No Slide Title
... Protein folding is a “grand challenge” problem in biology the deciphering of the second half of the genetic code, of pressing practical significance Problem 1: given a protein’s amino acid sequence, predict its 3D structure, which is related to its function Problem 2: “… use the protein’s known 3D s ...
... Protein folding is a “grand challenge” problem in biology the deciphering of the second half of the genetic code, of pressing practical significance Problem 1: given a protein’s amino acid sequence, predict its 3D structure, which is related to its function Problem 2: “… use the protein’s known 3D s ...
De Novo Design of an Enzyme
... (RBP) into an enzyme that is enediol intermediate. Ribbon diagrams are shown with α helices in red above background. The most active RBP variant highly active as a triose phos- and β strands in yellow. The catalytically essential residues glutamate (E), phate isomerase (TIM). histidine (H), and lysi ...
... (RBP) into an enzyme that is enediol intermediate. Ribbon diagrams are shown with α helices in red above background. The most active RBP variant highly active as a triose phos- and β strands in yellow. The catalytically essential residues glutamate (E), phate isomerase (TIM). histidine (H), and lysi ...
Lecture 33
... protein synthesis is tightly regulated by environmental stimuli as well as intrinsic processes (e.g., hormonal, developmental). ...
... protein synthesis is tightly regulated by environmental stimuli as well as intrinsic processes (e.g., hormonal, developmental). ...
File
... Translation requires two other types of RNA: rRNA (Ribosomal RNA) -- joins with ribosomal proteins (from nucleolus) to form ribosomes. -- produced in the nucleolus. -- one ribosome has two subunits: a. Large subunit (3 rRNAs and proteins) b. Small subunit (1 rRNA and proteins) -- the two subunits re ...
... Translation requires two other types of RNA: rRNA (Ribosomal RNA) -- joins with ribosomal proteins (from nucleolus) to form ribosomes. -- produced in the nucleolus. -- one ribosome has two subunits: a. Large subunit (3 rRNAs and proteins) b. Small subunit (1 rRNA and proteins) -- the two subunits re ...
12010_2017_2424_MOESM1_ESM
... R192K mutation is the next important and common mutation found in all the mutant enzymes under consideration. Amino acid at position 192 is present at the entrance of the active site of enzyme through which the substrate molecules enter into the active site cavity of the enzyme. Supplementary Fig 4 ...
... R192K mutation is the next important and common mutation found in all the mutant enzymes under consideration. Amino acid at position 192 is present at the entrance of the active site of enzyme through which the substrate molecules enter into the active site cavity of the enzyme. Supplementary Fig 4 ...
Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis experiment pathway(II)
... iron-containing protein ferritin(铁蛋白). • Because of the iron atoms, ferritin molecules are able to scatter a beam of electrons and thus can be visualized in electron microscope. • A temperature of 4℃ Ligands(配体) can bind to the cell surface but cannot be internalized(内化), LDLferritin particles were ...
... iron-containing protein ferritin(铁蛋白). • Because of the iron atoms, ferritin molecules are able to scatter a beam of electrons and thus can be visualized in electron microscope. • A temperature of 4℃ Ligands(配体) can bind to the cell surface but cannot be internalized(内化), LDLferritin particles were ...
Biology 2107/03
... the reaction stopped. However, when I added more substrate, the reaction started back again. What type of substance is substance “XYZ”? ...
... the reaction stopped. However, when I added more substrate, the reaction started back again. What type of substance is substance “XYZ”? ...
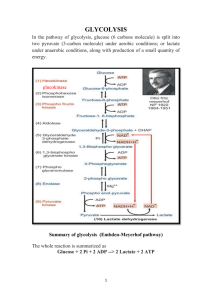
Summary of glycolysis (Embden
... chain reactions). When energy is trapped by oxidation of reducing equivalents such as NADH, it is called oxidative phosphorylation. In the 5th step, for each molecule of glucose entering in the pathway, two molecules of NAD+ are reduced to NADH. The availability of co-enzymes inside a cell is lim ...
... chain reactions). When energy is trapped by oxidation of reducing equivalents such as NADH, it is called oxidative phosphorylation. In the 5th step, for each molecule of glucose entering in the pathway, two molecules of NAD+ are reduced to NADH. The availability of co-enzymes inside a cell is lim ...
cytology_chemicals
... polypeptide chains form one macromolecule Collagen is a fibrous protein consisting of three polypeptides coiled like a rope Hemoglobin is a globular protein consisting of four polypeptides: two alpha and two beta chains ...
... polypeptide chains form one macromolecule Collagen is a fibrous protein consisting of three polypeptides coiled like a rope Hemoglobin is a globular protein consisting of four polypeptides: two alpha and two beta chains ...
13 respiration overview 9 30 05
... (a) A closed hydroelectric system. Water flowing downhill turns a turbine that drives a generator providing electricity to a light bulb, but only until ...
... (a) A closed hydroelectric system. Water flowing downhill turns a turbine that drives a generator providing electricity to a light bulb, but only until ...
Bio-chemistry(Enzymes)
... Co-enzyme: The non-protein, organic, Iow molecular weight and dialysable substance associated with enzyme function is known as coenzyme. Ribozymes are a group of ribonucleic acids that function as biological catalysts and they are regarded as non-protein enzymes Isozymes: The multiple forms of an en ...
... Co-enzyme: The non-protein, organic, Iow molecular weight and dialysable substance associated with enzyme function is known as coenzyme. Ribozymes are a group of ribonucleic acids that function as biological catalysts and they are regarded as non-protein enzymes Isozymes: The multiple forms of an en ...
HMH 2.3 notes
... Carbon atoms have unique bonding properties. • Carbon forms covalent bonds with up to four other atoms, including other carbon atoms. ...
... Carbon atoms have unique bonding properties. • Carbon forms covalent bonds with up to four other atoms, including other carbon atoms. ...
lecture4-BW
... small changes within different kinds of plants and animals through evolution. E. God created everything from nothing in 7 days (counting a day of rest) about 10,000 years ago. 6- None of the above describes my view of life’s origin. T/F 7- I think that genetically modified organisms are: A. Good bec ...
... small changes within different kinds of plants and animals through evolution. E. God created everything from nothing in 7 days (counting a day of rest) about 10,000 years ago. 6- None of the above describes my view of life’s origin. T/F 7- I think that genetically modified organisms are: A. Good bec ...
Amino acid transport systems of lysosomes
... organelles, including for example the hepatic mitochondrion and epithelial brush borders, have shown apparently different sets of such systems. We proceeded to characterize a system by which basic amino acids can be exchanged, one molecule for another, possibly a different but analogous one, across ...
... organelles, including for example the hepatic mitochondrion and epithelial brush borders, have shown apparently different sets of such systems. We proceeded to characterize a system by which basic amino acids can be exchanged, one molecule for another, possibly a different but analogous one, across ...
Department of Chemistry and Clinical Biochemistry
... - molecular weight, - spatial structure: homo- and copolymers, cross-linking. 2. Polymerization reactions: - addition polymerization (chain-reaction polymerization), - condensation (step-reaction polymerization). 3. Polymers as biomaterials: - polymer composites, - polymers used as biomaterials, - a ...
... - molecular weight, - spatial structure: homo- and copolymers, cross-linking. 2. Polymerization reactions: - addition polymerization (chain-reaction polymerization), - condensation (step-reaction polymerization). 3. Polymers as biomaterials: - polymer composites, - polymers used as biomaterials, - a ...
(CH14) Translation (Slides)
... novel archael aminoacyltRNA synthetase, PylS are required for incorporation of pyrrolysine. ...
... novel archael aminoacyltRNA synthetase, PylS are required for incorporation of pyrrolysine. ...
Department of Chemistry and Clinical Biochemistry
... - molecular weight, - spatial structure: homo- and copolymers, cross-linking. 2. Polymerization reactions: - addition polymerization (chain-reaction polymerization), - condensation (step-reaction polymerization). 3. Polymers as biomaterials: - polymer composites, - polymers used as biomaterials, - a ...
... - molecular weight, - spatial structure: homo- and copolymers, cross-linking. 2. Polymerization reactions: - addition polymerization (chain-reaction polymerization), - condensation (step-reaction polymerization). 3. Polymers as biomaterials: - polymer composites, - polymers used as biomaterials, - a ...
Laura/Lauren
... Zhang, Webb Miller, and David J. Lipman (1997), "Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs", Nucleic Acids Res. 25:33893402. • Kanehisa, M. and Goto, S.; KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. ...
... Zhang, Webb Miller, and David J. Lipman (1997), "Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs", Nucleic Acids Res. 25:33893402. • Kanehisa, M. and Goto, S.; KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. ...
Document
... Polar compounds composed of alcohol attached by a مربوط بـ رابطهphosphodiester bridge to either diacylglycerol or sphingosine. ...
... Polar compounds composed of alcohol attached by a مربوط بـ رابطهphosphodiester bridge to either diacylglycerol or sphingosine. ...
Tracing Protein Backbones in Electron Density Maps using a
... 3D density function ρ(x,y,z) provided over unit cell Unit cell may contain multiple copies of the protein ...
... 3D density function ρ(x,y,z) provided over unit cell Unit cell may contain multiple copies of the protein ...
Exam #2 BMB 514 – Medical Biochemistry 10/10/11
... 6) One of the main reasons tumors become more dependent upon glycolysis is because they are hypoxic in nature. This means they have a deficiency of oxygen. In fact, central portions of the tumor are almost anoxic, completely lacking oxygen. Anoxia is capable of impacting the electron transport chai ...
... 6) One of the main reasons tumors become more dependent upon glycolysis is because they are hypoxic in nature. This means they have a deficiency of oxygen. In fact, central portions of the tumor are almost anoxic, completely lacking oxygen. Anoxia is capable of impacting the electron transport chai ...
Slide 1
... a) Saturated fat- a fat in which all 3 fatty acid chains contain the maximum possible number of hydrogen atoms 1) Diets rich in this type of fat are said to be unhealthy because they promote the buildup of lipid-containing deposits called plaques, within the walls of blood vessels. 2) They are sol ...
... a) Saturated fat- a fat in which all 3 fatty acid chains contain the maximum possible number of hydrogen atoms 1) Diets rich in this type of fat are said to be unhealthy because they promote the buildup of lipid-containing deposits called plaques, within the walls of blood vessels. 2) They are sol ...
The Central Dogma of Genetics
... • RNAs can have complex 3D structures • They can store genetic information • Some RNAs known as ribozymes can catalyze reactions • Thus it has been hypothesized that life may have arisen first through ...
... • RNAs can have complex 3D structures • They can store genetic information • Some RNAs known as ribozymes can catalyze reactions • Thus it has been hypothesized that life may have arisen first through ...