thoracic wall - Yeditepe University Dentistry Anatomy
... The true thoracic wall includes the thoracic cage and the muscles that extend between the ribs as well as the skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscles, and fascia covering its anterolateral aspect. The same structures covering its posterior aspect are considered to belong to the back. The mammary glands o ...
... The true thoracic wall includes the thoracic cage and the muscles that extend between the ribs as well as the skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscles, and fascia covering its anterolateral aspect. The same structures covering its posterior aspect are considered to belong to the back. The mammary glands o ...
The formation of urine
... • Each nephron has an independent blood supply • Blood moves through afferent arteriole into glomerulus (high pressure filter) then out through the efferent arteriole • Dissolved solutes (ex: ions, glucose, amino acids,urea) pass through the walls of the glomerulus into the Bowman’s capsule moving f ...
... • Each nephron has an independent blood supply • Blood moves through afferent arteriole into glomerulus (high pressure filter) then out through the efferent arteriole • Dissolved solutes (ex: ions, glucose, amino acids,urea) pass through the walls of the glomerulus into the Bowman’s capsule moving f ...
Quantitative Fluid Analysis
... When this cellular component is not functioning optimally, the entire body will greatly suffer, experiencing fatigue, lowered immune response and ultimately death. Mitochondrial function is pH and can therefore be monitored by examining the balance of pH between all of the bodily fluids. Even though ...
... When this cellular component is not functioning optimally, the entire body will greatly suffer, experiencing fatigue, lowered immune response and ultimately death. Mitochondrial function is pH and can therefore be monitored by examining the balance of pH between all of the bodily fluids. Even though ...
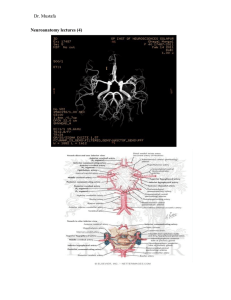
The central arteries
... It is the largest and direct branch of the internal carotid artery. It passes within the lateral sulcus and supply the insula. It supplies the lateral surface of the cerebral cortex except the periphery of about one gyrus breadth, so it supplies the contralateral part of the body with the speech and ...
... It is the largest and direct branch of the internal carotid artery. It passes within the lateral sulcus and supply the insula. It supplies the lateral surface of the cerebral cortex except the periphery of about one gyrus breadth, so it supplies the contralateral part of the body with the speech and ...
aorta thoracica
... ARTERIES Arteries carry blood from the heart. The pressure wave dilates the vascular wall and it is palpated as a pulse. Blood is ejected from the left ventricle during systole into the aorta, a tube about 2,5 cm diameter in the adult, with a wall thickness of about 1,5 mm. Three zones have classica ...
... ARTERIES Arteries carry blood from the heart. The pressure wave dilates the vascular wall and it is palpated as a pulse. Blood is ejected from the left ventricle during systole into the aorta, a tube about 2,5 cm diameter in the adult, with a wall thickness of about 1,5 mm. Three zones have classica ...
SUMMARY TERMS-Thoracic Cavity
... Inferior-mainly right ventricle with some left ventricle Superior-where great vessels enter and leave the heart Chambers Right atrium-makes up the right border of the heart and receives blood from the inferior and superior vena cava, coronary sinus, and anterior cardiac veins; located posterior to t ...
... Inferior-mainly right ventricle with some left ventricle Superior-where great vessels enter and leave the heart Chambers Right atrium-makes up the right border of the heart and receives blood from the inferior and superior vena cava, coronary sinus, and anterior cardiac veins; located posterior to t ...
Lecture 12- Venous System by Dr. Istiak Mahfuz
... The venous system of birds is nearly identical to that of reptiles except that in birds the renal portal circulation is almost completely lost, and the iliac veins drain directly into the postcavals (although some branches pass through the kidney, perhaps with slight renal portal circulation). Beca ...
... The venous system of birds is nearly identical to that of reptiles except that in birds the renal portal circulation is almost completely lost, and the iliac veins drain directly into the postcavals (although some branches pass through the kidney, perhaps with slight renal portal circulation). Beca ...
Secretion
... that are in contact with distal tubule. • Have mechano-receptors for blood pressure • The macula densa is an area of closely packed specialized cells lining the distal convoluted tubule where it lies next to the juxtaglomerular apparatus. • Cells of macula densa are taller and have more prominent nu ...
... that are in contact with distal tubule. • Have mechano-receptors for blood pressure • The macula densa is an area of closely packed specialized cells lining the distal convoluted tubule where it lies next to the juxtaglomerular apparatus. • Cells of macula densa are taller and have more prominent nu ...
Blood-113-(L1
... Destruction of Erythrocytes • At the end of RBC life span is 120 days: • Cell membrane ruptures during passage in capillaries of the spleen, bone marrow & liver. ...
... Destruction of Erythrocytes • At the end of RBC life span is 120 days: • Cell membrane ruptures during passage in capillaries of the spleen, bone marrow & liver. ...
Sympathetic reflex compensations in shock
... This leads to extreme stimulation of sympathetic nervous system. This can also be called last ditch stand of the sympathetic nervous reflexes to keep arterial pressure from falling too low. Protection of coronary and cerebral blood flow by reflexes The sympathetic nervous reflexes do not cause si ...
... This leads to extreme stimulation of sympathetic nervous system. This can also be called last ditch stand of the sympathetic nervous reflexes to keep arterial pressure from falling too low. Protection of coronary and cerebral blood flow by reflexes The sympathetic nervous reflexes do not cause si ...
Irreversible shock
... This leads to extreme stimulation of sympathetic nervous system. This can also be called last ditch stand of the sympathetic nervous reflexes to keep arterial pressure from falling too low. Protection of coronary and cerebral blood flow by reflexes The sympathetic nervous reflexes do not cause si ...
... This leads to extreme stimulation of sympathetic nervous system. This can also be called last ditch stand of the sympathetic nervous reflexes to keep arterial pressure from falling too low. Protection of coronary and cerebral blood flow by reflexes The sympathetic nervous reflexes do not cause si ...
Seeley Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th
... A. are not homeostatic. B. are rare in healthy individuals. ...
... A. are not homeostatic. B. are rare in healthy individuals. ...
Fall Guide Part I Answers
... the lungs are lateral to the heart. Negative feedback systems operate in such a way that the initial stimulus is shutoff or reduced Which orientation and directional terms have the same meaning in humans: anterior and ventral Your body thermostat is located in a part of the brain called the hypothal ...
... the lungs are lateral to the heart. Negative feedback systems operate in such a way that the initial stimulus is shutoff or reduced Which orientation and directional terms have the same meaning in humans: anterior and ventral Your body thermostat is located in a part of the brain called the hypothal ...
RAT DISSECTION PHYLUM: Chordata
... the VISCERAL MASS, which contains the heart, excretory,digestive, and reproductive organs. ...
... the VISCERAL MASS, which contains the heart, excretory,digestive, and reproductive organs. ...
Branch
... Ⅱ) The Arteries of Head and Neck The blood supply of the head and neck is chiefly from the branches of the common carotid arteries and partly from those of the subclavian ...
... Ⅱ) The Arteries of Head and Neck The blood supply of the head and neck is chiefly from the branches of the common carotid arteries and partly from those of the subclavian ...
Chapter 17 The Respiratory System: Gas Exchange and Regulation
... o P = partial pressure of gas in atmospheres The partial pressure of a gas affects the amount of gas that goes into solution Partial pressures of vaporized and dissolved gases will be equal at equilibrium Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide Solubility At 100 mm Hg partial pressure in water o [O2] in water ...
... o P = partial pressure of gas in atmospheres The partial pressure of a gas affects the amount of gas that goes into solution Partial pressures of vaporized and dissolved gases will be equal at equilibrium Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide Solubility At 100 mm Hg partial pressure in water o [O2] in water ...
Reading 1
... 1. Dorsal cavity is divided into the cranial cavity, containing the brain, and the spinal cavity, containing the spinal cord. Organs in the dorsal cavity coordinate the body’s functions via the nervous system. 2. Ventral cavity which comprises the thorax (chest) – this encases the heart and the lun ...
... 1. Dorsal cavity is divided into the cranial cavity, containing the brain, and the spinal cavity, containing the spinal cord. Organs in the dorsal cavity coordinate the body’s functions via the nervous system. 2. Ventral cavity which comprises the thorax (chest) – this encases the heart and the lun ...
Jacaranda page proofs
... Carpals, metacarpals and phalanges. These are the bones of the wrist and fingers. Carpals are short bones; metacarpals and phalanges are long. Collectively they provide structure to the hand allowing it to perform important fine motor movements such as catching, holding a bat, flicking as part of a ...
... Carpals, metacarpals and phalanges. These are the bones of the wrist and fingers. Carpals are short bones; metacarpals and phalanges are long. Collectively they provide structure to the hand allowing it to perform important fine motor movements such as catching, holding a bat, flicking as part of a ...
Heart Pump and Cardiac Cycle
... Aortic Pressure Curve Aortic pressure starts increasing during systole after the aortic valve opens. Aortic pressure decreases toward the end of the ejection phase. After the aortic valve closes, an incisura occurs because of sudden cessation of back-flow toward left ventricle. Aortic pressure ...
... Aortic Pressure Curve Aortic pressure starts increasing during systole after the aortic valve opens. Aortic pressure decreases toward the end of the ejection phase. After the aortic valve closes, an incisura occurs because of sudden cessation of back-flow toward left ventricle. Aortic pressure ...
Physiology Ch 15 p167-175 [4-25
... Clinical Estimation of Venous Pressure – can often be estimated by degree of distention of peripheral veins, especially of neck veins -in the sitting position, neck veins are never distended in the normal person -when R atrial pressure increases to as much as +10mmHg, the lower veins of the neck beg ...
... Clinical Estimation of Venous Pressure – can often be estimated by degree of distention of peripheral veins, especially of neck veins -in the sitting position, neck veins are never distended in the normal person -when R atrial pressure increases to as much as +10mmHg, the lower veins of the neck beg ...
Look Inside - Dog Gear Publishing Ltd
... Eyelids get blood laterally from the a. palpebralis inferior et superior lateralis (originating from the a. temporalis superf.), and medially from a. palpebralis inferior et superior medialis (from a. malaris). The third eyelid is supplied by the a. palpebrae tertiae (a. malaris). Venous blood goes ...
... Eyelids get blood laterally from the a. palpebralis inferior et superior lateralis (originating from the a. temporalis superf.), and medially from a. palpebralis inferior et superior medialis (from a. malaris). The third eyelid is supplied by the a. palpebrae tertiae (a. malaris). Venous blood goes ...
Movement - Cloudfront.net
... (food substances) through membranes and into body fluids • Circulation - Movement of substances throughout the body • Assimilation - Changing absorbed substances into chemically different substances • Excretion - Removal of wastes ...
... (food substances) through membranes and into body fluids • Circulation - Movement of substances throughout the body • Assimilation - Changing absorbed substances into chemically different substances • Excretion - Removal of wastes ...
Circulatory system
The circulatory system, also called the cardiovascular system, is an organ system that permits blood to circulate and transport nutrients (such as amino acids and electrolytes), oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood cells to and from the cells in the body to provide nourishment and help in fighting diseases, stabilize temperature and pH, and maintain homeostasis. The study of the blood flow is called hemodynamics. The study of the properties of the blood flow is called hemorheology.The circulatory system is often seen to comprise both the cardiovascular system, which distributes blood, and the lymphatic system, which circulates lymph. These are two separate systems. The passage of lymph for example takes a lot longer than that of blood. Blood is a fluid consisting of plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets that is circulated by the heart through the vertebrate vascular system, carrying oxygen and nutrients to and waste materials away from all body tissues. Lymph is essentially recycled excess blood plasma after it has been filtered from the interstitial fluid (between cells) and returned to the lymphatic system. The cardiovascular (from Latin words meaning 'heart' and 'vessel') system comprises the blood, heart, and blood vessels. The lymph, lymph nodes, and lymph vessels form the lymphatic system, which returns filtered blood plasma from the interstitial fluid (between cells) as lymph.While humans, as well as other vertebrates, have a closed cardiovascular system (meaning that the blood never leaves the network of arteries, veins and capillaries), some invertebrate groups have an open cardiovascular system. The lymphatic system, on the other hand, is an open system providing an accessory route for excess interstitial fluid to be returned to the blood. The more primitive, diploblastic animal phyla lack circulatory systems.