Chapter5 The Structure and Functionof Macromolecules Discussion
... 12. Distinguish between a protein and a polypeptide. 13. Explain how a peptide bond forms between two amino acids. 14. List and describe the four major components of an amino acid. Explain how amino acids may be grouped according to the physical and chemical properties of the R group. 15. Explain wh ...
... 12. Distinguish between a protein and a polypeptide. 13. Explain how a peptide bond forms between two amino acids. 14. List and describe the four major components of an amino acid. Explain how amino acids may be grouped according to the physical and chemical properties of the R group. 15. Explain wh ...
The Organic Macromolecules of Life
... Proteins More than one half of the dry weight of your body is made of proteins. Proteins are large, complex molecules composed of many smaller molecules called amino acids. Amino acids have an amino group on one end, an R group, and a carboxyl group on the other end. An amino group consists of one n ...
... Proteins More than one half of the dry weight of your body is made of proteins. Proteins are large, complex molecules composed of many smaller molecules called amino acids. Amino acids have an amino group on one end, an R group, and a carboxyl group on the other end. An amino group consists of one n ...
Outline05 Enzymes - Napa Valley College
... - regulation of enzyme via covalent binding of a chemical group - usually involves addition of phosphate group which activates the enzyme E (inactive enzyme) + ATP → E~P (active enzyme) + ADP - protein kinase enzymes catalyze phosphorylation of other enzymes; important in cell signaling b. allosteri ...
... - regulation of enzyme via covalent binding of a chemical group - usually involves addition of phosphate group which activates the enzyme E (inactive enzyme) + ATP → E~P (active enzyme) + ADP - protein kinase enzymes catalyze phosphorylation of other enzymes; important in cell signaling b. allosteri ...
7.016 Problem Set 1 - MIT OpenCourseWare
... 50kD. However, this enzyme in its active form has a molecular weight of 250KD. Why might the active form of Enzyme E1 be heavier than the product encoded by its corresponding gene? ...
... 50kD. However, this enzyme in its active form has a molecular weight of 250KD. Why might the active form of Enzyme E1 be heavier than the product encoded by its corresponding gene? ...
Macs Notes
... All of the examples listed above are polymers of glucose! So if they are all made of only glucose how are they different? They differ in the way the glucose molecules are attached. Cellulose and chitin are STRUCTURAL polymers made with one type of glucose. Glycogen and starch are ENERGY polymers ...
... All of the examples listed above are polymers of glucose! So if they are all made of only glucose how are they different? They differ in the way the glucose molecules are attached. Cellulose and chitin are STRUCTURAL polymers made with one type of glucose. Glycogen and starch are ENERGY polymers ...
Biochemistry - english for biology
... concerned with local morphology. Some combinations of amino acids will tend to curl up in a coil called an α-helix or into a sheet called a β-sheet; some α-helixes can be seen in the hemoglobin schematic above. Tertiary structure is the entire three-dimensional shape of the protein. This shape is de ...
... concerned with local morphology. Some combinations of amino acids will tend to curl up in a coil called an α-helix or into a sheet called a β-sheet; some α-helixes can be seen in the hemoglobin schematic above. Tertiary structure is the entire three-dimensional shape of the protein. This shape is de ...
Lecture 15a
... CTP is the product of this pathway and it is also a precursor for the synthesis of DNA and RNA (nucleic acids). The rapid synthesis of DNA and/or RNA depletes the CTP pool in the cell, causing CTP to be released from ATCase and increasing its activity. When the activity of ATCase is greater than th ...
... CTP is the product of this pathway and it is also a precursor for the synthesis of DNA and RNA (nucleic acids). The rapid synthesis of DNA and/or RNA depletes the CTP pool in the cell, causing CTP to be released from ATCase and increasing its activity. When the activity of ATCase is greater than th ...
MOLECULES of LIFE Matter is anything that has mass and takes up
... Monosaccharides are single sugar units. They are the building blocks of carbohydrates. Each monosaccharide is made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen with a formula of C6H12O6 or C5H12O5. There are different kinds of monosaccharide molecules. They are different because their atoms are arranged differe ...
... Monosaccharides are single sugar units. They are the building blocks of carbohydrates. Each monosaccharide is made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen with a formula of C6H12O6 or C5H12O5. There are different kinds of monosaccharide molecules. They are different because their atoms are arranged differe ...
Basic organic chemistry of important macromolecules (Lecture 11-12)
... 6. Proteins Proteins are very important in biological systems as: structural support, storage, transport of other substances, signaling, movement and defense against foreign susbstances. The building block of any protein is the amino acid, which has an amino end (NH2) and a carboxyl end (COOH) and R ...
... 6. Proteins Proteins are very important in biological systems as: structural support, storage, transport of other substances, signaling, movement and defense against foreign susbstances. The building block of any protein is the amino acid, which has an amino end (NH2) and a carboxyl end (COOH) and R ...
Carbon-Based Molecules
... point on the hexagon represents a glucose are both sugars that have six carbon atoms. The carbon, except the point that has sugar that you might use in the kitchen is made of two sugar an O, for oxygen. molecules bonded together. Many glucose molecules bonded together form polymers such as starch an ...
... point on the hexagon represents a glucose are both sugars that have six carbon atoms. The carbon, except the point that has sugar that you might use in the kitchen is made of two sugar an O, for oxygen. molecules bonded together. Many glucose molecules bonded together form polymers such as starch an ...
Amino acid substitution and protein structure
... A viable mutation that changes a protein so that the amino acid that was at some location becomes another amino acid ...
... A viable mutation that changes a protein so that the amino acid that was at some location becomes another amino acid ...
GO C1 Common Substances Essential To Living Things
... vegetable oils, nut oils, some dairy products ...
... vegetable oils, nut oils, some dairy products ...
Peptide bond Polypeptide
... variable group R is another H atom. But there are 20 different amino acids which are naturally-occurring, and they all have different structures around the R group. There are other amino acids (in fact, thousands more) but these have all been manufactured artificially, and only those 20 occur natura ...
... variable group R is another H atom. But there are 20 different amino acids which are naturally-occurring, and they all have different structures around the R group. There are other amino acids (in fact, thousands more) but these have all been manufactured artificially, and only those 20 occur natura ...
Unit 05 - Lessons 1-4
... C. Hydrogen bonds are responsible for three important properties of water. 1. high specific heat – water absorbs large amounts of energy without raising its temperature very much 2. cohesion – molecules stick to themselves Ex) water rising above the level of a glass without spilling 3. adhesion – mo ...
... C. Hydrogen bonds are responsible for three important properties of water. 1. high specific heat – water absorbs large amounts of energy without raising its temperature very much 2. cohesion – molecules stick to themselves Ex) water rising above the level of a glass without spilling 3. adhesion – mo ...
Chapter 02 The Molecules of Life
... tails; thereby, introducing a number of double bonds between the carbon atoms. 2. The double bonds would physically put a kink in the long chain of carbons. This kink would not allow the molecules to associate in a manner necessary to produce a solid. In essence, the molecules would not pack togethe ...
... tails; thereby, introducing a number of double bonds between the carbon atoms. 2. The double bonds would physically put a kink in the long chain of carbons. This kink would not allow the molecules to associate in a manner necessary to produce a solid. In essence, the molecules would not pack togethe ...
File
... 22. Why is the shape of a protein important? _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 23. What are the 7 functions of proteins? 1. ________________ 2. _______________ 3. __________ 4. ...
... 22. Why is the shape of a protein important? _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ 23. What are the 7 functions of proteins? 1. ________________ 2. _______________ 3. __________ 4. ...
Lecture Notes
... • Three-dimensional arrangement of amino acids with the polypeptide chain in a corkscrew shape • Held by __________ between the H of –N-H group and the –O of C=O of the fourth amino acid along the chain ...
... • Three-dimensional arrangement of amino acids with the polypeptide chain in a corkscrew shape • Held by __________ between the H of –N-H group and the –O of C=O of the fourth amino acid along the chain ...
Name:______________________________
... [HA]=[AT]/(1+R) [A-]=[AT]R/(1+R) R=[A-]/[HA] Beer’s law: A=ε[X]l Amino Acid Names: Alanine: Ala Arginine: Arg Asparagine: Asn Aspartic Acid: Asp Cystine: Cys Glycine: Gly Histindine: His Glutamine: Gln Glutamic Acid: Glu ...
... [HA]=[AT]/(1+R) [A-]=[AT]R/(1+R) R=[A-]/[HA] Beer’s law: A=ε[X]l Amino Acid Names: Alanine: Ala Arginine: Arg Asparagine: Asn Aspartic Acid: Asp Cystine: Cys Glycine: Gly Histindine: His Glutamine: Gln Glutamic Acid: Glu ...
Basic amino acid in the pathogenesis of caries
... Arginine and histidine are conditionally conside red essential amino acids in childhood, because of increaed requirements or diminished synthesis needed for nitrogen balance maintenance. The refore, their intake in nutrition is very important (10). Later in life, histidine also plays an impor tan ...
... Arginine and histidine are conditionally conside red essential amino acids in childhood, because of increaed requirements or diminished synthesis needed for nitrogen balance maintenance. The refore, their intake in nutrition is very important (10). Later in life, histidine also plays an impor tan ...
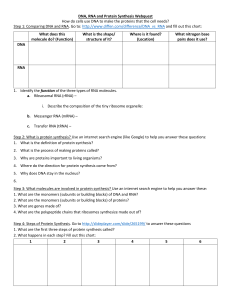
DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis Webquest
... i. Describe the composition of the tiny ribosome organelle: b. Messenger RNA (mRNA) – c. Transfer RNA (tRNA) – Step 2: What is protein synthesis? Use an internet search engine (like Google) to help you answer these questions: 1. What is the definition of protein synthesis? 2. What is the process of ...
... i. Describe the composition of the tiny ribosome organelle: b. Messenger RNA (mRNA) – c. Transfer RNA (tRNA) – Step 2: What is protein synthesis? Use an internet search engine (like Google) to help you answer these questions: 1. What is the definition of protein synthesis? 2. What is the process of ...
Investigation of the enzymatic processes depending on the ty
... Some metabolic processes are regulated by enzymes that exist in different molecular forms - isoenzymes Isoenzymes - multiple forms of an enzyme which differ in amino acid sequence but catalyze the same reaction Isoenzymes can differ in: kinetics, regulatory properties, the form of coenzyme the ...
... Some metabolic processes are regulated by enzymes that exist in different molecular forms - isoenzymes Isoenzymes - multiple forms of an enzyme which differ in amino acid sequence but catalyze the same reaction Isoenzymes can differ in: kinetics, regulatory properties, the form of coenzyme the ...