Cell communication Premedical Biology
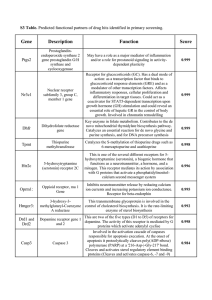
... transduction function of protein Cell responds to external signals. Signal molecule (ligand/first messenger) binds to a receptor protein in membrane and causes change of its shape (enzyme). On internal side is the signal ...
... transduction function of protein Cell responds to external signals. Signal molecule (ligand/first messenger) binds to a receptor protein in membrane and causes change of its shape (enzyme). On internal side is the signal ...
Lecture 23 - Signaling 2
... function encoded in the cytoplasmic tail of the receptor. 2) Activation of the intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity requires receptor dimerization, which is often stimulated, or at least stabilized, by ligand binding. 3) Autophosphorylation of tyrosine residues within the receptor creates phosphotyros ...
... function encoded in the cytoplasmic tail of the receptor. 2) Activation of the intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity requires receptor dimerization, which is often stimulated, or at least stabilized, by ligand binding. 3) Autophosphorylation of tyrosine residues within the receptor creates phosphotyros ...
Mechanisms of cell communication
... The three largest classes of cell-surface receptor proteins are ion-channel-linked, G-protein-linked, and enzyme-linked receptors ...
... The three largest classes of cell-surface receptor proteins are ion-channel-linked, G-protein-linked, and enzyme-linked receptors ...
BL 616 Test 1 study guide. The test will probably have 20 multiple
... plasma membrane receptors and intracellular signal transduction Kinases and phosphatases Examples: nicotinic Ach receptor is ion channel; acetylcholinesterase Receptor tyrosine kinases, such as EGFR and EGF peptide hormone nuclear hormone receptors (steroid receptors) and estrogen, retinoic acid G-p ...
... plasma membrane receptors and intracellular signal transduction Kinases and phosphatases Examples: nicotinic Ach receptor is ion channel; acetylcholinesterase Receptor tyrosine kinases, such as EGFR and EGF peptide hormone nuclear hormone receptors (steroid receptors) and estrogen, retinoic acid G-p ...
Chapter 11
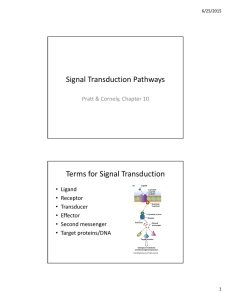
... 3 Stages of Cell Signaling: 1. Reception: Detection of a signal molecule (ligand) coming from outside the cell 2. Transduction: Convert signal to a form that can bring about a cellular response ...
... 3 Stages of Cell Signaling: 1. Reception: Detection of a signal molecule (ligand) coming from outside the cell 2. Transduction: Convert signal to a form that can bring about a cellular response ...
Cell Communication
... • Testosterone passes through the cell membrane, binds with the receptor molecule becoming active. • The active form then enters the nucleus and turns on specific genes that control male sex characteristics • Transcription factors – control which genes are turned on (transcribed into mRNA) ...
... • Testosterone passes through the cell membrane, binds with the receptor molecule becoming active. • The active form then enters the nucleus and turns on specific genes that control male sex characteristics • Transcription factors – control which genes are turned on (transcribed into mRNA) ...
Cell Communication Part I
... causing a cellular response. How do concentration levels of signal affect the cellular response? ...
... causing a cellular response. How do concentration levels of signal affect the cellular response? ...
Cell Communication PPT
... distance between the cell it is trying to signal • 4 Main types of cell signaling: - Direct Communication - Paracrine Signaling - Endocrine Signaling - Synaptic Signaling • Autocrine Signaling is another important signaling event - This occurs when a cell signals itself - Important in the immune sys ...
... distance between the cell it is trying to signal • 4 Main types of cell signaling: - Direct Communication - Paracrine Signaling - Endocrine Signaling - Synaptic Signaling • Autocrine Signaling is another important signaling event - This occurs when a cell signals itself - Important in the immune sys ...
Document
... • Cytokinesis- division of cytoplasm • Animals – cleavage furrow • Plants – Cell plate ...
... • Cytokinesis- division of cytoplasm • Animals – cleavage furrow • Plants – Cell plate ...
038-Signal Transduction Pathways Activity-V Morris
... Step 2: "The binding of the ligand causes a conformation change to the subunits on G-protein. The alpha subunit will move to a protein called adenlyl cyclase." Move the alpha subunit to the adenylyl cyclase. Step 3: Adenylyl cyclase is now ready to convert ATP into cAMP. Take off 2 phosphates from A ...
... Step 2: "The binding of the ligand causes a conformation change to the subunits on G-protein. The alpha subunit will move to a protein called adenlyl cyclase." Move the alpha subunit to the adenylyl cyclase. Step 3: Adenylyl cyclase is now ready to convert ATP into cAMP. Take off 2 phosphates from A ...
RAS (overview) Midwest 2013
... The Ras mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade, including Raf, Mek and Erk, is a ubiquitous signaling module that couples receptor-mediated events at the cell surface to cytoplasmic and nuclear effectors. The Ras MAPK cascade is perhaps best known for its crucial role in mediating the trans ...
... The Ras mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade, including Raf, Mek and Erk, is a ubiquitous signaling module that couples receptor-mediated events at the cell surface to cytoplasmic and nuclear effectors. The Ras MAPK cascade is perhaps best known for its crucial role in mediating the trans ...
POGIL “Cellular Communication” KEY
... 10. The researcher could develop a medicine that blocks the receptor on the cell that normally receives the signal. Another possible solution could be to develop a medicine that prevents the release of the signal. 11. Develop a medicine that mimics the signal (ligand) or a medicine that makes the ce ...
... 10. The researcher could develop a medicine that blocks the receptor on the cell that normally receives the signal. Another possible solution could be to develop a medicine that prevents the release of the signal. 11. Develop a medicine that mimics the signal (ligand) or a medicine that makes the ce ...
How do cells communicate?
... • Phosphorylation - converts from inactive form to active form. • hundreds of protein kinases, each specific – 1% of genes code for protein kinases ...
... • Phosphorylation - converts from inactive form to active form. • hundreds of protein kinases, each specific – 1% of genes code for protein kinases ...
PowerPoint 簡報
... Oncogenes are mutant forms of the genes for protein that regulate the cell cycle ...
... Oncogenes are mutant forms of the genes for protein that regulate the cell cycle ...
HD1Intro
... While there are many known intracellular signals, surprisingly the major inductive cues for almost all developmental events turn out to be members of just a few families of proteins ...
... While there are many known intracellular signals, surprisingly the major inductive cues for almost all developmental events turn out to be members of just a few families of proteins ...
邵吉民_Signal_and_dis
... up regulation: increase in number of receptors hypersensitivity: increased response to ligand stimulation, or self-activation without ligands ...
... up regulation: increase in number of receptors hypersensitivity: increased response to ligand stimulation, or self-activation without ligands ...
Cell Communication Problem Set
... Problem 8: Protein Kinase Cascades Some receptors for growth factors activate a protein kinase cascade, with the participation of multiple enzymes to effect a change in gene expression. Which of the following statements about a protein kinase cascade are true? A. B. C. D. E. ...
... Problem 8: Protein Kinase Cascades Some receptors for growth factors activate a protein kinase cascade, with the participation of multiple enzymes to effect a change in gene expression. Which of the following statements about a protein kinase cascade are true? A. B. C. D. E. ...
Outline Section 4
... b. Convergent, or redundant, cross-talk for essential responses occurs when two or more ligands can produce the same target mechanism 3. Multiple target mechanism pathways and divergent crosstalk a. Divergent cross-talk for complex, integrated responses where a single ligand can activate two or mor ...
... b. Convergent, or redundant, cross-talk for essential responses occurs when two or more ligands can produce the same target mechanism 3. Multiple target mechanism pathways and divergent crosstalk a. Divergent cross-talk for complex, integrated responses where a single ligand can activate two or mor ...
Signal Transduction Pathways Terms for Signal Transduction
... • Second major class of receptors – Insulin binding as prototype – Mostly monomers that bind ligand and then dimerize • One subunit binds ligand • Second subunit become active kinases ...
... • Second major class of receptors – Insulin binding as prototype – Mostly monomers that bind ligand and then dimerize • One subunit binds ligand • Second subunit become active kinases ...
Cell Communication Study Guide
... 8. Explain the term ligand. Give an example of how a ligand is used. ...
... 8. Explain the term ligand. Give an example of how a ligand is used. ...
CELL SIGNALLING
... Conformational change in G – protein, causing it to bind GTP. G protein (with GTP bound) migrates in membrane Binds to and activates adenyl cyclase enzyme (ATP cAMP) ...
... Conformational change in G – protein, causing it to bind GTP. G protein (with GTP bound) migrates in membrane Binds to and activates adenyl cyclase enzyme (ATP cAMP) ...
Rohatgi Lab - Stanford Biochemistry
... Rohatgi Lab Cell Biology of Signal Transduction in Development and Disease Background Developmental signaling pathways, initially studied for their roles in embryogenesis, have been implicated in adult organ regeneration, stem-cell function, and cancer. Our long term goal is to understand the spatia ...
... Rohatgi Lab Cell Biology of Signal Transduction in Development and Disease Background Developmental signaling pathways, initially studied for their roles in embryogenesis, have been implicated in adult organ regeneration, stem-cell function, and cancer. Our long term goal is to understand the spatia ...
Paracrine signalling

Paracrine signaling is a form of cell-cell communication in which a cell produces a signal to induce changes in nearby cells, altering the behavior or differentiation of those cells. Signaling molecules known as paracrine factors diffuse over a relatively short distance (local action), as opposed to endocrine factors (hormones which travel considerably longer distances via the circulatory system), juxtacrine interactions, and autocrine signaling. Cells that produce paracrine factors secrete them into the immediate extracellular environment. Factors then travel to nearby cells in which the gradient of factor received determines the outcome. However, the exact distance that paracrine factors can travel is not certain.Although paracrine signaling elicits a diverse array of responses in the induced cells, most paracrine factors utilize a relatively streamlined set of receptors and pathways. In fact, different organs in the body -even between different species - are known to utilize a similar sets of paracrine factors in differential development. The highly conserved receptors and pathways can be organized into four major families based on similar structures: Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family, Hedgehog family, Wnt family, and TGF-β superfamily. Binding of a paracrine factor to its respective receptor initiates signal transduction cascades, eliciting different responses.