Document
... reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) and oxidized flavin adenine dinucleotide (FADþ ).1 Because of their role in mitochondrial electron transport, their relative fluorescence intensity, defined as the “optical redox ratio (ORR),” can be used to estimate the contribution of oxidative phos ...
... reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) and oxidized flavin adenine dinucleotide (FADþ ).1 Because of their role in mitochondrial electron transport, their relative fluorescence intensity, defined as the “optical redox ratio (ORR),” can be used to estimate the contribution of oxidative phos ...
AP Biology Question Set
... 48. The ultimate goal of metabolism is to drive ATP synthesis. ATP is considered the energy currency of the cell. Discuss how ATP couples endergonic and exergonic reactions and why it is so important in cellular functions. ...
... 48. The ultimate goal of metabolism is to drive ATP synthesis. ATP is considered the energy currency of the cell. Discuss how ATP couples endergonic and exergonic reactions and why it is so important in cellular functions. ...
Chapter 2: Major Metabolic Pathway
... With the advent of genetic engineering, it is possible to remove or add genes to an organism to alter its metabolic functions in a predetermined manner (metabolic engineering) It is important to understand the metabolic pathways in natural organisms either to use them directly or to metabolically en ...
... With the advent of genetic engineering, it is possible to remove or add genes to an organism to alter its metabolic functions in a predetermined manner (metabolic engineering) It is important to understand the metabolic pathways in natural organisms either to use them directly or to metabolically en ...
Chapter 18 Notes
... but this is wasteful production of enzymes Oh, I remember this from our Metabolism Unit! ...
... but this is wasteful production of enzymes Oh, I remember this from our Metabolism Unit! ...
Major Metabolic Pathway
... With the advent of genetic engineering, it is possible to remove or add genes to an organism to alter its metabolic functions in a predetermined manner (metabolic engineering) It is important to understand the metabolic pathways in natural organisms either to use them directly or to metabolically en ...
... With the advent of genetic engineering, it is possible to remove or add genes to an organism to alter its metabolic functions in a predetermined manner (metabolic engineering) It is important to understand the metabolic pathways in natural organisms either to use them directly or to metabolically en ...
Alkaptonuria and Aspergillus nidulans
... particularly nose bleeds. Jaundice may or may not be prominent. Despite vigorous therapy, death from hepatic failure frequently occurs between three and nine months of age unless a liver transplantation is performed. ...
... particularly nose bleeds. Jaundice may or may not be prominent. Despite vigorous therapy, death from hepatic failure frequently occurs between three and nine months of age unless a liver transplantation is performed. ...
Functional Conservation of Calreticulin in Euglena gracilis
... Ideal location for signal transduction pathways Converting one signal/stimulus into another Influences how cell can react and respond to environment. ...
... Ideal location for signal transduction pathways Converting one signal/stimulus into another Influences how cell can react and respond to environment. ...
Global Properties of the Metabolic Map of
... count of a protein complex is the number of different genes whose products are contained within the complex; the subunit count of a protein complex is the number of monomers within the complex (the subunit count takes into account the coefficient of each monomer within the complex; the component cou ...
... count of a protein complex is the number of different genes whose products are contained within the complex; the subunit count of a protein complex is the number of monomers within the complex (the subunit count takes into account the coefficient of each monomer within the complex; the component cou ...
Photosynthesis
... (a) Describe how membrane structure is related to the transport of material across a membrane. (b) Describe the role of membranes in the synthesis of ATP in either cellular respiration or photosynthesis. Energy transfer occurs in all cellular activities. For 3 of the following 5 processes involving ...
... (a) Describe how membrane structure is related to the transport of material across a membrane. (b) Describe the role of membranes in the synthesis of ATP in either cellular respiration or photosynthesis. Energy transfer occurs in all cellular activities. For 3 of the following 5 processes involving ...
Name Date ______ Your
... F. Define Anaerobic Process: ________________________________________________________ G. Define Aerobic Respiration: ______________________________________________________ ...
... F. Define Anaerobic Process: ________________________________________________________ G. Define Aerobic Respiration: ______________________________________________________ ...
Eph receptor signaling in C. elegans
... chromatin modifiers, have been proposed to act as buffers for genetic variation among unrelated processes (Lehner et al., 2006). RNAi of these hub genes can increase the frequency of the notched head phenotype in vab-1 mutants. Thus, hub genes may maintain robust biological outcomes despite variatio ...
... chromatin modifiers, have been proposed to act as buffers for genetic variation among unrelated processes (Lehner et al., 2006). RNAi of these hub genes can increase the frequency of the notched head phenotype in vab-1 mutants. Thus, hub genes may maintain robust biological outcomes despite variatio ...
Unit 2 – pupil notes
... Enzyme action can be regulated by the level of gene expression. Some metabolic reactions e.g. respiration are always required; others may need to operate only in certain circumstances. To avoid wasting resources, the genes coding for enzymes are ‘switched on’ or ‘off’ as required. ...
... Enzyme action can be regulated by the level of gene expression. Some metabolic reactions e.g. respiration are always required; others may need to operate only in certain circumstances. To avoid wasting resources, the genes coding for enzymes are ‘switched on’ or ‘off’ as required. ...
Dissection of the Blue-Light-Dependent Signal
... can be inhibited by treatment with the protein-synthesis inhibitors cycloheximide and anisomycin. The absolute requirement for light allowed us to screen for mutants that undergo gametogenesis in the dark (Buerkle et al., 1993). Three of these mutations induce light-independent expression of gamete- ...
... can be inhibited by treatment with the protein-synthesis inhibitors cycloheximide and anisomycin. The absolute requirement for light allowed us to screen for mutants that undergo gametogenesis in the dark (Buerkle et al., 1993). Three of these mutations induce light-independent expression of gamete- ...
Complexity of dopamine metabolism | Cell Communication and
... Recent publications, that have been made possible by the advancement of new technologies, describe in detail the underlying molecular mechanisms favoring these metabolic changes. In terms of today’s research these advancements pushed our limits and opened new horizons. Key technologies are very sens ...
... Recent publications, that have been made possible by the advancement of new technologies, describe in detail the underlying molecular mechanisms favoring these metabolic changes. In terms of today’s research these advancements pushed our limits and opened new horizons. Key technologies are very sens ...
General principles of cellular communication
... alter the activity of numerous cellular processes simultaneously. These processes could include DNA transcription, protein synthesis or changes in metabolic activity. The overall effect of switching various processes on or off determines the consequent change in cellular behaviour. The fidelity, acc ...
... alter the activity of numerous cellular processes simultaneously. These processes could include DNA transcription, protein synthesis or changes in metabolic activity. The overall effect of switching various processes on or off determines the consequent change in cellular behaviour. The fidelity, acc ...
Metabolic transformation in cancer
... glycolysis. Forcing proliferating cells into a resting, differentiated phenotype can decrease glycolytic rate and promote oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) as the major ATP generating process (7), indicating that, at least in the case of normal cells, this loss of the mitochondrial inhibition of gl ...
... glycolysis. Forcing proliferating cells into a resting, differentiated phenotype can decrease glycolytic rate and promote oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) as the major ATP generating process (7), indicating that, at least in the case of normal cells, this loss of the mitochondrial inhibition of gl ...
Learning Guide: Origins of Life
... 2. In the absence of oxygen, fermentation occurs. Explain the primary purpose of this process. 3. Identify the source of the electrons that travel down the electron transport chain. Explain why oxygen is the final electron acceptor in aerobic cellular respiration. 4. Create a graphic organizer that ...
... 2. In the absence of oxygen, fermentation occurs. Explain the primary purpose of this process. 3. Identify the source of the electrons that travel down the electron transport chain. Explain why oxygen is the final electron acceptor in aerobic cellular respiration. 4. Create a graphic organizer that ...
The Human Body An Orientation 1
... afferent pathway. b) efferent pathway. c) motor pathway. d) reflex pathway. a) ...
... afferent pathway. b) efferent pathway. c) motor pathway. d) reflex pathway. a) ...
Schizosaccharomyces pombe Git1 Is a C2
... cAMP signal due to the activation of adenylate cyclase (Byrne and Hoffman 1993). The genes required for S. pombe adenylate cyclase activation compose at least two functional groups on the basis of genetic interactions involving a mutationally activated form of the gpa21 gene. On the basis of biochem ...
... cAMP signal due to the activation of adenylate cyclase (Byrne and Hoffman 1993). The genes required for S. pombe adenylate cyclase activation compose at least two functional groups on the basis of genetic interactions involving a mutationally activated form of the gpa21 gene. On the basis of biochem ...
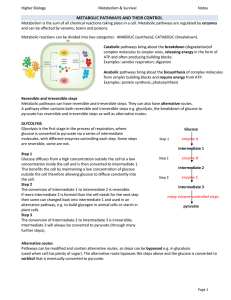
`Metabolic flux` describes the rate of flow of intermediates through a
... The R-state of PFK promotes binding of F6P; the T-state has low affinity for F6P In T-state (blue), charge repulsion between Glu & F6P disfavors binding ...
... The R-state of PFK promotes binding of F6P; the T-state has low affinity for F6P In T-state (blue), charge repulsion between Glu & F6P disfavors binding ...
Water - University of California, Los Angeles
... The R-state of PFK promotes binding of F6P; the T-state has low affinity for F6P In T-state (blue), charge repulsion between Glu & F6P disfavors binding ...
... The R-state of PFK promotes binding of F6P; the T-state has low affinity for F6P In T-state (blue), charge repulsion between Glu & F6P disfavors binding ...