Turgor Pressure
... plants are able to regulate the amount of these to control turgor pressure. Turgor pressure is also reduced by transpiration, which causes significant negative pressures (or tensions) to be generated in the xylem and propagated to the walls of many cell types. Additionally, some rapidly growing cells ...
... plants are able to regulate the amount of these to control turgor pressure. Turgor pressure is also reduced by transpiration, which causes significant negative pressures (or tensions) to be generated in the xylem and propagated to the walls of many cell types. Additionally, some rapidly growing cells ...
Section 2 Active Transport Chapter 4
... particle’s positive or negative electrical charge. • A more positively charged ion located outside the cell is more likely to diffuse into the cell, where the charge is negative. • A more negatively charged ion located inside the cell is more likely to diffuse out of the cell. Chapter menu ...
... particle’s positive or negative electrical charge. • A more positively charged ion located outside the cell is more likely to diffuse into the cell, where the charge is negative. • A more negatively charged ion located inside the cell is more likely to diffuse out of the cell. Chapter menu ...
Bio 226: Cell and Molecular Biology
... Cellulose: ordered chains made of glucose linked b 1-4 • Cross-link with neighbors to form strong, stable fibers • Made by enzyme embedded in the plasma membrane • Guided by cytoskeleton • Other wall chemicals are made in Golgi & secreted • Only cellulose pattern is tightly controlled ...
... Cellulose: ordered chains made of glucose linked b 1-4 • Cross-link with neighbors to form strong, stable fibers • Made by enzyme embedded in the plasma membrane • Guided by cytoskeleton • Other wall chemicals are made in Golgi & secreted • Only cellulose pattern is tightly controlled ...
Root cytoskeleton: its role in perception of and response to gravity
... gravity is also indicated by their active role in signal transduction across the cell periphery (Sastry and Horwitz 1993; Pavalko and Otey 1994) and in controlling the spatial organization of MFs (Miyamoto et al. 1995). Importantly, the integrity of F-actin networks was shown to aect formation of t ...
... gravity is also indicated by their active role in signal transduction across the cell periphery (Sastry and Horwitz 1993; Pavalko and Otey 1994) and in controlling the spatial organization of MFs (Miyamoto et al. 1995). Importantly, the integrity of F-actin networks was shown to aect formation of t ...
MS Word Version - Interactive Physiology
... ** Carefully note the following steps that occur during this animation: 1. Acetylcholine (light blue ball) binds to the acetyl choline receptor (green). 2. The chemically regulated ion channel (purple) opens. 3. Sodium ions, Na+ (gold balls) ,diffuse from their higher concentration (in the synaptic ...
... ** Carefully note the following steps that occur during this animation: 1. Acetylcholine (light blue ball) binds to the acetyl choline receptor (green). 2. The chemically regulated ion channel (purple) opens. 3. Sodium ions, Na+ (gold balls) ,diffuse from their higher concentration (in the synaptic ...
Biology 12 - Chapter 17 - Biology12-Lum
... called Schwann Cells. • This protects the axon and also makes signals travel faster down the axon. • Between the myelin sheaths are spaces. These spaces are called the Nodes of Ranvier ...
... called Schwann Cells. • This protects the axon and also makes signals travel faster down the axon. • Between the myelin sheaths are spaces. These spaces are called the Nodes of Ranvier ...
The learners demonstrate an understanding of: The learners shall
... Structures and Functions of Biological Molecules - Carbohydrates - Lipids - Proteins - Enzymes - Nucleic Acids ...
... Structures and Functions of Biological Molecules - Carbohydrates - Lipids - Proteins - Enzymes - Nucleic Acids ...
PDF with detailed project information
... Carbohydrate metabolism is fundamental to plant growth and biomass production. Sugars provide the building blocks and energy for life, but also act as modulators of key developmental and physiological processes. Presently, we have a limited understanding of the precise molecular pathways that underp ...
... Carbohydrate metabolism is fundamental to plant growth and biomass production. Sugars provide the building blocks and energy for life, but also act as modulators of key developmental and physiological processes. Presently, we have a limited understanding of the precise molecular pathways that underp ...
A novel live cell assay to measure diacylglycerol lipase α activity
... Diacylglycerol lipase α (DAGLα) hydrolyses DAG to generate the principal endocannabinoid (eCB) 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) in the central nervous system. DAGLα dependent cannabinoid (CB) signalling has been implicated in numerous processes including axonal growth and guidance, adult neurogenesis a ...
... Diacylglycerol lipase α (DAGLα) hydrolyses DAG to generate the principal endocannabinoid (eCB) 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) in the central nervous system. DAGLα dependent cannabinoid (CB) signalling has been implicated in numerous processes including axonal growth and guidance, adult neurogenesis a ...
Slide 1
... CELL SURFACES AND JUNCTIONS 4.19 Cell surfaces protect, support, and join cells • Cells interact with their environments and each other via their surfaces. ...
... CELL SURFACES AND JUNCTIONS 4.19 Cell surfaces protect, support, and join cells • Cells interact with their environments and each other via their surfaces. ...
Plant Cell Walls
... partial hydrolysis of wall polysaccharides, possess hormone-like or signalling activity, regulating growth, development and metabolism. Such oligosaccharides are termed oligosaccharins. For instance, xyloglucan-derived oligosaccharins can regulate cell expansion, and pectin-derived oligosaccharins c ...
... partial hydrolysis of wall polysaccharides, possess hormone-like or signalling activity, regulating growth, development and metabolism. Such oligosaccharides are termed oligosaccharins. For instance, xyloglucan-derived oligosaccharins can regulate cell expansion, and pectin-derived oligosaccharins c ...
A Nascent Membrane Protein Is Located Adjacent to ER Membrane
... designated the signal sequence receptor by Wiedmann et al. (1987b) after being crosslinked using a short nascent chain (the arrested fragment, •70 amino acids long) with photoprobes located only in the signal sequence. Recent experiments have confirmed that nascent chains longer than the arrested fr ...
... designated the signal sequence receptor by Wiedmann et al. (1987b) after being crosslinked using a short nascent chain (the arrested fragment, •70 amino acids long) with photoprobes located only in the signal sequence. Recent experiments have confirmed that nascent chains longer than the arrested fr ...
A Nascent Membrane Protein Is Located Adjacent to
... designated the signal sequence receptor by Wiedmann et al. (1987b) after being crosslinked using a short nascent chain (the arrested fragment, •70 amino acids long) with photoprobes located only in the signal sequence. Recent experiments have confirmed that nascent chains longer than the arrested fr ...
... designated the signal sequence receptor by Wiedmann et al. (1987b) after being crosslinked using a short nascent chain (the arrested fragment, •70 amino acids long) with photoprobes located only in the signal sequence. Recent experiments have confirmed that nascent chains longer than the arrested fr ...
The Neuromuscular Junction
... When the chemically regulated ion channel opens, this charge reverses so now there is more negative charge in the synaptic cleft and more positive charge inside the cell. This occurs because much more sodium (which is positive) enters the cell, than potassium which leaves the cell. In fact, there is ...
... When the chemically regulated ion channel opens, this charge reverses so now there is more negative charge in the synaptic cleft and more positive charge inside the cell. This occurs because much more sodium (which is positive) enters the cell, than potassium which leaves the cell. In fact, there is ...
Matching Terms Test
... Basic unit of structure and function in all living things Outer protective covering of a cell Study of form and structure of an organism Controls many cell activities Furnaces or powerhouses of the cell Semi-fluid inside the cell Located inside the nucleus and important in cell reproduction Tissues ...
... Basic unit of structure and function in all living things Outer protective covering of a cell Study of form and structure of an organism Controls many cell activities Furnaces or powerhouses of the cell Semi-fluid inside the cell Located inside the nucleus and important in cell reproduction Tissues ...
Chapter 6
... Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells • The plasma membrane is a selective barrier that allows sufficient passage of oxygen, nutrients, and waste to service the volume of every cell • The general structure of a biological membrane is a double layer of phospholipids – Polar hydrophillic side ou ...
... Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells • The plasma membrane is a selective barrier that allows sufficient passage of oxygen, nutrients, and waste to service the volume of every cell • The general structure of a biological membrane is a double layer of phospholipids – Polar hydrophillic side ou ...
Nucleocytoplasmic transport
... across the nuclear envelope, therefore determines the nucleocytoplasmic distribution ratios of many macromolecules [17,17a]. For at least some classes of macromolecules, both signal-receptor interaction at the pore-complex and extensive nuclear and ...
... across the nuclear envelope, therefore determines the nucleocytoplasmic distribution ratios of many macromolecules [17,17a]. For at least some classes of macromolecules, both signal-receptor interaction at the pore-complex and extensive nuclear and ...
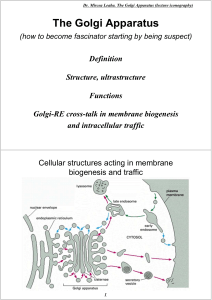
The Golgi Apparatus
... 7. Sorting and transport of biomolecules to final cellular location. N.B. Step by step ordered biochemical events in Golgi apparatus ...
... 7. Sorting and transport of biomolecules to final cellular location. N.B. Step by step ordered biochemical events in Golgi apparatus ...
The importance of the five phosphoribosyl
... growth were fixed in formaldehyde\methanol exactly as described by Wente et al. (1992). Antisera AK39 (peptide 1) and AK41 (peptide 2), described by Carter et al. (1997), were pre-adsorbed onto fixed cells and subsequently used at a 1 : 2700 (AK39) and a 1 : 900 (AK41) dilution. Binding of AK39 or A ...
... growth were fixed in formaldehyde\methanol exactly as described by Wente et al. (1992). Antisera AK39 (peptide 1) and AK41 (peptide 2), described by Carter et al. (1997), were pre-adsorbed onto fixed cells and subsequently used at a 1 : 2700 (AK39) and a 1 : 900 (AK41) dilution. Binding of AK39 or A ...
Evolution of Gamete Recognition Proteins
... during fertilization to form a diploid zygote, occurs in almost all eukaryotes. Fertilization is the bridge between generations. Although studied for more than a century, it remains one of the least understood fundamental biological processes. The interactions of sex cells (gametes) are mediated by ...
... during fertilization to form a diploid zygote, occurs in almost all eukaryotes. Fertilization is the bridge between generations. Although studied for more than a century, it remains one of the least understood fundamental biological processes. The interactions of sex cells (gametes) are mediated by ...
9-Ear Final (2o15-16)
... • It consists of a thin plate of elastic cartilage covered by a double layer of skin. • It receives the insertion of extrinsic muscles, which are supplied by the facial nerve. Sensation is carried by great auricular & auriculotemporal nerves. ...
... • It consists of a thin plate of elastic cartilage covered by a double layer of skin. • It receives the insertion of extrinsic muscles, which are supplied by the facial nerve. Sensation is carried by great auricular & auriculotemporal nerves. ...
Biao Ding*, Myoung-Ok Kwon and Leif Warnberg
... indicated that in CD/F-dextran co-injections, cell-to-cell movement of dextran was due to the presence of CD, but not due to DMSO. Although CD is generally considered to be very specific for actin, we were still concerned about its possible effects on other cellular targets.Therefore,the actin-bindi ...
... indicated that in CD/F-dextran co-injections, cell-to-cell movement of dextran was due to the presence of CD, but not due to DMSO. Although CD is generally considered to be very specific for actin, we were still concerned about its possible effects on other cellular targets.Therefore,the actin-bindi ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.