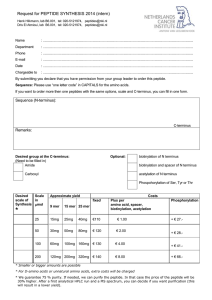
Polyomaviridae
... 1. in regulating the viral life cycle by binding to the viral origin of DNA replication where it promotes DNA synthesis. 2. replicate the host cell needs to be in s-phase for this to begin 3. modulates cellular signaling pathways • This is achieved by a two prong attack of inhibiting tumor suppressi ...
... 1. in regulating the viral life cycle by binding to the viral origin of DNA replication where it promotes DNA synthesis. 2. replicate the host cell needs to be in s-phase for this to begin 3. modulates cellular signaling pathways • This is achieved by a two prong attack of inhibiting tumor suppressi ...
Meiosis and Genetic Variation
... – Some of the chromatids are very clos to each other. – One chromatid from each chromosome breaks off and reattaches to the other chromosome (there is a swap of DNA between chromatids). – Crossing over (the swap of DNA) can occur multiple times within the same pair of homologous chromosomes. ...
... – Some of the chromatids are very clos to each other. – One chromatid from each chromosome breaks off and reattaches to the other chromosome (there is a swap of DNA between chromatids). – Crossing over (the swap of DNA) can occur multiple times within the same pair of homologous chromosomes. ...
to get the file
... Studies are indicating that the profitability of GE crops for farmers may not be as expected. A report on over 8000 university-based field studies has found lower yields and increased use of herbicide compared to conventionally bred soy. Connection between glyphosate (Roundup from Monsanto) and Canc ...
... Studies are indicating that the profitability of GE crops for farmers may not be as expected. A report on over 8000 university-based field studies has found lower yields and increased use of herbicide compared to conventionally bred soy. Connection between glyphosate (Roundup from Monsanto) and Canc ...
Biology 122, Spring 2014 Activities for the week of March 10
... G1>S checkpoint and the role of the retinoblastoma protein. Assignment 2. Write an essay describing the differences between oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes. Include in your essay explanations for why mutations in proto-oncogenes lead to tumor formation and why this can also be true for tumor su ...
... G1>S checkpoint and the role of the retinoblastoma protein. Assignment 2. Write an essay describing the differences between oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes. Include in your essay explanations for why mutations in proto-oncogenes lead to tumor formation and why this can also be true for tumor su ...
Chapter 13
... Bacterial regulator RNAs are called sRNAs. Several of the sRNAs are bound by the protein Hfq, which increases their effectiveness. The OxyS sRNA activates or represses expression of 10 loci at the posttranscriptional level. ...
... Bacterial regulator RNAs are called sRNAs. Several of the sRNAs are bound by the protein Hfq, which increases their effectiveness. The OxyS sRNA activates or represses expression of 10 loci at the posttranscriptional level. ...
Genomics I - Faculty Web Pages
... number of pedigrees or crosses involving many markers – They determine probabilities that are used to calculate the lod score Probability of a certain degree of linkage Probability of independent assortment ...
... number of pedigrees or crosses involving many markers – They determine probabilities that are used to calculate the lod score Probability of a certain degree of linkage Probability of independent assortment ...
Anna Yu`s ppt - The University of Texas at Austin
... Other Three Sequenced Diatoms • Gene Loss/Gain/Pseudonization and Functional Gene Transfer from Plastid to Nucleus • Expanded IR and Conserved IR boundary in Thalassiosirales • Conserved Gene Order Within Thalassiosirales Compared to Other Three Sequenced Diatoms ...
... Other Three Sequenced Diatoms • Gene Loss/Gain/Pseudonization and Functional Gene Transfer from Plastid to Nucleus • Expanded IR and Conserved IR boundary in Thalassiosirales • Conserved Gene Order Within Thalassiosirales Compared to Other Three Sequenced Diatoms ...
secret codon
... for the 20 different amino acids that compose proteins. Each amino acid is encoded by a sequence of three DNA bases, called a codon. Since it takes three DNA bases to designate an amino acid, there are enough combinations of the 4 different bases to represent all of the amino acids, as well as three ...
... for the 20 different amino acids that compose proteins. Each amino acid is encoded by a sequence of three DNA bases, called a codon. Since it takes three DNA bases to designate an amino acid, there are enough combinations of the 4 different bases to represent all of the amino acids, as well as three ...
postulate that the repolarisation ab
... results (10 with negative family histories). Five of the 16 patients with doubtful disease were shown to have the typical expansion (two with negative family histories). In two of the patients with confirmed diagnoses and negative family histories the parents were still alive. In one, non-paternity ...
... results (10 with negative family histories). Five of the 16 patients with doubtful disease were shown to have the typical expansion (two with negative family histories). In two of the patients with confirmed diagnoses and negative family histories the parents were still alive. In one, non-paternity ...
OPTIMISING GENE TRANSFER INTO EMBRYONIC KIDNEYS AS A
... 3-phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK) promoter. Kidneys were grown in organ culture for up to three days and transgene expression visualised as green fluorescent cells. RESULTS. Intact kidneys, unexposed to virus, differentiated in culture to form Ecadherin+ collecting ducts and Wilms tumour 1+ glomeruli. ...
... 3-phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK) promoter. Kidneys were grown in organ culture for up to three days and transgene expression visualised as green fluorescent cells. RESULTS. Intact kidneys, unexposed to virus, differentiated in culture to form Ecadherin+ collecting ducts and Wilms tumour 1+ glomeruli. ...
How To Use GOstats Testing Gene Lists for GO Term Association 1 Introduction
... men and women by group, probes measuring genes on the Y chromosome were dropped. The inter-quartile range was used with a cutoff of 0.5 to select probes with sufficient variability across samples to be informative; probes with little variability across all samples are inherently uninteresting. Final ...
... men and women by group, probes measuring genes on the Y chromosome were dropped. The inter-quartile range was used with a cutoff of 0.5 to select probes with sufficient variability across samples to be informative; probes with little variability across all samples are inherently uninteresting. Final ...
Biology - Raleigh Charter High School
... Nucleosome: The basic, beadlike unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes, consisting of a segment of DNA wound twice around a protein core composed of two copies of each of four types of histone. Histone: A small protein with a high proportion of positively charged amino acids that binds to the negativel ...
... Nucleosome: The basic, beadlike unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes, consisting of a segment of DNA wound twice around a protein core composed of two copies of each of four types of histone. Histone: A small protein with a high proportion of positively charged amino acids that binds to the negativel ...
Genomics I
... number of pedigrees or crosses involving many markers – They determine probabilities that are used to calculate the lod score Probability of a certain degree of linkage Probability of independent assortment ...
... number of pedigrees or crosses involving many markers – They determine probabilities that are used to calculate the lod score Probability of a certain degree of linkage Probability of independent assortment ...
AIMS Review Packet
... 31) How many cells are produced during mitosis? _____ cells 32) Are the resulting daughter cells genetically identical or different from the parent (original) cell? 33) Why is process of meiosis important for an organism? 34) How many times does the genetic information get split in meiosis? _______ ...
... 31) How many cells are produced during mitosis? _____ cells 32) Are the resulting daughter cells genetically identical or different from the parent (original) cell? 33) Why is process of meiosis important for an organism? 34) How many times does the genetic information get split in meiosis? _______ ...
Biology Exam Chapter 23
... 29. In sexual_ reproduction, two parent cells join together to form a new individual. 30. The physical expression of an organism’s genes is its _phenotype_. 31. If there are 46 chromosomes in a human cell, how many chromosomes are present in a human sex cell? 23 ...
... 29. In sexual_ reproduction, two parent cells join together to form a new individual. 30. The physical expression of an organism’s genes is its _phenotype_. 31. If there are 46 chromosomes in a human cell, how many chromosomes are present in a human sex cell? 23 ...
The story “Taming the Wild” http://ngm.nationalgeographic.com/2011
... The experiment itself has a strange and colorful history, dating to a time when the Soviet scientific establishment rejected Mendelian genetics. Belyaev’s older brother, also a geneticist, was sent to a labor camp based on his work, and died there. So Belyaev started the fox study in Siberia, away f ...
... The experiment itself has a strange and colorful history, dating to a time when the Soviet scientific establishment rejected Mendelian genetics. Belyaev’s older brother, also a geneticist, was sent to a labor camp based on his work, and died there. So Belyaev started the fox study in Siberia, away f ...
SURVEY OF BIOCHEMISTRY
... 2. Once an RNAP has moved from the promoter, another can bind 3. Transcription is fast: constitutive enzymes vs. inducible enzymes ...
... 2. Once an RNAP has moved from the promoter, another can bind 3. Transcription is fast: constitutive enzymes vs. inducible enzymes ...
Chapter07_Outline
... • When two phage particles that have different genotypes infect a single bacterial cell, new genotypes can arise by genetic recombination • This process differs from genetic recombination in eukaryotes: the number of participating DNA molecules varies from one cell to the next reciprocal recombi ...
... • When two phage particles that have different genotypes infect a single bacterial cell, new genotypes can arise by genetic recombination • This process differs from genetic recombination in eukaryotes: the number of participating DNA molecules varies from one cell to the next reciprocal recombi ...
Kelso High School
... If you get a tongue rolling gene from one parent and a non-tongue rolling gene from the other parent the two genes will be in competition. In this case the person will be a tongue roller because the gene for tongue rolling is more powerful than the gene for non-tongue rolling. Genes which are more ...
... If you get a tongue rolling gene from one parent and a non-tongue rolling gene from the other parent the two genes will be in competition. In this case the person will be a tongue roller because the gene for tongue rolling is more powerful than the gene for non-tongue rolling. Genes which are more ...
Summary - marric
... seed shape did not affect the gene controlling seed color. Mendel concluded that genes can segregate independently, or undergo independent assortment, during gamete formation. Not all genes show simple patterns of dominant and recessive alleles. In incomplete dominance, one allele is not completely ...
... seed shape did not affect the gene controlling seed color. Mendel concluded that genes can segregate independently, or undergo independent assortment, during gamete formation. Not all genes show simple patterns of dominant and recessive alleles. In incomplete dominance, one allele is not completely ...
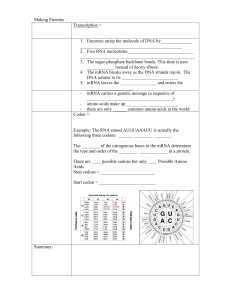
DNA Transcription
... The genetic code is ______________. (i.e. all organisms use this code and follow it to make proteins) Translation = Translation happens in the ___________________ 1. The strand of mRNA attaches to the ________________. 2. A ___________ molecule brings the first amino acid to the mRNA strand that is ...
... The genetic code is ______________. (i.e. all organisms use this code and follow it to make proteins) Translation = Translation happens in the ___________________ 1. The strand of mRNA attaches to the ________________. 2. A ___________ molecule brings the first amino acid to the mRNA strand that is ...