Vessel Imaging by Interferometric Phase-Contrast X
... values compared with the d␦ of liver tissue (3.5⫻10⫺8). The measured d␦ of FC-43 was lower than the theoretical value. We speculate that the density of FC-43 decreased during stabilization of the interferometer (⬇5 to 10 minutes) because of the nature of its rapid precipitation. Because the differen ...
... values compared with the d␦ of liver tissue (3.5⫻10⫺8). The measured d␦ of FC-43 was lower than the theoretical value. We speculate that the density of FC-43 decreased during stabilization of the interferometer (⬇5 to 10 minutes) because of the nature of its rapid precipitation. Because the differen ...
A Guide to Clinical PET in Oncology
... vivo, and the addition of CT imaging underlines the site of malignancy. More accurate and precise interpretation of cancer lesions can therefore be performed by PET/CT imaging than PET or CT imaging alone. Clinical PET, in particular with fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FDG), has already proven ...
... vivo, and the addition of CT imaging underlines the site of malignancy. More accurate and precise interpretation of cancer lesions can therefore be performed by PET/CT imaging than PET or CT imaging alone. Clinical PET, in particular with fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FDG), has already proven ...
Advances in Magnetic Resonance Imaging: How They Are
... time was 35 min. In 68 patients with similar characteristics, Hambrock and colleagues [21] analyzed the results of multiparametric 3T MR-guided biopsy and compared them with results from a matched population of patients who underwent multisession TRUS-guided biopsy. The tumour detection rate for MR- ...
... time was 35 min. In 68 patients with similar characteristics, Hambrock and colleagues [21] analyzed the results of multiparametric 3T MR-guided biopsy and compared them with results from a matched population of patients who underwent multisession TRUS-guided biopsy. The tumour detection rate for MR- ...
Evaluation of the Reliability and Accuracy of Using Cone
... none of these were accurate. Recently, studies on preoperative differential diagnosis using advanced imaging technology, such as computed tomographic (CT) (7) and cone-beam computed tomographic imaging (CBCT) (8, 9), have become available in the literature. Aggarwal et al (7) used computed tomograph ...
... none of these were accurate. Recently, studies on preoperative differential diagnosis using advanced imaging technology, such as computed tomographic (CT) (7) and cone-beam computed tomographic imaging (CBCT) (8, 9), have become available in the literature. Aggarwal et al (7) used computed tomograph ...
Reducing Radiation Dose to the Female Breast During
... things at once. For providing valuable guidance, especially that which is in the form of a six-year-old binder of notes on the mathematics and statistics of computed tomography, which I referred to countless times throughout my research, I thank Dr. Anne Clough. I would also like to thank Dominic Cr ...
... things at once. For providing valuable guidance, especially that which is in the form of a six-year-old binder of notes on the mathematics and statistics of computed tomography, which I referred to countless times throughout my research, I thank Dr. Anne Clough. I would also like to thank Dominic Cr ...
rsd product brochure - Radiology Support Devices
... work statement had to be changed to permit a splash-down landing.The complications caused by this program led to insolvency of the company. Mr. Alderson then moved to California, where he had grown up, and started Humanetics Inc., devoted to the further development and manufacture of crash-test dumm ...
... work statement had to be changed to permit a splash-down landing.The complications caused by this program led to insolvency of the company. Mr. Alderson then moved to California, where he had grown up, and started Humanetics Inc., devoted to the further development and manufacture of crash-test dumm ...
An Overview of Elastography–An Emerging Branch of Medical Imaging
... Bamber who showed that the time rate of decorrelation between successive A-mode scans may be a useful discriminator between hard and soft tissues subjected to either secondary or externally induced movement [28, 29]. Tristam and coworkers moved Hill’s ideas to more practical implementation. They wer ...
... Bamber who showed that the time rate of decorrelation between successive A-mode scans may be a useful discriminator between hard and soft tissues subjected to either secondary or externally induced movement [28, 29]. Tristam and coworkers moved Hill’s ideas to more practical implementation. They wer ...
Diagnostic Reference Levels in Medical Imaging
... newer imaging technologies. This report is intended as a further source of information and guidance on these issues. Some terminology has been clarified. In addition, the report recommends quantities for use as DRLs for various imaging modalities, and provides information on use of DRLs for interven ...
... newer imaging technologies. This report is intended as a further source of information and guidance on these issues. Some terminology has been clarified. In addition, the report recommends quantities for use as DRLs for various imaging modalities, and provides information on use of DRLs for interven ...
the Abstract-Book here
... the discussion of 63 scientific posters. Both days have two morning and two afternoon sessions with intermediate coffee breaks. For the first time in our event history, 2014 will feature three one-hour symposia over lunch and dinner which are hosted by our gold and silver sponsors. Our technical exh ...
... the discussion of 63 scientific posters. Both days have two morning and two afternoon sessions with intermediate coffee breaks. For the first time in our event history, 2014 will feature three one-hour symposia over lunch and dinner which are hosted by our gold and silver sponsors. Our technical exh ...
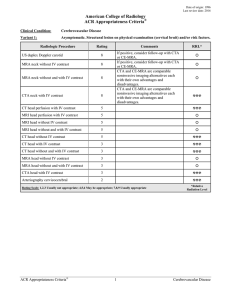
American College of Radiology ACR Appropriateness Criteria
... Gold standard test. Usually performed after initial noninvasive imaging with MR or CT. Parenchymal imaging and CT or MR vascular brain imaging should be considered. MRI is superior to CT for parenchymal evaluation due to greater range of soft-tissue contrast and improved anatomic detail. It is helpf ...
... Gold standard test. Usually performed after initial noninvasive imaging with MR or CT. Parenchymal imaging and CT or MR vascular brain imaging should be considered. MRI is superior to CT for parenchymal evaluation due to greater range of soft-tissue contrast and improved anatomic detail. It is helpf ...
Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging - MS-MRI
... injury and potential clinical outcome. SWI is particularly helpful for the evaluation of diffuse axonal injury (DAI), often associated with punctate hemorrhages in the deep subcortical white matter, which are not routinely visible on CT or conventional MR imaging sequences. SWI exploits the magnetic ...
... injury and potential clinical outcome. SWI is particularly helpful for the evaluation of diffuse axonal injury (DAI), often associated with punctate hemorrhages in the deep subcortical white matter, which are not routinely visible on CT or conventional MR imaging sequences. SWI exploits the magnetic ...
Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) Dosimetry
... 10. Visualization of the 2D dose distribution for each new CBCT scan protocol: (a) head, (b) pelvis, (c) pelvis spotlight, and (d) low-dose thorax scans............. 47-48 11. HU linearity test for the new CBCT protocols. Legends are as follows. CBSDH: standard dose head, CBLDH: low dose head, CBHQH ...
... 10. Visualization of the 2D dose distribution for each new CBCT scan protocol: (a) head, (b) pelvis, (c) pelvis spotlight, and (d) low-dose thorax scans............. 47-48 11. HU linearity test for the new CBCT protocols. Legends are as follows. CBSDH: standard dose head, CBLDH: low dose head, CBHQH ...
portal dosimetry in radiotherapy
... 1.2 EXTERNAL MEGAVOLT PHOTON BEAM TREATMENT Worldwide, the most frequently applied radiotherapy technique is an external MV photon beam treatment with linear accelerators (LINACs)4‐6. With these devices, electrons are generated and accelerated to high energies of 4‐25 MeV. Th ...
... 1.2 EXTERNAL MEGAVOLT PHOTON BEAM TREATMENT Worldwide, the most frequently applied radiotherapy technique is an external MV photon beam treatment with linear accelerators (LINACs)4‐6. With these devices, electrons are generated and accelerated to high energies of 4‐25 MeV. Th ...
Biologically conformal radiation therapy and Monte
... biology distribution within each target volume and aims at achieving geometrically conformal dose distributions. By using the spatially heterogeneous biology distribution provided by one or several biological imaging modalities to guide the IMRT dose prescription, biologically conformal radiation th ...
... biology distribution within each target volume and aims at achieving geometrically conformal dose distributions. By using the spatially heterogeneous biology distribution provided by one or several biological imaging modalities to guide the IMRT dose prescription, biologically conformal radiation th ...
Effect of Voxel Size on Detection of External Root Resorption
... Background: Selecting a voxel size that yields minimal radiation dose with no significant compromise of the diagnostic accuracy of cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) is particularly important. Objectives: This study aimed to assess the effect of voxel size on detection accuracy of simulated extern ...
... Background: Selecting a voxel size that yields minimal radiation dose with no significant compromise of the diagnostic accuracy of cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) is particularly important. Objectives: This study aimed to assess the effect of voxel size on detection accuracy of simulated extern ...
Safety Code 35: Radiation Protection in Radiology
... X-ray exposures remain unchanged. X-rays have the potential for damaging healthy cells and tissues, and therefore all medical procedures employing X-ray equipment must be carefully managed. In all facilities and for all equipment types, procedures must be in place in order to ensure that exposures t ...
... X-ray exposures remain unchanged. X-rays have the potential for damaging healthy cells and tissues, and therefore all medical procedures employing X-ray equipment must be carefully managed. In all facilities and for all equipment types, procedures must be in place in order to ensure that exposures t ...
Safety Code 35: Radiation Protection in Radiology
... X-ray exposures remain unchanged. X-rays have the potential for damaging healthy cells and tissues, and therefore all medical procedures employing X-ray equipment must be carefully managed. In all facilities and for all equipment types, procedures must be in place in order to ensure that exposures t ...
... X-ray exposures remain unchanged. X-rays have the potential for damaging healthy cells and tissues, and therefore all medical procedures employing X-ray equipment must be carefully managed. In all facilities and for all equipment types, procedures must be in place in order to ensure that exposures t ...
Delivery accuracy of image guided radiation therapy using Elekta
... 1999). The areas in red (GTV) and orange (CTV) represent the cancerous volume that requires treatment. To treat 100% of these areas, one creates internal margins (dark grey) and setup margins (blue) in the healthy adjacent tissue. Setting internal and setup margins consequently requires irradiating ...
... 1999). The areas in red (GTV) and orange (CTV) represent the cancerous volume that requires treatment. To treat 100% of these areas, one creates internal margins (dark grey) and setup margins (blue) in the healthy adjacent tissue. Setting internal and setup margins consequently requires irradiating ...
PET/MR — a rapidly growing technique of imaging in oncology and
... tomography (PET) plays a key role in oncological diagnostics (staging before treatment, evaluation of treatment response, detection of recurrence etc.), as well as other areas, e.g. cardiology, neurology, psychiatry and others. Despite the large role these scans fulfil in imaging diagnostics of vari ...
... tomography (PET) plays a key role in oncological diagnostics (staging before treatment, evaluation of treatment response, detection of recurrence etc.), as well as other areas, e.g. cardiology, neurology, psychiatry and others. Despite the large role these scans fulfil in imaging diagnostics of vari ...
MotionFree - GE Healthcare
... Gated PET acquisition was the first step toward motion-free PET imaging. The most important application of Gated PET imaging is in radiation treatment planning. It allows users to see where the tumor was at a given time and how it moves during patient respiration. The ability to see the tumor in its ...
... Gated PET acquisition was the first step toward motion-free PET imaging. The most important application of Gated PET imaging is in radiation treatment planning. It allows users to see where the tumor was at a given time and how it moves during patient respiration. The ability to see the tumor in its ...
RADIATION PROTECTION IN DIAGNOSTIC RADIOLOGY
... The Standard Deviation of CT numbers in the central 500 mm2 ROI for a water or tissue equivalent phantom should not deviate more than 20% from the baseline. • CT number values The deviation in the CT number values for water or tissue equivalent material and materials of different densities should <± ...
... The Standard Deviation of CT numbers in the central 500 mm2 ROI for a water or tissue equivalent phantom should not deviate more than 20% from the baseline. • CT number values The deviation in the CT number values for water or tissue equivalent material and materials of different densities should <± ...
Development and testing of extra-cranial tumour tracking
... respiratory signal is extracted from the external surface displacement and modelled to derive the instantaneous values of amplitude and phase variables. To take into account possible inter-fraction anatomical variations that may occur between planning and treatment time, the tumour baseline in the ...
... respiratory signal is extracted from the external surface displacement and modelled to derive the instantaneous values of amplitude and phase variables. To take into account possible inter-fraction anatomical variations that may occur between planning and treatment time, the tumour baseline in the ...
UNIT 5 biomedical
... In spiral CT, the X-ray beam is emitted on a continuous basis and rotates around the subject, as the subject is moved through. Micro Computed Tomography: In micro CT, the pixel size of the images is in micrometer. It is used in cases involving small animals, biomedical samples and other studies ...
... In spiral CT, the X-ray beam is emitted on a continuous basis and rotates around the subject, as the subject is moved through. Micro Computed Tomography: In micro CT, the pixel size of the images is in micrometer. It is used in cases involving small animals, biomedical samples and other studies ...
Thermal Ablation of Osteoid Osteoma: Overview and Step
... defect that may be vulnerable to fracture and, in some cases, may necessitate internal fixation and bone grafting. To minimize the amount of excised bone, precise intraoperative localization of the lesion is important. Yet localization is difficult in some cases, even with the use of various special ...
... defect that may be vulnerable to fracture and, in some cases, may necessitate internal fixation and bone grafting. To minimize the amount of excised bone, precise intraoperative localization of the lesion is important. Yet localization is difficult in some cases, even with the use of various special ...
Imaging the posterior mediastinum: a multimodality approach
... on both T1- and T2-weighted MRI. Inactive lesions have low or high attenuation values on CT, depending on the presence of fat or the iron content of the masses (Fig. 4). For the same reason, inactive lesions have high-signal intensity on both T1- and T2-weighted images if there is fatty replacement ...
... on both T1- and T2-weighted MRI. Inactive lesions have low or high attenuation values on CT, depending on the presence of fat or the iron content of the masses (Fig. 4). For the same reason, inactive lesions have high-signal intensity on both T1- and T2-weighted images if there is fatty replacement ...