The essence of multicellularity - Introduction to concepts of gene
... stable, and do not gradually “drift” away into one another? The main reason why an egg can so robustly develop into a multicellular organism with distinct and stable cell types is that gene expression is regulated. Often the expression of one gene is regulated by the gene product of another gene. Th ...
... stable, and do not gradually “drift” away into one another? The main reason why an egg can so robustly develop into a multicellular organism with distinct and stable cell types is that gene expression is regulated. Often the expression of one gene is regulated by the gene product of another gene. Th ...
The Cell, 5e
... • Stromal cells secrete growth factors • Cytokines signal via membrane receptors ...
... • Stromal cells secrete growth factors • Cytokines signal via membrane receptors ...
Metabolic Crosstalk: Interactions between the
... The phenylpropanoid pathway is big in plants—particularly in trees, which can get big in no small part because of the lignin produced through this pathway. In addition to the huge carbon sink represented by lignin (reviewed in Eudes et al., 2014), the phenylpropanoid pathway also produces important ...
... The phenylpropanoid pathway is big in plants—particularly in trees, which can get big in no small part because of the lignin produced through this pathway. In addition to the huge carbon sink represented by lignin (reviewed in Eudes et al., 2014), the phenylpropanoid pathway also produces important ...
Describe the structure/ function of blood cell types
... Bone marrow stromal cells secrete growth factors Hematopoietc stem cells respond ...
... Bone marrow stromal cells secrete growth factors Hematopoietc stem cells respond ...
Section Slides
... • Large enough that ions and small molecules (e.g. metabolites) can freely diffuse through them, but proteins and ...
... • Large enough that ions and small molecules (e.g. metabolites) can freely diffuse through them, but proteins and ...
Lecture # 7 Pentose Phosphate Pathway
... The pentose pathway is a shunt. • The pathway begins with the glycolytic intermediate glucose 6-P. • It reconnects with glycolysis because two of the end products of the pentose pathway are glyceraldehyde 3-P and fructose 6-P; two intermediates further down in the glycolytic pathway. • It is for th ...
... The pentose pathway is a shunt. • The pathway begins with the glycolytic intermediate glucose 6-P. • It reconnects with glycolysis because two of the end products of the pentose pathway are glyceraldehyde 3-P and fructose 6-P; two intermediates further down in the glycolytic pathway. • It is for th ...
7-JF-S`15
... Regulation of metabolic pathways In Feedback Inhibition, high concentration of the product of a pathway controls the rate of its own synthesis by inhibiting an early step Flux through the pathway is regulated depending on the concentration of Product (K below) In Allosteric Activation, high concent ...
... Regulation of metabolic pathways In Feedback Inhibition, high concentration of the product of a pathway controls the rate of its own synthesis by inhibiting an early step Flux through the pathway is regulated depending on the concentration of Product (K below) In Allosteric Activation, high concent ...
Table S3 The genes modulated after administration of EV71
... a gene expressed strongly in cortical glutamatergic neurons and as a regulator of radial neuronal migration; be associated with various diseases is crucial for molecular transport mediate the transport of newly synthesized lysosomal enzymes with an M6P recognition motif from the TGN to lysosomes ...
... a gene expressed strongly in cortical glutamatergic neurons and as a regulator of radial neuronal migration; be associated with various diseases is crucial for molecular transport mediate the transport of newly synthesized lysosomal enzymes with an M6P recognition motif from the TGN to lysosomes ...
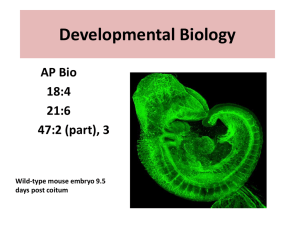
Developmental Biology
... • The other important source of developmental information is the environment around the cell, especially signals from nearby embryonic cells • In the process called induction, signal molecules from embryonic cells cause transcriptional changes in nearby target cells • Thus, interactions between cel ...
... • The other important source of developmental information is the environment around the cell, especially signals from nearby embryonic cells • In the process called induction, signal molecules from embryonic cells cause transcriptional changes in nearby target cells • Thus, interactions between cel ...
Supplementary Materials and Methods
... Two additional NSCLC microarray datasets were employed in this study to verify the identified gene predictors. One data set contained 25 NSCLC cell line and the other contained 96 primary NSCLC cases from Duke University. The validation cell lines and tumors were transcriptionally profiled with Affy ...
... Two additional NSCLC microarray datasets were employed in this study to verify the identified gene predictors. One data set contained 25 NSCLC cell line and the other contained 96 primary NSCLC cases from Duke University. The validation cell lines and tumors were transcriptionally profiled with Affy ...
Exam 1 454 Study Guide
... Identify the electron donor and acceptor, oxidizing agent, reducing agent, redox pair in an oxidation-reduction reaction. Write oxidation-reduction reactions given the reduction potentials. Identify sources of electron for oxidative phosphorylation. Describe the organization of the mitochond ...
... Identify the electron donor and acceptor, oxidizing agent, reducing agent, redox pair in an oxidation-reduction reaction. Write oxidation-reduction reactions given the reduction potentials. Identify sources of electron for oxidative phosphorylation. Describe the organization of the mitochond ...
Human Systems
... a. produces enzymes that are help break down food b. produces a substance that neutralizes stomach acid c. produces hormones that regulate blood sugar ...
... a. produces enzymes that are help break down food b. produces a substance that neutralizes stomach acid c. produces hormones that regulate blood sugar ...
Chapter 9 Signal Transduction and Cell Growth
... and functions of the cell by activating intracellular signal transduction proteins, and regulates gene expression through the relocation of intracellular signaling molecules to the nucleus. While a large number of physical and chemical stimuli exist in the environment, organisms respond only to part ...
... and functions of the cell by activating intracellular signal transduction proteins, and regulates gene expression through the relocation of intracellular signaling molecules to the nucleus. While a large number of physical and chemical stimuli exist in the environment, organisms respond only to part ...
Ratcheting the evolution of multicellularity
... of a chain of Ub proteins [polyubiquitin (poly-Ub)] targets a substrate for destruction by complexes called proteasomes (1). But unanchored poly-Ub chains are emerging as key factors in multiple cellular responses, including innate antiviral pathways (2, 3). Such free chains can also activate the ag ...
... of a chain of Ub proteins [polyubiquitin (poly-Ub)] targets a substrate for destruction by complexes called proteasomes (1). But unanchored poly-Ub chains are emerging as key factors in multiple cellular responses, including innate antiviral pathways (2, 3). Such free chains can also activate the ag ...
Developmental Biology
... signals from nearby embryonic cells • In the process called induction, signal molecules from embryonic cells cause transcriptional changes in nearby target cells • Thus, interactions between cells induce differentiation of specialized cell types ...
... signals from nearby embryonic cells • In the process called induction, signal molecules from embryonic cells cause transcriptional changes in nearby target cells • Thus, interactions between cells induce differentiation of specialized cell types ...
REVIEW A STRUCTURAL APPROACH TO G
... Guanine nucleotide binding proteins regulate a variety of physiological processes, including sensual perception, protein synthesis, hormonal regulation, vesicular and nuclear transport, cell growth and differentiation. They act as molecular mediators, cycling between inactive guanosine diphosphate ( ...
... Guanine nucleotide binding proteins regulate a variety of physiological processes, including sensual perception, protein synthesis, hormonal regulation, vesicular and nuclear transport, cell growth and differentiation. They act as molecular mediators, cycling between inactive guanosine diphosphate ( ...
Study Guide for Exam 1 Dr. Osborne
... The process of respiration is carried out by all living cells, all the time B. Anaerobic respiration (fermentation) I. Anaerobic respiration does not require air or oxygen ...
... The process of respiration is carried out by all living cells, all the time B. Anaerobic respiration (fermentation) I. Anaerobic respiration does not require air or oxygen ...
Mitochondrial Mechanisms of Photobiomodulation in Context of New
... therefore on ATP synthesis), which can be regulated by irradiation. Understanding of the multiple role of ATP in cellular metabolism will also provide a better appreciation of the cellular and molecular mechanisms of LLLT. A recent review16 indicates that laboratories worldwide are now racing to tur ...
... therefore on ATP synthesis), which can be regulated by irradiation. Understanding of the multiple role of ATP in cellular metabolism will also provide a better appreciation of the cellular and molecular mechanisms of LLLT. A recent review16 indicates that laboratories worldwide are now racing to tur ...