sensitivity of tryptophan, tyrosine and phenylalanine
... 1946). For some experiments MV was supplemented as follows: adenine (ade), 30 mg/liter; Lhistidine (his), 20 mg/liter; L-lysine (lys), 40 mg/liter; L-phenylalanine (phe),50 mg/liter; L-threonine (thr), 150 mg/liter; L-tryptophan (trp), 30 mg/liter; or L-tyrosine (tyr) 20 mg/liter. MB (minimal + biot ...
... 1946). For some experiments MV was supplemented as follows: adenine (ade), 30 mg/liter; Lhistidine (his), 20 mg/liter; L-lysine (lys), 40 mg/liter; L-phenylalanine (phe),50 mg/liter; L-threonine (thr), 150 mg/liter; L-tryptophan (trp), 30 mg/liter; or L-tyrosine (tyr) 20 mg/liter. MB (minimal + biot ...
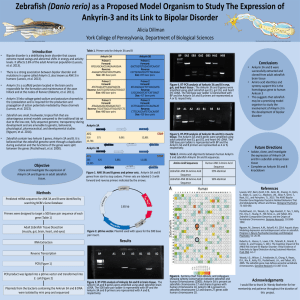
Figure 1 - York College of Pennsylvania
... extreme mood swings and abnormal shifts in energy and activity levels. It affects 2.6% of the adult American population (Luessis, et al. 2013). There is a strong association between bipolar disorder and mutations in a gene called Ankyrin 3, also known as ANK 3 in humans (Luessis, et al. 2013). ...
... extreme mood swings and abnormal shifts in energy and activity levels. It affects 2.6% of the adult American population (Luessis, et al. 2013). There is a strong association between bipolar disorder and mutations in a gene called Ankyrin 3, also known as ANK 3 in humans (Luessis, et al. 2013). ...
Iron mediated methylthiolation of tRNA as a regulator of operon
... mutants we found that there was indeed greater expression of the trp operon during iron restricted growth. This increase was attributable solely to the tRNA alteration induced by iron restriction. ...
... mutants we found that there was indeed greater expression of the trp operon during iron restricted growth. This increase was attributable solely to the tRNA alteration induced by iron restriction. ...
Cfe Higher Biology Metabolism and Survival
... The membrane has proteins dispersed and embedded in the phospholipid bilayer that vary in both structure and function. The variety of functions carried out by membrane proteins are described below. • Channel (pore) proteins - these proteins allow specific molecules and ions to pass through the membr ...
... The membrane has proteins dispersed and embedded in the phospholipid bilayer that vary in both structure and function. The variety of functions carried out by membrane proteins are described below. • Channel (pore) proteins - these proteins allow specific molecules and ions to pass through the membr ...
Genomic Insights into Methanotrophy: The Complete Genome Sequence of Methylococcus capsulatus (Bath)
... 3.3-Mb genome highly specialized for a methanotrophic lifestyle, including redundant pathways predicted to be involved in methanotrophy and duplicated genes for essential enzymes such as the methane monooxygenases. We used phylogenomic analysis, gene order information, and comparative analysis with ...
... 3.3-Mb genome highly specialized for a methanotrophic lifestyle, including redundant pathways predicted to be involved in methanotrophy and duplicated genes for essential enzymes such as the methane monooxygenases. We used phylogenomic analysis, gene order information, and comparative analysis with ...
Unit 2 - eduBuzz.org
... Metabolism is the term used to describe the enormous number of integrated and complex biochemical reactions that occur in an organism. These reactions are ordered into pathways and controlled at each stage by an enzyme. By means of these metabolic pathways, the cell is able to transform energy, degr ...
... Metabolism is the term used to describe the enormous number of integrated and complex biochemical reactions that occur in an organism. These reactions are ordered into pathways and controlled at each stage by an enzyme. By means of these metabolic pathways, the cell is able to transform energy, degr ...
Fyzikální a analytická chemie - Institute of Medical Biochemistry and
... for expressing quantity values of catalytic activity of enzymes and other catalysts Catalytic transformation of 1 Mol of substrate in 1 Second. 1 International unit (abbreviation 1 IU) [mol.s-1]; IU=16,67 nkat 60 IU=1 µkat Amount of enzyme activity which catalyzes transformation of 1 mol of substrat ...
... for expressing quantity values of catalytic activity of enzymes and other catalysts Catalytic transformation of 1 Mol of substrate in 1 Second. 1 International unit (abbreviation 1 IU) [mol.s-1]; IU=16,67 nkat 60 IU=1 µkat Amount of enzyme activity which catalyzes transformation of 1 mol of substrat ...
Distribution and phylogenies of enzymes of the Embden
... has gained wide acceptance, although it has detractors. However, even a putative RNA-based “organism” could have arisen only from a prebiotic chemical environment conducive to its existence (Poole et al. 1999). Although these theories and their associated predictions have done much to provide explan ...
... has gained wide acceptance, although it has detractors. However, even a putative RNA-based “organism” could have arisen only from a prebiotic chemical environment conducive to its existence (Poole et al. 1999). Although these theories and their associated predictions have done much to provide explan ...
Changes in cardiac metabolism: a critical step from stable angina to
... off two carbon acetyl-CoA units, generating NADH and ...
... off two carbon acetyl-CoA units, generating NADH and ...
Glucose Metabolism
... A. Glucose in the bloodstream comes from the digestion and/or from glycogen stored in the liver and muscle. B. When glucose in the bloodstream enters the cytosol (internal fluid) of our cells, it is immediately converted to glucose – 6 – phosphate. 1. This is an exergonic process and not reversible. ...
... A. Glucose in the bloodstream comes from the digestion and/or from glycogen stored in the liver and muscle. B. When glucose in the bloodstream enters the cytosol (internal fluid) of our cells, it is immediately converted to glucose – 6 – phosphate. 1. This is an exergonic process and not reversible. ...
Eds., M. Kawaguchi, K. Misaki, H. Sato, T. Yokokawa, T.... and S. Tanabe, pp. 35–40.
... in the liver. However, it has been suggested that taurine is also synthesized in the brain (Pasantes-Morales et al., 1980) and the testis (Yang et al., 2010). Furthermore, recent studies have shown that both CDO and CSD are expressed in the mammary gland (Ueki and Stipanuk, 2007) and that CSD mRNAs ...
... in the liver. However, it has been suggested that taurine is also synthesized in the brain (Pasantes-Morales et al., 1980) and the testis (Yang et al., 2010). Furthermore, recent studies have shown that both CDO and CSD are expressed in the mammary gland (Ueki and Stipanuk, 2007) and that CSD mRNAs ...
exam2_2011_key
... Entropy: The pre-ordered residues in the active site of the enzyme reduces the entropy loss that would otherwise occur to organize these groups around the substrate. In other words, the requirement to organize these groups in the uncatalyzed reaction raises the energy of the transition state (+ 6 pt ...
... Entropy: The pre-ordered residues in the active site of the enzyme reduces the entropy loss that would otherwise occur to organize these groups around the substrate. In other words, the requirement to organize these groups in the uncatalyzed reaction raises the energy of the transition state (+ 6 pt ...
... Entropy: The pre-ordered residues in the active site of the enzyme reduces the entropy loss that would otherwise occur to organize these groups around the substrate. In other words, the requirement to organize these groups in the uncatalyzed reaction raises the energy of the transition state (+ 6 pt ...
Best Plant Protein
... Dietary protein is consumed from myriad food sources, and each contains a unique non-protein content that can have different health related effects aside from their respective contributions on muscle protein synthesis (MPS). 1,2,3 Little argument remains about whole animal, non-milk proteins (so-cal ...
... Dietary protein is consumed from myriad food sources, and each contains a unique non-protein content that can have different health related effects aside from their respective contributions on muscle protein synthesis (MPS). 1,2,3 Little argument remains about whole animal, non-milk proteins (so-cal ...
(lip) that - Repositories
... phenotypes of these mutants were determined in order to define functions for the disrupted genes. The chromosomal location of each mutation was determined by either cotransduction with adjacent genetic markers or by conjugation in order to establish whether or not the genes encoding lipoic acid bio ...
... phenotypes of these mutants were determined in order to define functions for the disrupted genes. The chromosomal location of each mutation was determined by either cotransduction with adjacent genetic markers or by conjugation in order to establish whether or not the genes encoding lipoic acid bio ...
David Rittenberg - National Academy of Sciences
... presents almost insuperable difficulties. If substances such as natural fatty acids, amino acids, etc., are administered to an animal, we lose track of them the moment they enter the body, since they are mixed with the same substances already present. Furthermore, if a substance A is given to an ani ...
... presents almost insuperable difficulties. If substances such as natural fatty acids, amino acids, etc., are administered to an animal, we lose track of them the moment they enter the body, since they are mixed with the same substances already present. Furthermore, if a substance A is given to an ani ...
Enzyme promiscuity: evolutionary and mechanistic aspects
... The above observation has important implications regarding our understanding of the early steps in the evolution of new protein functions [37]. There is no doubt that gene duplication is a necessary step. But the most-widely accepted model, by Ohno [38], surmises that the generation of a redundant g ...
... The above observation has important implications regarding our understanding of the early steps in the evolution of new protein functions [37]. There is no doubt that gene duplication is a necessary step. But the most-widely accepted model, by Ohno [38], surmises that the generation of a redundant g ...
Optimizing cofactor availability for the production of recombinant
... allowed higher yields of active recombinant heme protein in S. cerevisiae [11]. Thus, we cooverexpressed either of the eight involved HEM genes (Table 1) using the strong constitutive promoter PGAP [20] in a P. pastoris strain recombinantly producing the heme protein HRP. The screenings revealed tre ...
... allowed higher yields of active recombinant heme protein in S. cerevisiae [11]. Thus, we cooverexpressed either of the eight involved HEM genes (Table 1) using the strong constitutive promoter PGAP [20] in a P. pastoris strain recombinantly producing the heme protein HRP. The screenings revealed tre ...
ribosomal defects in a mutant deficient in the yajl homolog of the
... determination of acetate, lactate, ethanol, succinate and formate. These determinations were made by using the corresponding Megazyme assay kits for acetic acid, lactic acid, ethanol, acetic acid and formic acid, following instructions of the manufacturer (Megazyme International Ireland Limited). Th ...
... determination of acetate, lactate, ethanol, succinate and formate. These determinations were made by using the corresponding Megazyme assay kits for acetic acid, lactic acid, ethanol, acetic acid and formic acid, following instructions of the manufacturer (Megazyme International Ireland Limited). Th ...