1. Name of a subject Chemistry (1st year, Faculty of Medicine
... week time. 2. A way of evaluation seminars – not applied 3. A way and a form of final evaluation the whole course at the unit: to get credit of the whole course students have to pass all labs and mid term tests. Students are allowed to pass failures (in the second term) – not more than 4 (one Mid te ...
... week time. 2. A way of evaluation seminars – not applied 3. A way and a form of final evaluation the whole course at the unit: to get credit of the whole course students have to pass all labs and mid term tests. Students are allowed to pass failures (in the second term) – not more than 4 (one Mid te ...
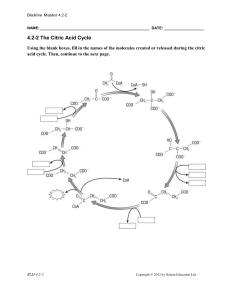
Blackline Master 4.2-2 NAME: DATE: 4.2
... Complete the summaries below by filling in the blanks. 1. Pyruvate oxidation ________________ enters the mitochondrion from the cytoplasm. One ________________ atom is removed via ___________________, and ________________ is removed using ________. ________________ becomes attached to the remaining ...
... Complete the summaries below by filling in the blanks. 1. Pyruvate oxidation ________________ enters the mitochondrion from the cytoplasm. One ________________ atom is removed via ___________________, and ________________ is removed using ________. ________________ becomes attached to the remaining ...
Protein Synthesis - VCC Library
... amino acid, Pro, to be used. Note: There are no tRNAs for stop codons. Practice: Given the above strand of mRNA, determine the anticodon of the tRNAs that would complement them. Solution: UCA – GAU – CGC – AAG – UCA – GGC Note: Because tRNA uses RNA nucleotides, no thymine is present. © 2013 Vancouv ...
... amino acid, Pro, to be used. Note: There are no tRNAs for stop codons. Practice: Given the above strand of mRNA, determine the anticodon of the tRNAs that would complement them. Solution: UCA – GAU – CGC – AAG – UCA – GGC Note: Because tRNA uses RNA nucleotides, no thymine is present. © 2013 Vancouv ...
No Slide Title
... + CH3CH + H+ 3. Enantiomer of ethanol - none of deuterium is transferred from this isomer of ethanol to NAD+ in the reverse reaction ...
... + CH3CH + H+ 3. Enantiomer of ethanol - none of deuterium is transferred from this isomer of ethanol to NAD+ in the reverse reaction ...
BIOMOLECULES : CARBOHYDRATES - IDC
... Carbohydrates (CHOs) are among the most complex of biological molecules. If you have ever "counted" your carbs, you know that one biological function of CHOs is to store and, on oxidation, provide energy to the body for required functions. Instead of concentrating on how CHOs are used for energy pro ...
... Carbohydrates (CHOs) are among the most complex of biological molecules. If you have ever "counted" your carbs, you know that one biological function of CHOs is to store and, on oxidation, provide energy to the body for required functions. Instead of concentrating on how CHOs are used for energy pro ...
Document
... a polypeptide chain. • The number peptides possible from the 20 protein-derived amino acids is enormous. • there are 20 x 20 = 400 dipeptides possible. • there are 20 x 20 x 20 = 8000 tripeptides possible. • the number of peptides possible for a chain of n amino acids is 20n. • for a small protein o ...
... a polypeptide chain. • The number peptides possible from the 20 protein-derived amino acids is enormous. • there are 20 x 20 = 400 dipeptides possible. • there are 20 x 20 x 20 = 8000 tripeptides possible. • the number of peptides possible for a chain of n amino acids is 20n. • for a small protein o ...
Development of Amino Acid as Parenteral Nutrition P N
... The dietary components of a standard PN regimen are the macronutrients (protein or amino acids, carbohydrate, and lipids or fats), electrolytes, the micronutrients (vitamins and minerals) and water. Carbohydrate in the form of glucose or dextrose, protein in the form of amino acid and lipids are use ...
... The dietary components of a standard PN regimen are the macronutrients (protein or amino acids, carbohydrate, and lipids or fats), electrolytes, the micronutrients (vitamins and minerals) and water. Carbohydrate in the form of glucose or dextrose, protein in the form of amino acid and lipids are use ...
Lh6Ch04aProt
... • Unlike most organic polymers, protein molecules adopt a specific threedimensional conformation. • This structure is able to fulfill a specific biological function • This structure is called the native fold • The native fold has a large number of favorable interactions within the protein • There is ...
... • Unlike most organic polymers, protein molecules adopt a specific threedimensional conformation. • This structure is able to fulfill a specific biological function • This structure is called the native fold • The native fold has a large number of favorable interactions within the protein • There is ...
Lecture 10, molecular diversity - Cal State LA
... Step 2: each column adds a different second amino acid. (results in 96 different dipeptides) Step 3: Remove dipeptide from the bead Note: Each well contains one compound Step 4: Test each for biological activity. ...
... Step 2: each column adds a different second amino acid. (results in 96 different dipeptides) Step 3: Remove dipeptide from the bead Note: Each well contains one compound Step 4: Test each for biological activity. ...
The Citric Acid Cycle
... Net Result of the Citric Acid Cycle Acetyl-CoA + 3NAD+ + FAD + GDP + Pi + 2 H2O 2CO2 + 3NADH + FADH2 + GTP + CoA + 3H+ • Net oxidation of two carbons to CO2 ...
... Net Result of the Citric Acid Cycle Acetyl-CoA + 3NAD+ + FAD + GDP + Pi + 2 H2O 2CO2 + 3NADH + FADH2 + GTP + CoA + 3H+ • Net oxidation of two carbons to CO2 ...
Enzymes - WordPress.com
... • Temperature – increasing it increases rate of reaction • Temperature coefficient or Q10 is a value for the reaction that shows how much the rate increases when you increase the temperature by 10oC • At temperatures before optimum if the Q10 is 2 then the rate doubles for 10oC increase • A value of ...
... • Temperature – increasing it increases rate of reaction • Temperature coefficient or Q10 is a value for the reaction that shows how much the rate increases when you increase the temperature by 10oC • At temperatures before optimum if the Q10 is 2 then the rate doubles for 10oC increase • A value of ...
Review Sheet : DNA, RNA & Protein Synthesis
... Refer to the illustration. Suppose that you are given a protein containing the following sequence of amino acids: tyrosine, proline, aspartic acid, isoleucine, and cysteine. Use the portion of the genetic code given to determine which of the following contains a DNA sequence that codes for this amin ...
... Refer to the illustration. Suppose that you are given a protein containing the following sequence of amino acids: tyrosine, proline, aspartic acid, isoleucine, and cysteine. Use the portion of the genetic code given to determine which of the following contains a DNA sequence that codes for this amin ...
C485 Exam I
... Outline (structures please) how this molecule would be processed via beta oxidation. (You do not need to enumerate repeated steps.) Make sure you show any products that cannot be processed via beta-oxidation. Outline the intermediates involved in converting this remnant into a commonly used metabol ...
... Outline (structures please) how this molecule would be processed via beta oxidation. (You do not need to enumerate repeated steps.) Make sure you show any products that cannot be processed via beta-oxidation. Outline the intermediates involved in converting this remnant into a commonly used metabol ...
Chapter 11 Vitamins and proteins
... regular basis as part of a healthy diet. Thirteen vitamins are required but they generally cannot be synthesised by humans, except for vitamin D. If, however, vitamins are present in excess or are deficient, diseases such as beriberi, scurvy, anaemia, rickets and skin disorders may occur. Some vitam ...
... regular basis as part of a healthy diet. Thirteen vitamins are required but they generally cannot be synthesised by humans, except for vitamin D. If, however, vitamins are present in excess or are deficient, diseases such as beriberi, scurvy, anaemia, rickets and skin disorders may occur. Some vitam ...
citric acid cycle
... Other amino acids contribute to gluconeogenesis because their carbon skeletons give rise to citric acid cycle intermediates: 1- alanine, cysteine, glycine, hydroxyproline, serine, threonine, and tryptophan yield pyruvate. 2- arginine, histidine, glutamine, and proline yield -ketoglutarate. 3- isole ...
... Other amino acids contribute to gluconeogenesis because their carbon skeletons give rise to citric acid cycle intermediates: 1- alanine, cysteine, glycine, hydroxyproline, serine, threonine, and tryptophan yield pyruvate. 2- arginine, histidine, glutamine, and proline yield -ketoglutarate. 3- isole ...
Bellwork:
... SUMMARY: 5 Steps of Protein Synthesis 1. Transcription: DNA makes RNA (in the nucleus) 2. RNA now becomes mRNA which will leave the nucleus (take the code to ribosome) 3. mRNA tells ribosomes what proteins to make 4. mRNA attaches to ribosome and forms a pattern (codon) to make a protein 5. tRNA in ...
... SUMMARY: 5 Steps of Protein Synthesis 1. Transcription: DNA makes RNA (in the nucleus) 2. RNA now becomes mRNA which will leave the nucleus (take the code to ribosome) 3. mRNA tells ribosomes what proteins to make 4. mRNA attaches to ribosome and forms a pattern (codon) to make a protein 5. tRNA in ...
Protein Synthesis
... The genetic code of _____ is trapped inside the nucleus because it is ____________ to fit through the pores in the nuclear envelope. __________ is the process of copying the genetic code of _____ onto a single strand of _____. The single stranded _____ molecule falls on it’s side with it’s nitrogen ...
... The genetic code of _____ is trapped inside the nucleus because it is ____________ to fit through the pores in the nuclear envelope. __________ is the process of copying the genetic code of _____ onto a single strand of _____. The single stranded _____ molecule falls on it’s side with it’s nitrogen ...
How Enzymes Are Named - Our biological products and solutions
... protein, they are catalysts. This means that by their mere presence, and without being consumed in the process, enzymes can speed up chemical processes that would otherwise run very slowly, if at all.; Enzymes are specific Contrary to inorganic catalysts such as acids, bases, metals and metal oxides ...
... protein, they are catalysts. This means that by their mere presence, and without being consumed in the process, enzymes can speed up chemical processes that would otherwise run very slowly, if at all.; Enzymes are specific Contrary to inorganic catalysts such as acids, bases, metals and metal oxides ...
Chapter 2b Packet answers
... 15. Protein folding is determined by the sequence of the _amino acids__. 16. Examples of _proteins__ in your body include collagen and hemoglobin. 17. Monosaccharide, glycogen, cellulose are terms is associated with __carbohydrates__. 18. The speed of a chemical reaction is increased by an _enzyme__ ...
... 15. Protein folding is determined by the sequence of the _amino acids__. 16. Examples of _proteins__ in your body include collagen and hemoglobin. 17. Monosaccharide, glycogen, cellulose are terms is associated with __carbohydrates__. 18. The speed of a chemical reaction is increased by an _enzyme__ ...
AS Biology - TavistockCollegeScience
... It exists in long chains Chains lie side by side and hydrogen bonds form ...
... It exists in long chains Chains lie side by side and hydrogen bonds form ...