Instructor`s Answer Key
... 3. Potato starch and liver glycogen are polysaccharides of glucose, a monosaccharide. The potato plant produces glucose monomers during photosynthesis reactions. Using dehydration synthesis reactions the potato polymerizes glucose monomers into its stored form as starch. When the potato is eaten and ...
... 3. Potato starch and liver glycogen are polysaccharides of glucose, a monosaccharide. The potato plant produces glucose monomers during photosynthesis reactions. Using dehydration synthesis reactions the potato polymerizes glucose monomers into its stored form as starch. When the potato is eaten and ...
Solutions to 7.014 Quiz I
... ATP is used as energy to drive cellular processes, Pyruvate accepts electrons from NADH to form lactic acid (or ethanol and CO2) thereby regenerating the NAD+ required for glycolysis to continue. ...
... ATP is used as energy to drive cellular processes, Pyruvate accepts electrons from NADH to form lactic acid (or ethanol and CO2) thereby regenerating the NAD+ required for glycolysis to continue. ...
Introduction Document
... atom and the N atom) and ψ (between the Cα atom and the other C atom) for the different amino acids would give exact structure. Very difficult problem. The three dimensional form of a protein is related to its function. A folded protein has varied nooks and bulges to bind to other molecules to build ...
... atom and the N atom) and ψ (between the Cα atom and the other C atom) for the different amino acids would give exact structure. Very difficult problem. The three dimensional form of a protein is related to its function. A folded protein has varied nooks and bulges to bind to other molecules to build ...
Information on Formula
... FS-72 also contains a rich organic protein base of amino acids & other trace minerals which are necessary for blood cell & muscle manufacturing. Creation of highly active anabolic environment with increased protein synthesis executing mental focused, strength and size immediately! ...
... FS-72 also contains a rich organic protein base of amino acids & other trace minerals which are necessary for blood cell & muscle manufacturing. Creation of highly active anabolic environment with increased protein synthesis executing mental focused, strength and size immediately! ...
Answers to Quiz 4 BIol203 Fall 2013ppt
... Are those fragments single stranded or double stranded (circle one)? 4. Is the oligonucleotide used in this process incorporated into replication reaction? __Yes__ Q3. (2pts) ...
... Are those fragments single stranded or double stranded (circle one)? 4. Is the oligonucleotide used in this process incorporated into replication reaction? __Yes__ Q3. (2pts) ...
Translation
... Translation ● Converts mRNA from transcription into protein (polypeptide) ● Codon- a sequence of 3 RNA nucleotides that code for an amino acid ○ there are 20 amino acids in our body ○ amino acid- monomer of protein ...
... Translation ● Converts mRNA from transcription into protein (polypeptide) ● Codon- a sequence of 3 RNA nucleotides that code for an amino acid ○ there are 20 amino acids in our body ○ amino acid- monomer of protein ...
Carbs Review
... storing energy because they have larger numbers of carbon-hydrogen bonds. True! We just said that lipids have few oxygens. This ...
... storing energy because they have larger numbers of carbon-hydrogen bonds. True! We just said that lipids have few oxygens. This ...
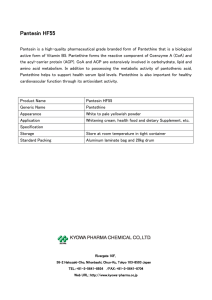
Pantesin HF55
... Pantesin is a high-quality pharmaceutical grade branded form of Pantethine that is a biological active form of Vitamin B5. Pantethine forms the reactive component of Coenzyme A (CoA) and the acyl-carrier protein (ACP). CoA and ACP are extensively involved in carbohydrate, lipid and amino acid metabo ...
... Pantesin is a high-quality pharmaceutical grade branded form of Pantethine that is a biological active form of Vitamin B5. Pantethine forms the reactive component of Coenzyme A (CoA) and the acyl-carrier protein (ACP). CoA and ACP are extensively involved in carbohydrate, lipid and amino acid metabo ...
Chapter 4 - Organic Chemistry, Biochemistry
... of atoms of a particular arrangement that gives the entire molecule certain characteristics. Functional groups are named according to the composition of the group. ...
... of atoms of a particular arrangement that gives the entire molecule certain characteristics. Functional groups are named according to the composition of the group. ...
Chapter 1
... – Glycerol portion only from fat – Fatty acids with odd # of C atoms – Glucogenic amino acids ...
... – Glycerol portion only from fat – Fatty acids with odd # of C atoms – Glucogenic amino acids ...
Amino Acids 20 – Bloodspot
... The Body’s Fundamental Building Blocks Amino acids make up proteins found in every tissue of the body. They play a major role in nearly every chemical process that affects both physical and mental ...
... The Body’s Fundamental Building Blocks Amino acids make up proteins found in every tissue of the body. They play a major role in nearly every chemical process that affects both physical and mental ...
4.2.1 Liver MS - Mrs Miller`s Blog
... long loop of Henlé or/ deep / wide, medulla ; very low water potential in medulla / AW ; A higher concentration of salts collecting duct more permeable to water ; large number of, water permeable channels / aquaporins, in collecting duct ; more sensitive to ADH / more ADH produced ; AVP ; e.g. other ...
... long loop of Henlé or/ deep / wide, medulla ; very low water potential in medulla / AW ; A higher concentration of salts collecting duct more permeable to water ; large number of, water permeable channels / aquaporins, in collecting duct ; more sensitive to ADH / more ADH produced ; AVP ; e.g. other ...
No Slide Title
... Bradford (Coomassie-blue G-250) • Amax of CB G-250 shifts from 465 t0 595 nm when bound to protein • dye reacts primarily with Arg • lesser extent with His, Lys, Tyr, Trp, Phe • sensitivity is 1-100 mg/ml depending on circumstances • single step and few interfering substances • protein concentratio ...
... Bradford (Coomassie-blue G-250) • Amax of CB G-250 shifts from 465 t0 595 nm when bound to protein • dye reacts primarily with Arg • lesser extent with His, Lys, Tyr, Trp, Phe • sensitivity is 1-100 mg/ml depending on circumstances • single step and few interfering substances • protein concentratio ...
Macromolecules
... bond between monomers and releases water in the process. This type of reaction is also referred to as dehydration synthesis. The reverse of this reaction can also occur. Addition of water to a polymer results in the hydrolysis of the molecule, which breaks the covalent bond between monomers and adds ...
... bond between monomers and releases water in the process. This type of reaction is also referred to as dehydration synthesis. The reverse of this reaction can also occur. Addition of water to a polymer results in the hydrolysis of the molecule, which breaks the covalent bond between monomers and adds ...
Use of Reduced Carbon Compounds
... Most bacteria synthesize almost all the monomers that they need for cell growth directly, whereas we are more used to thinking of animals that get many of their monomers from food. --- The simplest building blocks for biosynthesis are the one carbon, oxidized molecules such as CO2 (carbon fixation) ...
... Most bacteria synthesize almost all the monomers that they need for cell growth directly, whereas we are more used to thinking of animals that get many of their monomers from food. --- The simplest building blocks for biosynthesis are the one carbon, oxidized molecules such as CO2 (carbon fixation) ...
Amino Acids Interactions
... These are all joined to a central α-carbon atom (see following diagram) When used as the building blocks for polypeptide chains (protein) they will be linked to each other through the NH2 and COOH groups (shown later). ...
... These are all joined to a central α-carbon atom (see following diagram) When used as the building blocks for polypeptide chains (protein) they will be linked to each other through the NH2 and COOH groups (shown later). ...
GEE Science Assessment PowerPoint WITH answers
... • Thorugh, RNA, the DNA code leaves the nucleus and guides the construction of the protein in the ribosomes in cytoplasm. OR • RNA is used to pick up amino acids and bring them to where the protein is being made (that is, the ribosome). OR • RNA makes sure the building blocks of proteins (that is, a ...
... • Thorugh, RNA, the DNA code leaves the nucleus and guides the construction of the protein in the ribosomes in cytoplasm. OR • RNA is used to pick up amino acids and bring them to where the protein is being made (that is, the ribosome). OR • RNA makes sure the building blocks of proteins (that is, a ...
Gene A - Biology
... nucleotides in DNA determines the sequence of amino acids in polypeptides, and thus the structure of proteins. In a process called transcription, which takes place in the nucleus of the cell, messenger RNA (mRNA) reads and copies the DNA’s nucleotide sequences in the form of a complementary RNA mole ...
... nucleotides in DNA determines the sequence of amino acids in polypeptides, and thus the structure of proteins. In a process called transcription, which takes place in the nucleus of the cell, messenger RNA (mRNA) reads and copies the DNA’s nucleotide sequences in the form of a complementary RNA mole ...
Chapter 3 - Evangel University
... • Side-chain carbons in other amino acids designated with Greek symbols, starting at a carbon (…etc) • Amino acids can be referred to by three-letter or oneletter codes. Table 3.1 (KNOW THESE) ...
... • Side-chain carbons in other amino acids designated with Greek symbols, starting at a carbon (…etc) • Amino acids can be referred to by three-letter or oneletter codes. Table 3.1 (KNOW THESE) ...
Enzymes - WordPress.com
... 12. Lemurs’ bodies are adapted to efficiently store energy for times when food is scarce. This adaptation may help to explain how lemur ancestors survived the trip across the Mozambique Channel from mainland Africa to Madagascar. Which of the following types of molecules are primarily used for long ...
... 12. Lemurs’ bodies are adapted to efficiently store energy for times when food is scarce. This adaptation may help to explain how lemur ancestors survived the trip across the Mozambique Channel from mainland Africa to Madagascar. Which of the following types of molecules are primarily used for long ...