
organelles - Fillingham
... • Surrounded by a lipid bilayer (membrane) called the nuclear envelope which is connected to the rough endoplasmic reticulum and contains nuclear pores to allow things to enter and leave the ...
... • Surrounded by a lipid bilayer (membrane) called the nuclear envelope which is connected to the rough endoplasmic reticulum and contains nuclear pores to allow things to enter and leave the ...
Chapter 8 Notes - Crestwood Local Schools
... There are two ways in which cells must use energy to move material into and out of the cell. They are called passive transport and active transport. Passive Transport In passive transport, substances cross the cell membrane down their concentration gradient. Passive transport does not use energy to ...
... There are two ways in which cells must use energy to move material into and out of the cell. They are called passive transport and active transport. Passive Transport In passive transport, substances cross the cell membrane down their concentration gradient. Passive transport does not use energy to ...
cell structure and function 2010
... • Molecules are modified and packaged into vesicles for transport ...
... • Molecules are modified and packaged into vesicles for transport ...
Microworlds Study Guide
... Vinegar eels are made of many cells. It is one of the lowest animal forms that can digest food. It has a mouth and an anus. Females have their babies lined up inside of them by age. Vinegar eels are only found in unpasteurized vinegar. Pasteurization is a process where a liquid is heated to ...
... Vinegar eels are made of many cells. It is one of the lowest animal forms that can digest food. It has a mouth and an anus. Females have their babies lined up inside of them by age. Vinegar eels are only found in unpasteurized vinegar. Pasteurization is a process where a liquid is heated to ...
Bioelectrical Signal Recording
... cell binds to its ligand on the extracellular matrix secreted by another cell; ...
... cell binds to its ligand on the extracellular matrix secreted by another cell; ...
Bioelectrical Signal Recording
... cell binds to its ligand on the extracellular matrix secreted by another cell; ...
... cell binds to its ligand on the extracellular matrix secreted by another cell; ...
Worksheet Qs for revision File
... What is the cell theory? Compare and contrast eukaryotic & prokaryotic cells (similarlties & differences) What are examples of cell organelles, what are their functions? Compare and contrast cellular respiratio ...
... What is the cell theory? Compare and contrast eukaryotic & prokaryotic cells (similarlties & differences) What are examples of cell organelles, what are their functions? Compare and contrast cellular respiratio ...
Unit 2A Neurophysiology
... Voltage across a membrane due to differential concentration and charges of ions inside/outside the cell Two types of signals: a. ___________________: Small changes in membrane potential, leads to action potential b. ___________________: Neuron sends an impulse, an all-or-none response Graded Poten ...
... Voltage across a membrane due to differential concentration and charges of ions inside/outside the cell Two types of signals: a. ___________________: Small changes in membrane potential, leads to action potential b. ___________________: Neuron sends an impulse, an all-or-none response Graded Poten ...
Looking Inside Cells 3.2 Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus
... b. What was the name given to these tiny organs? ______________________ 10. What are the 3 basic functions of the organelles inside the cytoplasm? a. Produce _______________ b. ____________ and transport materials. c. Store and recycle _____________ 11. What organelle is referred to as the “energy p ...
... b. What was the name given to these tiny organs? ______________________ 10. What are the 3 basic functions of the organelles inside the cytoplasm? a. Produce _______________ b. ____________ and transport materials. c. Store and recycle _____________ 11. What organelle is referred to as the “energy p ...
Chapter 34
... • Recognition that there are two fundamentally different kinds of prokaryotes – Bacteria – Archaea ...
... • Recognition that there are two fundamentally different kinds of prokaryotes – Bacteria – Archaea ...
Lecture Outline 5
... needs of the cell. A network of tubes and tiny sacs extend from the nucleus to the cell membrane. Hormones and enzymes are transported to the extracellular environment via the golgi apparatus. ...
... needs of the cell. A network of tubes and tiny sacs extend from the nucleus to the cell membrane. Hormones and enzymes are transported to the extracellular environment via the golgi apparatus. ...
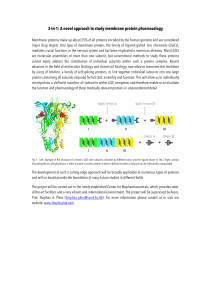
3-in-1: A novel approach to study membrane protein pharmacology
... 3-in-1: A novel approach to study membrane protein pharmacology Membrane proteins make up about 25% of all proteins encoded by the human genome and are considered major drug targets. One type of membrane protein, the family of ligand-gated ion channels (LGICs), mediates crucial functions in the nerv ...
... 3-in-1: A novel approach to study membrane protein pharmacology Membrane proteins make up about 25% of all proteins encoded by the human genome and are considered major drug targets. One type of membrane protein, the family of ligand-gated ion channels (LGICs), mediates crucial functions in the nerv ...
10. Plasmolysis and the effect of Osmosis on Cells
... water has a higher concentration (because it has fewer solutes) to an area where it has a lower concentration (because it has more solutes). In cells the semi-permeable membrane is the cell or plasma membrane. In plant cells this membrane is normally not seen because it is: very thin and pressed ...
... water has a higher concentration (because it has fewer solutes) to an area where it has a lower concentration (because it has more solutes). In cells the semi-permeable membrane is the cell or plasma membrane. In plant cells this membrane is normally not seen because it is: very thin and pressed ...
Movement through cell membranes
... • Molecules or other particles that are too large to enter a cell by diffusion, facilitated diffusion or active transport. • Three types – Phagocytosis: cell eating, takes in solids, ie. Bacteria – Pinocytosis: cell drinking, takes in tiny droplets, ie. Water – Receptor-mediated endocytosis: moves s ...
... • Molecules or other particles that are too large to enter a cell by diffusion, facilitated diffusion or active transport. • Three types – Phagocytosis: cell eating, takes in solids, ie. Bacteria – Pinocytosis: cell drinking, takes in tiny droplets, ie. Water – Receptor-mediated endocytosis: moves s ...
Cells_Alive_Lab[1] 2
... Big is a…”, the animal cell model, the plant cell model, and the bacterial cell model. Part A: “How big is a…” Here you will look at objects found on the head of a pin. Your job is to rank them in order of size on the chart below and estimate the length of each (in nanometers, micrometers, or millim ...
... Big is a…”, the animal cell model, the plant cell model, and the bacterial cell model. Part A: “How big is a…” Here you will look at objects found on the head of a pin. Your job is to rank them in order of size on the chart below and estimate the length of each (in nanometers, micrometers, or millim ...
Cell Brochure
... The organelles of the cell work together for the cell to do all of its daily jobs. For example, the nucleus tells the cell membrane what materials are needed; the cell membrane lets them in; these materials may go to the ribosomes where they are used to make proteins and are then are finished by the ...
... The organelles of the cell work together for the cell to do all of its daily jobs. For example, the nucleus tells the cell membrane what materials are needed; the cell membrane lets them in; these materials may go to the ribosomes where they are used to make proteins and are then are finished by the ...
Cell Transport
... 2. Plasmolysis- dehydration of a plant cell 3. Cytolysis- cell bursting, usually occurs in animal cells ...
... 2. Plasmolysis- dehydration of a plant cell 3. Cytolysis- cell bursting, usually occurs in animal cells ...
Document
... chromosome coiled structures of genetic material in the nucleus, made of long chains of DNA. mitochondrion transforms the unusable energy in food molecules, into a form of usable energy. prokaryotic cell a cell without a nucleus and most other organelles. cell wall a rigid wall that surrounds the ce ...
... chromosome coiled structures of genetic material in the nucleus, made of long chains of DNA. mitochondrion transforms the unusable energy in food molecules, into a form of usable energy. prokaryotic cell a cell without a nucleus and most other organelles. cell wall a rigid wall that surrounds the ce ...
2-4cellstructure
... • The nucleus acts like the cells “brain”- it is the control center of the cell directing all of its activities like growth and reproduction. • It is filled with a substance called chromatin. Chromatin contains genetic material, the instructions that direct the functions of the cell. For example, it ...
... • The nucleus acts like the cells “brain”- it is the control center of the cell directing all of its activities like growth and reproduction. • It is filled with a substance called chromatin. Chromatin contains genetic material, the instructions that direct the functions of the cell. For example, it ...
NCERT Short Notes - vaisesika.org.in
... membrane. This process is known as membrane biogenesis. • Some other proteins and lipids function ...
... membrane. This process is known as membrane biogenesis. • Some other proteins and lipids function ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.















![Cells_Alive_Lab[1] 2](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/011540557_1-c3f606b1b33bc1e29b015c6b59251a13-300x300.png)






