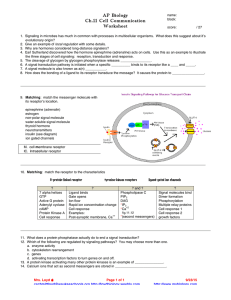
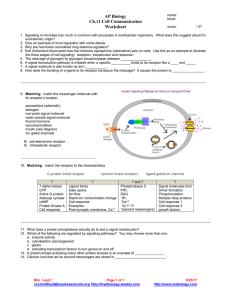
Subject Description Form
... functions. Structure and Function of Cell Organelles The architecture of plasma membrane, transport across membrane, internal membranes and cell energetic; cytoskeleton and cell movement; endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, Golgi apparatus, mitochondrion, and the nucleus. Control of Cell Growth and Ce ...
... functions. Structure and Function of Cell Organelles The architecture of plasma membrane, transport across membrane, internal membranes and cell energetic; cytoskeleton and cell movement; endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, Golgi apparatus, mitochondrion, and the nucleus. Control of Cell Growth and Ce ...
Six Kingdoms of Life
... Fungus is eukaryotic and has cell walls. • Decomposer, feed on dead or decaying tissue. Fungi digest food by releasing enzymes to break down organic matter into a form the https://www. fungus can absorb. youtube.com Type of Reproduction: – Asexually reproduces with SPORES. /watch?v=k WSYawl0KjQ ...
... Fungus is eukaryotic and has cell walls. • Decomposer, feed on dead or decaying tissue. Fungi digest food by releasing enzymes to break down organic matter into a form the https://www. fungus can absorb. youtube.com Type of Reproduction: – Asexually reproduces with SPORES. /watch?v=k WSYawl0KjQ ...
Cell: Fundamental Unit of Life
... Answer: Substances move in and out of the cell because of diffusion. Diffusion is the random movement of particles in order to attain concentration equilibrium. The movement of water through a semi-permeable membrane is called osmosis. It is important to note that plasma membrane is a semi-permeable ...
... Answer: Substances move in and out of the cell because of diffusion. Diffusion is the random movement of particles in order to attain concentration equilibrium. The movement of water through a semi-permeable membrane is called osmosis. It is important to note that plasma membrane is a semi-permeable ...
Cellular Transport Notes
... the cell to swell and possibly explode/burst. Isotonic Solutions: contain the SAME concentration of solute as another solution. When a cell is placed in an isotonic solution, the water diffuses into and out of the cell at the same rate. ...
... the cell to swell and possibly explode/burst. Isotonic Solutions: contain the SAME concentration of solute as another solution. When a cell is placed in an isotonic solution, the water diffuses into and out of the cell at the same rate. ...
Components of the Cell System
... pigment that allows photosynthesis Inside, contains flattened sacs “thylakoids”, where photosynthesis occurs Only in plants… though bluegreen pigment like chlorophyll found in some bacteria ...
... pigment that allows photosynthesis Inside, contains flattened sacs “thylakoids”, where photosynthesis occurs Only in plants… though bluegreen pigment like chlorophyll found in some bacteria ...
Chapter_9_Teacher_Notes
... amino acids and are the building blocks of many structures in organisms -ex. Meats, eggs, and nuts -enzymes – proteins that regulate chemical reactions in cells ...
... amino acids and are the building blocks of many structures in organisms -ex. Meats, eggs, and nuts -enzymes – proteins that regulate chemical reactions in cells ...
Diffusion Lab Review
... 1. Cell membranes are said to be selectively permeable. Which statement best explains what selectively permeable means? A) The cell membrane prevents any harmful substance from entering the cell. B) The cell membrane lets certain substances enter the cell and keeps certain substances out of the cell ...
... 1. Cell membranes are said to be selectively permeable. Which statement best explains what selectively permeable means? A) The cell membrane prevents any harmful substance from entering the cell. B) The cell membrane lets certain substances enter the cell and keeps certain substances out of the cell ...
Organisms and Environments Test Review
... 17. Which Domain has organisms that can withstand harsh conditions? _______________ 18. How are organisms in Domain Eukarya different from those in Domain Bacteria? 19. What is the main organelle that a Eukaryotic cell has that a Prokaryotic Cell does not? ______________________ 20. Which Kingdom ha ...
... 17. Which Domain has organisms that can withstand harsh conditions? _______________ 18. How are organisms in Domain Eukarya different from those in Domain Bacteria? 19. What is the main organelle that a Eukaryotic cell has that a Prokaryotic Cell does not? ______________________ 20. Which Kingdom ha ...
CHAPTER 7 THE CELL
... organelle – part of a cell that has a specific function 1. ribosome located in cytoplasm and on rough endoplasmic reticulum combines amino acids together to make proteins 2. endoplasmic reticulum (ER) storage and delivery system for the cell makes lipids 2 types rough ER – ER that contain ...
... organelle – part of a cell that has a specific function 1. ribosome located in cytoplasm and on rough endoplasmic reticulum combines amino acids together to make proteins 2. endoplasmic reticulum (ER) storage and delivery system for the cell makes lipids 2 types rough ER – ER that contain ...
Chapter 5
... ground substance. (T) • 3. Active transport does not require the expenditure of energy. (F) • 4. Proteins that extend from the cytoskeleton within the cell, through the plasma membrane, and into the extracellular matrix are A. lysosomal proteins. B. metallo proteins. C. receptor proteins. *D. integr ...
... ground substance. (T) • 3. Active transport does not require the expenditure of energy. (F) • 4. Proteins that extend from the cytoskeleton within the cell, through the plasma membrane, and into the extracellular matrix are A. lysosomal proteins. B. metallo proteins. C. receptor proteins. *D. integr ...
Web Quest - Cells (biology4kids)
... 55. The Golgi either ____________ them for later use or ____________ them out of the cell. 56. The Golgi also builds _________________. 57. The Golgi works very close with the ______________. Cell Wall – What’s It For? 58. What are cell walls made of? ____________________ 59. What type of cell has a ...
... 55. The Golgi either ____________ them for later use or ____________ them out of the cell. 56. The Golgi also builds _________________. 57. The Golgi works very close with the ______________. Cell Wall – What’s It For? 58. What are cell walls made of? ____________________ 59. What type of cell has a ...
Cell Transport/Cell Cycle/Meiosis Study Guide
... 8. Draw, label, and describe the phases of meiosis. 9. The gametes (sex cells) produced in meiosis are all genetically different from each other. Explain this. 10. The cells produced in mitosis are identical to the parent cells. The cells produced in meiosis are not. Explain the differences between ...
... 8. Draw, label, and describe the phases of meiosis. 9. The gametes (sex cells) produced in meiosis are all genetically different from each other. Explain this. 10. The cells produced in mitosis are identical to the parent cells. The cells produced in meiosis are not. Explain the differences between ...
Organelle Web Activity Worksheet
... 2. What is the function of DNA and RNA in protein synthesis? 3. How do DNA, RNA, nucleotides, amino acids and proteins fit together in protein synthesis? 4F. The Endomembrane System 1. Read and go through all activities. 2. What organelles are involved in the synthesis and transport of proteins? Lis ...
... 2. What is the function of DNA and RNA in protein synthesis? 3. How do DNA, RNA, nucleotides, amino acids and proteins fit together in protein synthesis? 4F. The Endomembrane System 1. Read and go through all activities. 2. What organelles are involved in the synthesis and transport of proteins? Lis ...
Draw a labelled diagram of a prokaryotic cell as seen in electron
... Explain how the surface area to volume ratio influences cell sizes (3) ...
... Explain how the surface area to volume ratio influences cell sizes (3) ...
Cell Organelles
... 7.12D Differentiate between structure and function in plant and animal cell organelles, including cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondrion, chloroplast, and vacuole ...
... 7.12D Differentiate between structure and function in plant and animal cell organelles, including cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondrion, chloroplast, and vacuole ...
IFITM3 Peptide PRODUCT DATA SHEET Bioworld Technology CO., Ltd.
... IFITM3 (interferon induced transmembrane protein 3), also known as 1-8U or IP15, is a multi-pass membrane protein that belongs to the IFITM (interferon inducible transmembrane) family of proteins. IFITM proteins are induced by type I and type II interferons and contain multiple interferon (IFN)-stim ...
... IFITM3 (interferon induced transmembrane protein 3), also known as 1-8U or IP15, is a multi-pass membrane protein that belongs to the IFITM (interferon inducible transmembrane) family of proteins. IFITM proteins are induced by type I and type II interferons and contain multiple interferon (IFN)-stim ...
Carbon Compounds
... Active Transport ◦ The use of energy to move materials through a cell ◦ Typically a protein that acts like a escort through the cell membrane This protein is called a transport protein ...
... Active Transport ◦ The use of energy to move materials through a cell ◦ Typically a protein that acts like a escort through the cell membrane This protein is called a transport protein ...
Cell Membrane - Fort Bend ISD
... • 3.Osmosis: diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane • Water moves from high to low concentrations • * Higher the concentration of solute -lower the concentration of water ...
... • 3.Osmosis: diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane • Water moves from high to low concentrations • * Higher the concentration of solute -lower the concentration of water ...
Notes on Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells
... The endoplasmic reticulum is divided into two parts: Rough endoplasmic reticulum: is studded with ribosomes giving it a bumpy or rough appearance, it is the site of protein production for the cell Smooth endoplasmic reticulum: has a smooth appearance because it has no ribosomes. Its job is to manufa ...
... The endoplasmic reticulum is divided into two parts: Rough endoplasmic reticulum: is studded with ribosomes giving it a bumpy or rough appearance, it is the site of protein production for the cell Smooth endoplasmic reticulum: has a smooth appearance because it has no ribosomes. Its job is to manufa ...
Attachment 2
... Modifies, sorts and Rubber bands, All of these objects could look packages proteins packing like the gogli if arranged peanuts or properly. The rubber bands and gummi worms the packing peanuts have the added significance that they are either used for sorting (rubber bands) or as packing ...
... Modifies, sorts and Rubber bands, All of these objects could look packages proteins packing like the gogli if arranged peanuts or properly. The rubber bands and gummi worms the packing peanuts have the added significance that they are either used for sorting (rubber bands) or as packing ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.