Chapter 19 - Diagnostic Imaging
... A. Hazards – all tissues are sensitive a. Cells are damaged at the DNA level b. Younger tissues/organs more sensitive c. Cells that divide rapidly more sensitive d. Critical organs = dermis, thyroid, eyes, lymphatic system, blood forming tissue, bone, gonads B. Measurement – absorbed dose is measure ...
... A. Hazards – all tissues are sensitive a. Cells are damaged at the DNA level b. Younger tissues/organs more sensitive c. Cells that divide rapidly more sensitive d. Critical organs = dermis, thyroid, eyes, lymphatic system, blood forming tissue, bone, gonads B. Measurement – absorbed dose is measure ...
Dental CT scanners and physical quality parameters El
... Background: The use of cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) in dentistry has proven to be useful in the diagnosis and treatment planning of several oral and maxillofacial diseases. The quality of the resulting image is dictated by many factors related to the patient, unit and operator. Materials and ...
... Background: The use of cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) in dentistry has proven to be useful in the diagnosis and treatment planning of several oral and maxillofacial diseases. The quality of the resulting image is dictated by many factors related to the patient, unit and operator. Materials and ...
radiation dose patient information
... given off by the radioactive material in your body, forming a picture of your organs functioning on a computer monitor. The radioactive material typically disappears from your body within a few hours or days. Regulations There are no regulatory limits on the cumulative amount of radia ...
... given off by the radioactive material in your body, forming a picture of your organs functioning on a computer monitor. The radioactive material typically disappears from your body within a few hours or days. Regulations There are no regulatory limits on the cumulative amount of radia ...
Three-Dimensional Conformal Radiation Therapy
... • Powerful x-ray CT-simulation and three-dimensional treatment planning systems (3DTPS) have been commercially available since the early 1990's and threedimensional conformal radiation therapy (3DCRT) is now firmly in place as the standard of practice. ...
... • Powerful x-ray CT-simulation and three-dimensional treatment planning systems (3DTPS) have been commercially available since the early 1990's and threedimensional conformal radiation therapy (3DCRT) is now firmly in place as the standard of practice. ...
Complete dose study of double orbit cone
... of image-guided radiotherapy (IGRT). It allows the physician to take detailed volumetric images of the treatment area before and during radiation treatment to ensure an accurate delivery of planned treatment. The nature of radiotherapy is that the process itself is spread out over a period of time w ...
... of image-guided radiotherapy (IGRT). It allows the physician to take detailed volumetric images of the treatment area before and during radiation treatment to ensure an accurate delivery of planned treatment. The nature of radiotherapy is that the process itself is spread out over a period of time w ...
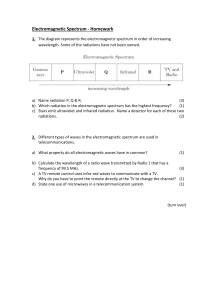
EM Spectrum 2
... Electromagnetic Spectrum Ex2 1. Different types of radiation are used to detect and treat illnesses and injuries. Four of these radiations are; ...
... Electromagnetic Spectrum Ex2 1. Different types of radiation are used to detect and treat illnesses and injuries. Four of these radiations are; ...
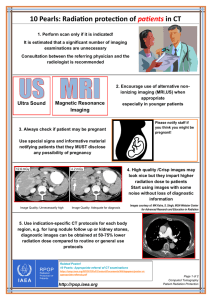
10 Pearls: Radiation protection of patients in CT - RPOP
... 1. Perform scan only if it is indicated! It is estimated that a significant number of imaging examinations are unnecessary Consultation between the referring physician and the radiologist is recommended ...
... 1. Perform scan only if it is indicated! It is estimated that a significant number of imaging examinations are unnecessary Consultation between the referring physician and the radiologist is recommended ...
the radiology trifecta - Atlanta Society of Radiologic Technologists
... Imaging Trifecta. Sports enthusiasts recognize trifecta as a horse racing term and more recently introduced by Dick Vitale as a basketball term of accomplishment. In this refresher course The Medical Imaging Trifecta – reduce patient radiation dose, control occupational radiation exposure, and produ ...
... Imaging Trifecta. Sports enthusiasts recognize trifecta as a horse racing term and more recently introduced by Dick Vitale as a basketball term of accomplishment. In this refresher course The Medical Imaging Trifecta – reduce patient radiation dose, control occupational radiation exposure, and produ ...
Medical Use of Radioisotopes
... Gamma Knife Radiosurgery (CyberKnife) Minimizing injury to healthy cells, radiation therapy involves rotating an external radiation beam around the patient. The radiation from the radioactive source is delivered from many directions, with the beam continually focused on the target abnormality with o ...
... Gamma Knife Radiosurgery (CyberKnife) Minimizing injury to healthy cells, radiation therapy involves rotating an external radiation beam around the patient. The radiation from the radioactive source is delivered from many directions, with the beam continually focused on the target abnormality with o ...
RT 101 - Mohawk Valley Community College
... 5. Explain the purpose of a radiation control program as based on ALARA. 6. Distinguish among the various general manifestations of radiation, and list the properties of X-ray. 7. Explain the radiation dose specification of Equivalent dose and the potential for biologic harm due to radiation exposur ...
... 5. Explain the purpose of a radiation control program as based on ALARA. 6. Distinguish among the various general manifestations of radiation, and list the properties of X-ray. 7. Explain the radiation dose specification of Equivalent dose and the potential for biologic harm due to radiation exposur ...
Useful Websites Related to Radiation and Imaging Technology
... Molecular imaging is a type of medical imaging that provides detailed pictures of what is happening inside the body at the molecular and cellular level that allows physicians to see how the body is functioning and to measure its chemical and biological processes. Learn more: www.DiscoverMI.org (SNMM ...
... Molecular imaging is a type of medical imaging that provides detailed pictures of what is happening inside the body at the molecular and cellular level that allows physicians to see how the body is functioning and to measure its chemical and biological processes. Learn more: www.DiscoverMI.org (SNMM ...
MR-LINAC image guided radiotherapy for cancer treatment
... The company state that the ability of the MR-LINAC system to provide real-time MR images during treatment, allows clinicians to visualise the patient’s internal anatomy, including soft tissue, and to respond to any changes by adjusting the treatment plan and delivery. The company add that this will ...
... The company state that the ability of the MR-LINAC system to provide real-time MR images during treatment, allows clinicians to visualise the patient’s internal anatomy, including soft tissue, and to respond to any changes by adjusting the treatment plan and delivery. The company add that this will ...
Electromagnetic Spectrum
... a) What type of radiation is used to treat skin conditions such as acne? b) State one medical use of X-rays. c) What can be used to detect X-rays? d) ...
... a) What type of radiation is used to treat skin conditions such as acne? b) State one medical use of X-rays. c) What can be used to detect X-rays? d) ...
IOM and IMRT - Heather L. Schultz
... therapeutic ratio by reducing the toxicity of radiation while ensuring the effective doses are delivered to the target volume. o Another goal of IMRT is to increase tumor dose without increasing morbidity or sacrificing tumor control What is it? o A form of 3D conformal therapy where the shape of ...
... therapeutic ratio by reducing the toxicity of radiation while ensuring the effective doses are delivered to the target volume. o Another goal of IMRT is to increase tumor dose without increasing morbidity or sacrificing tumor control What is it? o A form of 3D conformal therapy where the shape of ...
ADVANCED RADIOTHERAPY TECHNIQUES
... diagnostic imaging is used to correct the patient setup and positioning for treatment every day. IGRT processes have greatly increased the accuracy in the delivery of the radiation therapy that can be routinely achieved. This improved confidence in targeting accuracy has made possible the developmen ...
... diagnostic imaging is used to correct the patient setup and positioning for treatment every day. IGRT processes have greatly increased the accuracy in the delivery of the radiation therapy that can be routinely achieved. This improved confidence in targeting accuracy has made possible the developmen ...
Radiation therapy

Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, often abbreviated RT, RTx, or XRT, is therapy using ionizing radiation, generally as part of cancer treatment to control or kill malignant cells. Radiation therapy may be curative in a number of types of cancer if they are localized to one area of the body. It may also be used as part of adjuvant therapy, to prevent tumor recurrence after surgery to remove a primary malignant tumor (for example, early stages of breast cancer). Radiation therapy is synergistic with chemotherapy, and has been used before, during, and after chemotherapy in susceptible cancers. The subspecialty of oncology that focuses on radiotherapy is called radiation oncology.Radiation therapy is commonly applied to the cancerous tumor because of its ability to control cell growth. Ionizing radiation works by damaging the DNA of cancerous tissue leading to cellular death. To spare normal tissues (such as skin or organs which radiation must pass through to treat the tumor), shaped radiation beams are aimed from several angles of exposure to intersect at the tumor, providing a much larger absorbed dose there than in the surrounding, healthy tissue. Besides the tumour itself, the radiation fields may also include the draining lymph nodes if they are clinically or radiologically involved with tumor, or if there is thought to be a risk of subclinical malignant spread. It is necessary to include a margin of normal tissue around the tumor to allow for uncertainties in daily set-up and internal tumor motion. These uncertainties can be caused by internal movement (for example, respiration and bladder filling) and movement of external skin marks relative to the tumor position.Radiation oncology is the medical specialty concerned with prescribing radiation, and is distinct from radiology, the use of radiation in medical imaging and diagnosis. Radiation may be prescribed by a radiation oncologist with intent to cure (""curative"") or for adjuvant therapy. It may also be used as palliative treatment (where cure is not possible and the aim is for local disease control or symptomatic relief) or as therapeutic treatment (where the therapy has survival benefit and it can be curative). It is also common to combine radiation therapy with surgery, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, immunotherapy or some mixture of the four. Most common cancer types can be treated with radiation therapy in some way.The precise treatment intent (curative, adjuvant, neoadjuvant, therapeutic, or palliative) will depend on the tumor type, location, and stage, as well as the general health of the patient. Total body irradiation (TBI) is a radiation therapy technique used to prepare the body to receive a bone marrow transplant. Brachytherapy, in which a radiation source is placed inside or next to the area requiring treatment, is another form of radiation therapy that minimizes exposure to healthy tissue during procedures to treat cancers of the breast, prostate and other organs.Radiation therapy has several applications in non-malignant conditions, such as the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia, acoustic neuromas, severe thyroid eye disease, pterygium, pigmented villonodular synovitis, and prevention of keloid scar growth, vascular restenosis, and heterotopic ossification. The use of radiation therapy in non-malignant conditions is limited partly by worries about the risk of radiation-induced cancers.