Differentiate between active and passive transport
... The movement of large particles or whole cells into the cell in vesicles. – Receptor-mediated endocytosis (not in your book) When particles bind to receptor proteins it causes the cell to pull the bound particles into the cell. ...
... The movement of large particles or whole cells into the cell in vesicles. – Receptor-mediated endocytosis (not in your book) When particles bind to receptor proteins it causes the cell to pull the bound particles into the cell. ...
Plant and Animal Cells
... Using a red pen correct this piece of pupil work about animal and plant cells using the information you have learned. You may use the other side if you need more space. Cheek cell ...
... Using a red pen correct this piece of pupil work about animal and plant cells using the information you have learned. You may use the other side if you need more space. Cheek cell ...
Spring 2012 Lecture 1 - Department of Chemistry -
... Similar processes occur in ALL cells, including prokaryotes. In fact, much of the biochemistry that we understand was first uncovered in prokaryotic systems. ...
... Similar processes occur in ALL cells, including prokaryotes. In fact, much of the biochemistry that we understand was first uncovered in prokaryotic systems. ...
1a. What are the two major parts of the cell?
... 5a. Why is the cell membrane sometimes referred to as a fluid mosaic? What part of the cell membrane acts like a fluid? And what makes it like a mosaic? 5a. The cell membrane is sometimes referred to as a fluid mosaic because it is made of many parts that can float around in the membrane. 5c. Why do ...
... 5a. Why is the cell membrane sometimes referred to as a fluid mosaic? What part of the cell membrane acts like a fluid? And what makes it like a mosaic? 5a. The cell membrane is sometimes referred to as a fluid mosaic because it is made of many parts that can float around in the membrane. 5c. Why do ...
St. Bonaventure College and High School Form 4 Biology
... cells and plant cells • Cell is the basic unit of life. • There are more than 200 types of cells in our body. • The shape and size of cells vary, but some features are common to all. ...
... cells and plant cells • Cell is the basic unit of life. • There are more than 200 types of cells in our body. • The shape and size of cells vary, but some features are common to all. ...
Plasma Membrane
... water and eliminate wastes. The plasma membrane is selectively permeable – it will allow some things to pass through, while blocking other things. ...
... water and eliminate wastes. The plasma membrane is selectively permeable – it will allow some things to pass through, while blocking other things. ...
1st Semester Review
... 1. List the 6 characteristics of life that are true for all living things. 1._____________________________________________________________________________________ 2. _____________________________________________________________________________________ 3. _____________________________________________ ...
... 1. List the 6 characteristics of life that are true for all living things. 1._____________________________________________________________________________________ 2. _____________________________________________________________________________________ 3. _____________________________________________ ...
AP Biology - gwbiology
... cholesterol – moderates fluidity of membrane at different temperatures glycolipid – cell to cell recognition integral protein – channels for transport of molecules, etc. peripheral protein – cell recognition, enzymatic activity, etc. 5. List the six broad functions of membrane proteins. Transport, e ...
... cholesterol – moderates fluidity of membrane at different temperatures glycolipid – cell to cell recognition integral protein – channels for transport of molecules, etc. peripheral protein – cell recognition, enzymatic activity, etc. 5. List the six broad functions of membrane proteins. Transport, e ...
provides shape, structure and support for plant cells carries out
... provides shape, structure and support for plant cells carries out photosynthesis ...
... provides shape, structure and support for plant cells carries out photosynthesis ...
Slide 1 - AccessMedicine
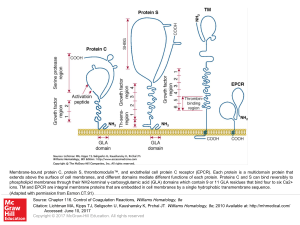
... Membrane-bound protein C, protein S, thrombomodulin™, and endothelial cell protein C receptor (EPCR). Each protein is a multidomain protein that extends above the surface of cell membranes, and different domains mediate different functions of each protein. Proteins C and S can bind reversibly to pho ...
... Membrane-bound protein C, protein S, thrombomodulin™, and endothelial cell protein C receptor (EPCR). Each protein is a multidomain protein that extends above the surface of cell membranes, and different domains mediate different functions of each protein. Proteins C and S can bind reversibly to pho ...
BCPS Biology Reteaching Guide Cells Vocab Card Definitions
... Strong supporting layer around the cell membrane in plants, algae, and some bacteria; composed of cellulose in plants ...
... Strong supporting layer around the cell membrane in plants, algae, and some bacteria; composed of cellulose in plants ...
Microtubules and Microfilaments
... • Site of protein synthesis (make proteins) – They link amino acids together ...
... • Site of protein synthesis (make proteins) – They link amino acids together ...
Organelles
... the nucleus; holds organelles in place Makes the essential proteins that are needed by the cell to carry out life processes The “transport system” of the cell. Once the protein is made, the E.R. takes it where it needs to go ...
... the nucleus; holds organelles in place Makes the essential proteins that are needed by the cell to carry out life processes The “transport system” of the cell. Once the protein is made, the E.R. takes it where it needs to go ...
Outer boundary of the cell, which regulates what, enters and exits
... Set of tubular passageways involved with the transport of proteins; it has many ribosomes attached and connects the nucleus to the cell membrane Rough endoplasmic reticulum ...
... Set of tubular passageways involved with the transport of proteins; it has many ribosomes attached and connects the nucleus to the cell membrane Rough endoplasmic reticulum ...
Effect of osmotic pressure on cells
... – Have a cytoskeleton made of microtubules • Allows for receptor mediated endocytosis, phagotcytosis, etc. • Cell membrane pinches in, creates vesicle ...
... – Have a cytoskeleton made of microtubules • Allows for receptor mediated endocytosis, phagotcytosis, etc. • Cell membrane pinches in, creates vesicle ...
Cell organelles
... Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) • Membrane bound network of interconnected vesicles • Enzymes are found embedded on the surface of the ER. • Materials synthesized here include: – Membrane phospholipids and cellular lipids - Sex hormones (testosterone and estrogen) (In Specialized cells ex. testicular ...
... Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) • Membrane bound network of interconnected vesicles • Enzymes are found embedded on the surface of the ER. • Materials synthesized here include: – Membrane phospholipids and cellular lipids - Sex hormones (testosterone and estrogen) (In Specialized cells ex. testicular ...
CELL STRUCTURE chart97
... Green, oval containing chlorophyll (green pigment) Double membrane with inner membrane modified into sacs called thylakoids Stacks of thylakoids called grana & interconnected Gel like innermost substance called stroma ...
... Green, oval containing chlorophyll (green pigment) Double membrane with inner membrane modified into sacs called thylakoids Stacks of thylakoids called grana & interconnected Gel like innermost substance called stroma ...
Organelle and Function Plant cell ONLY BOTH Animal cell ONLY
... Cytoskeleton: provides stability, shape, and produces movement for the cell Cell skeleton Vesicle: transport structure for carrying things into/out of cell; made by Golgi complex ...
... Cytoskeleton: provides stability, shape, and produces movement for the cell Cell skeleton Vesicle: transport structure for carrying things into/out of cell; made by Golgi complex ...
Experimental Biosciences: Introductory Laboratory Bios
... • Present in all living cells • More concentrated in muscle cells • The reason animals require oxygen ...
... • Present in all living cells • More concentrated in muscle cells • The reason animals require oxygen ...
Passive Transport in the Cell
... When water concentration is equal on the inside and outside of the cell, we refer to this as isotonic. ...
... When water concentration is equal on the inside and outside of the cell, we refer to this as isotonic. ...
File
... Regulates what enters and leaves the cell Composition: lipid bilayer Fluid Mosaic Model ...
... Regulates what enters and leaves the cell Composition: lipid bilayer Fluid Mosaic Model ...
4 A closer look at animal and plant cells KEY_2
... Lesson 4: A Closer Look at Animal and Plant Cells Read the printed pages and answer the questions below. 1. How did scientists discover the common structure of cells? Scientists used microscope to observe many kids of cells 2. What are some of the common structures of a cell? Common cell structures ...
... Lesson 4: A Closer Look at Animal and Plant Cells Read the printed pages and answer the questions below. 1. How did scientists discover the common structure of cells? Scientists used microscope to observe many kids of cells 2. What are some of the common structures of a cell? Common cell structures ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.