the corres ...
Glycolysis is the first stage of cellular respiration
... glucose into a cell is a type of passive transport. The digested glucose molecules move into the cytoplasm where the four stages of cellular respiration digest them further into water, ATP and oxygen. Glycolysis is the first stage of cellular respiration: In the cytoplasm a series of enzymatic react ...
... glucose into a cell is a type of passive transport. The digested glucose molecules move into the cytoplasm where the four stages of cellular respiration digest them further into water, ATP and oxygen. Glycolysis is the first stage of cellular respiration: In the cytoplasm a series of enzymatic react ...
Cellular Respiration
... broken into many smaller ones when it occurs in the body, most of which are redox reactions themselves. Although technically, cellular respiration is a combustion reaction, it clearly does not resemble one when it occurs in a living cell. This difference is because it occurs in many separate steps. ...
... broken into many smaller ones when it occurs in the body, most of which are redox reactions themselves. Although technically, cellular respiration is a combustion reaction, it clearly does not resemble one when it occurs in a living cell. This difference is because it occurs in many separate steps. ...
Protein Synthesis and the Stress Response
... several tRNA modification enzymes affect survival of E. coli in a milder oxidative stress condition (0.5 mM H2O2) [56]. Despite these reports, it is not clear how tRNA modifications improve survival to oxidative stress. It has been suggested that tRNA modifications increase the efficiency of transla ...
... several tRNA modification enzymes affect survival of E. coli in a milder oxidative stress condition (0.5 mM H2O2) [56]. Despite these reports, it is not clear how tRNA modifications improve survival to oxidative stress. It has been suggested that tRNA modifications increase the efficiency of transla ...
07_Metabolism of aminoacids
... Maple syrup urine disease - the disorder of the oxidative decarboxylation of -ketoacids derived from valine, isoleucine, and leucine caused by the missing or defect of branched-chain dehydrogenase. The levels of branched-chain amino acids and corresponding -ketoacids are markedly elevated in both ...
... Maple syrup urine disease - the disorder of the oxidative decarboxylation of -ketoacids derived from valine, isoleucine, and leucine caused by the missing or defect of branched-chain dehydrogenase. The levels of branched-chain amino acids and corresponding -ketoacids are markedly elevated in both ...
Chapter 4
... correct molar ratio of phosphorus to oxygen (2:5), no reaction will occur, after which P4O10 will form as more phosphorus is added. B. The amount of P4O10 product will accumulate as phosphorus is added until all oxygen is used up, at which point no more P4O10 can be produced. C. As long as oxygen is ...
... correct molar ratio of phosphorus to oxygen (2:5), no reaction will occur, after which P4O10 will form as more phosphorus is added. B. The amount of P4O10 product will accumulate as phosphorus is added until all oxygen is used up, at which point no more P4O10 can be produced. C. As long as oxygen is ...
(a) Name the monosaccharides of which the
... Describe how you could confirm that the granules contained starch. ...
... Describe how you could confirm that the granules contained starch. ...
T here has been intense interest in the coordination
... frequency being planar > tetrahedral > octahedral > distorted octahedral > pyramidal.19h The v(CN) band is known to undergo a blue shift in the dithiocarbamato complexes with bidentate or multidentate bonding mode, while for unidentate coordination this stretching is seen to be shifted towards lower ...
... frequency being planar > tetrahedral > octahedral > distorted octahedral > pyramidal.19h The v(CN) band is known to undergo a blue shift in the dithiocarbamato complexes with bidentate or multidentate bonding mode, while for unidentate coordination this stretching is seen to be shifted towards lower ...
Amino acid catabolism I
... 2. deamination of other compounds N-containing side chains of nucleotides neurotransmitters 3. ammonia production in the large intestine by bacteria portal vein, direct transport of ammonia. Urea cycle Function: 1. prevents ammonia levels from rising too high when large amounts of amino acids are ca ...
... 2. deamination of other compounds N-containing side chains of nucleotides neurotransmitters 3. ammonia production in the large intestine by bacteria portal vein, direct transport of ammonia. Urea cycle Function: 1. prevents ammonia levels from rising too high when large amounts of amino acids are ca ...
... 18. (6 pts) Please do one of the following questions. Choice A: Pretend you just finished the Pittsburgh marathon. As a consequence, your glycogen levels and ATP levels in the liver are quite low. Discuss the process, with the major focus on regulation in your answer, by which your glycogen levels a ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.