Molecular Genetic Analysis of Tunisian Patients with a Classic Form
... show a high homology with a nucleotide identity of 98% in their exon and 96% in their intron sequences (7, 8). The proximity and the high degree of homology between the two genes are believed to be the main reason for unequal crossover and gene conversion-like events, which give rise to mutations in ...
... show a high homology with a nucleotide identity of 98% in their exon and 96% in their intron sequences (7, 8). The proximity and the high degree of homology between the two genes are believed to be the main reason for unequal crossover and gene conversion-like events, which give rise to mutations in ...
SVD and PCA
... Deflation • Once we have found an eigenvector e1 with eigenvalue 1, can compute matrix A – 1 e1 e1 T • This makes eigenvalue of e1 equal to 0, but has no effect on other eigenvectors/values • In principle, could find all eigenvectors this way ...
... Deflation • Once we have found an eigenvector e1 with eigenvalue 1, can compute matrix A – 1 e1 e1 T • This makes eigenvalue of e1 equal to 0, but has no effect on other eigenvectors/values • In principle, could find all eigenvectors this way ...
DNA Mutation and Repair
... DNA Mutation and Repair • Spontaneous mutations • DNA polymerase has a proofreading activity that normally keeps mutation rates low but accidents happen and • Some types of mutation are invisible to the polymerase • Strand slippage is common in repetitive regions of the genome • DNA forms a tempora ...
... DNA Mutation and Repair • Spontaneous mutations • DNA polymerase has a proofreading activity that normally keeps mutation rates low but accidents happen and • Some types of mutation are invisible to the polymerase • Strand slippage is common in repetitive regions of the genome • DNA forms a tempora ...
Topic 1: Cells - Cardinal Newman High School
... 1.11 Discuss the theory that living organisms are composed of cells. Skeletal muscle and some fungal hyphae are not divided into cells but have a multinucleate cytoplasm. Some biologists consider unicellular organisms to be acellular. 1.1.2 State that a virus is a non-cellular structure consisting o ...
... 1.11 Discuss the theory that living organisms are composed of cells. Skeletal muscle and some fungal hyphae are not divided into cells but have a multinucleate cytoplasm. Some biologists consider unicellular organisms to be acellular. 1.1.2 State that a virus is a non-cellular structure consisting o ...
One amino acid makes the difference: the formation of ent
... poplar CPS and KS(L) proteins, truncated versions lacking the predicted signal peptides but still containing the N-terminal SxYDTxW motif reported to be conserved in KS and CPS enzymes [25] were heterologously expressed in Escherichia coli. In addition, an ent-CPS (AtCPS, Arabidopsis thaliana), a sy ...
... poplar CPS and KS(L) proteins, truncated versions lacking the predicted signal peptides but still containing the N-terminal SxYDTxW motif reported to be conserved in KS and CPS enzymes [25] were heterologously expressed in Escherichia coli. In addition, an ent-CPS (AtCPS, Arabidopsis thaliana), a sy ...
Whole body and tissue protein synthesis in cattle
... myofibrillar protein:specific radioactivity of total muscle were 0.96, 0.80 and 0.76 for the animals nos. 439, 440 and 981 respectively. In general the specific radioactivities of myofibrillar and sarcoplasmic proteins are similar in studies on other species (see Lobley & Lovie, 1979) and, if the si ...
... myofibrillar protein:specific radioactivity of total muscle were 0.96, 0.80 and 0.76 for the animals nos. 439, 440 and 981 respectively. In general the specific radioactivities of myofibrillar and sarcoplasmic proteins are similar in studies on other species (see Lobley & Lovie, 1979) and, if the si ...
2/8
... (usually allele-specific) •“Sequestration interactions” – product of one mutation sequesters the other to a suboptimal concentration in the cell (usually one allelespecific) •Combined haplo-insufficiency (allele non-specific) ...
... (usually allele-specific) •“Sequestration interactions” – product of one mutation sequesters the other to a suboptimal concentration in the cell (usually one allelespecific) •Combined haplo-insufficiency (allele non-specific) ...
Topic 1: Cells - Gimnasio del Norte
... 1.11 Discuss the theory that living organisms are composed of cells. Skeletal muscle and some fungal hyphae are not divided into cells but have a multinucleate cytoplasm. Some biologists consider unicellular organisms to be acellular. 1.1.2 State that a virus is a non-cellular structure consisting o ...
... 1.11 Discuss the theory that living organisms are composed of cells. Skeletal muscle and some fungal hyphae are not divided into cells but have a multinucleate cytoplasm. Some biologists consider unicellular organisms to be acellular. 1.1.2 State that a virus is a non-cellular structure consisting o ...
Heredity and Environment
... • The basic unit of inheritance is the gene; genes are units of DNA molecules • The cells are arranged in chromosomes, and we have 23 pairs of chromosomes in each cell • Genotype refers to what our genes are, but phenotype refers to what we actually express, or look like ...
... • The basic unit of inheritance is the gene; genes are units of DNA molecules • The cells are arranged in chromosomes, and we have 23 pairs of chromosomes in each cell • Genotype refers to what our genes are, but phenotype refers to what we actually express, or look like ...
Module 4: The Role of Genes in Cancer
... Chromosomes help ensure that DNA is accurately copied and distributed during cell division. In order for organisms to grow, cells must divide to produce new cells and replace old cells. The structure of chromosomes keeps the DNA in genes tightly wrapped around proteins during this process. Without t ...
... Chromosomes help ensure that DNA is accurately copied and distributed during cell division. In order for organisms to grow, cells must divide to produce new cells and replace old cells. The structure of chromosomes keeps the DNA in genes tightly wrapped around proteins during this process. Without t ...
Transcription and Translation RNA
... A tRNA is a single RNA chain that is folded into a two dimensional cloverleaf. This then folds in three dimensions to an L-like structure. tRNAs are small RNA molecules (usually in the range of 73 - 93 nucleotides) that participate in the translation of mRNAs. They are not part of the ribosome. But ...
... A tRNA is a single RNA chain that is folded into a two dimensional cloverleaf. This then folds in three dimensions to an L-like structure. tRNAs are small RNA molecules (usually in the range of 73 - 93 nucleotides) that participate in the translation of mRNAs. They are not part of the ribosome. But ...
transcriptomes of seeds germinating at temperature extremes
... sugar beets. Despite planting high-quality, technically-augmented seed for growers with very high germination (>92%), field emergence and persistence continues to hover at ~60% in Michigan. Previous research suggests this difference is the result of stress during germination in the field. Of stresse ...
... sugar beets. Despite planting high-quality, technically-augmented seed for growers with very high germination (>92%), field emergence and persistence continues to hover at ~60% in Michigan. Previous research suggests this difference is the result of stress during germination in the field. Of stresse ...
Postdoctoral Fellowship - CSOF4
... findings in appropriate publications and at conferences. CSIRO Agriculture is offering an opportunity for an innovative PhD graduate (or recent graduate of up to 3 years) to join their team as a prestigious CSIRO Postdoctoral Fellow (formerly OCE Postdocs). The Fellow will be embedded in a multi-dis ...
... findings in appropriate publications and at conferences. CSIRO Agriculture is offering an opportunity for an innovative PhD graduate (or recent graduate of up to 3 years) to join their team as a prestigious CSIRO Postdoctoral Fellow (formerly OCE Postdocs). The Fellow will be embedded in a multi-dis ...
Chapter 6 - Angelfire
... • Genetic rules (or Mendel’s Laws) apply equally to humans. • Many times doctors and family planners are interested to know about the history of recessive disorders in a family. They use a pedigree to analyze this. • The strength of pedigrees is that they can show recessive traits in the family, but ...
... • Genetic rules (or Mendel’s Laws) apply equally to humans. • Many times doctors and family planners are interested to know about the history of recessive disorders in a family. They use a pedigree to analyze this. • The strength of pedigrees is that they can show recessive traits in the family, but ...
Ch 8: Mendel and Heredity
... Symptoms appear in a person’s 30-40’s so may have already reproduced and passed on the allele. ...
... Symptoms appear in a person’s 30-40’s so may have already reproduced and passed on the allele. ...
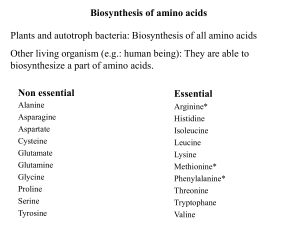
Biosynthesis of amino acids
... 1. All the amino nitrogen from amino acids that undergo transamination can be concentrated in glutamate. 2. Release of nitrogen as ammonia is catalyzed by hepatic Lglutamate dehydrogenase (GDH), 3. Glutamine synthase fixes ammonia as glutamine. Hydrolytic release of the amide nitrogen of glutamine a ...
... 1. All the amino nitrogen from amino acids that undergo transamination can be concentrated in glutamate. 2. Release of nitrogen as ammonia is catalyzed by hepatic Lglutamate dehydrogenase (GDH), 3. Glutamine synthase fixes ammonia as glutamine. Hydrolytic release of the amide nitrogen of glutamine a ...
Fusion Detection using Archer Analysis
... Each fusion candidate read that spans the same apparent breakpoint between two genes is grouped together and an initial consensus sequence is constructed by concatenating the two (or more) reference sequence fragments that are spanned by the supporting reads. The original fusion candidate reads are ...
... Each fusion candidate read that spans the same apparent breakpoint between two genes is grouped together and an initial consensus sequence is constructed by concatenating the two (or more) reference sequence fragments that are spanned by the supporting reads. The original fusion candidate reads are ...
Merging Gene Expression and Methylation Data
... • There can be additional columns (e.g., annotation), but these are not imported into the methylation project. ...
... • There can be additional columns (e.g., annotation), but these are not imported into the methylation project. ...
RNA Metabolism Summary Slides as Questions
... The DNA CODING strand is identical to the mRNA, except T is replaced with U. This is because mRNA is made complementary (and antiparallel) to the TEMPLATE strand, which in and of itself is complementary and antiparallel to the CODING strand. 2. How is 5'-3' directionality reflected in protein direct ...
... The DNA CODING strand is identical to the mRNA, except T is replaced with U. This is because mRNA is made complementary (and antiparallel) to the TEMPLATE strand, which in and of itself is complementary and antiparallel to the CODING strand. 2. How is 5'-3' directionality reflected in protein direct ...
Molecular Evolution in Nonrecombining Regions of the Drosophila
... ª The Author(s) 2012. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Molecular Biology and Evolution. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/ 3.0), which permi ...
... ª The Author(s) 2012. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Molecular Biology and Evolution. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/ 3.0), which permi ...
Chapter 14: Gene Transcription and RNA Modification
... to the more complex eukaryotic one. Before entering into the discussion of initiation, elongation, and termination, the section takes a good look at the structure of a bacterial promoter. A promoter is a regulatory sequence that plays a central role in transcriptional regulation. There are two thing ...
... to the more complex eukaryotic one. Before entering into the discussion of initiation, elongation, and termination, the section takes a good look at the structure of a bacterial promoter. A promoter is a regulatory sequence that plays a central role in transcriptional regulation. There are two thing ...