Cells - Cloudfront.net
... Thin flexible barrier made of a lipid bilayer that surrounds cells • Lipid bilayer – 2 layers of lipids with proteins embedded in it with CHO chains attached 1. Regulates what comes in & out of cell ...
... Thin flexible barrier made of a lipid bilayer that surrounds cells • Lipid bilayer – 2 layers of lipids with proteins embedded in it with CHO chains attached 1. Regulates what comes in & out of cell ...
Week2
... Resting Membrane Potential: Maintenance of Conc. Gradients For resting potentials to be maintained excitable cells must maintain [ions] different from equilibrium ...
... Resting Membrane Potential: Maintenance of Conc. Gradients For resting potentials to be maintained excitable cells must maintain [ions] different from equilibrium ...
cells
... 2. A micrometer is one-millionth of a meter long. A nanometer is one-billionth of a meter long. How many micrometers tall are you? 3. Describe the function of the nuclear envelope and nucleolus. 4. Describe the details of the structure of the chloroplast, the site of photosynthesis. 5. Mature, livin ...
... 2. A micrometer is one-millionth of a meter long. A nanometer is one-billionth of a meter long. How many micrometers tall are you? 3. Describe the function of the nuclear envelope and nucleolus. 4. Describe the details of the structure of the chloroplast, the site of photosynthesis. 5. Mature, livin ...
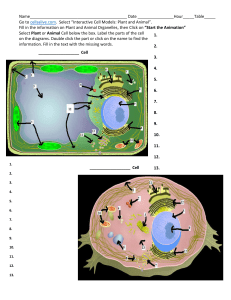
click here for plant cell rubric
... Name __________________________ Period ___ Cell Diagram Rubric---Plant Grade: 1-5 pts. possible for each component of your drawing. Please refer to your textbook on pages 90-91. Please do not directly copy the book; be creative! You may also use online resources from home, but please make sure they ...
... Name __________________________ Period ___ Cell Diagram Rubric---Plant Grade: 1-5 pts. possible for each component of your drawing. Please refer to your textbook on pages 90-91. Please do not directly copy the book; be creative! You may also use online resources from home, but please make sure they ...
Cells PPT
... 50 – 100 trillion (that’s 50 million million!) That means that if you lined all your cells up one after another they would stretch around the Earth 47 times!!! ...
... 50 – 100 trillion (that’s 50 million million!) That means that if you lined all your cells up one after another they would stretch around the Earth 47 times!!! ...
Concentration of solutes and solvent in a solution
... o Distinguish between structural formulas of unsaturated/saturated triglycerides o Saturated vs. unsaturated: which are ‘heart healthier”? Fats (animals) vs. oils (plants) o Different functions of lipids: function as long-term energy storage molecules function as structural molecules-in cell mem ...
... o Distinguish between structural formulas of unsaturated/saturated triglycerides o Saturated vs. unsaturated: which are ‘heart healthier”? Fats (animals) vs. oils (plants) o Different functions of lipids: function as long-term energy storage molecules function as structural molecules-in cell mem ...
Cell Structure and Function
... hydrophilic • Tails consist of fatty acids that are hydrophobic • Two layers in all • Proteins imbedded in and on membrane • Together they are called the “Fluid Mosaic Model” ...
... hydrophilic • Tails consist of fatty acids that are hydrophobic • Two layers in all • Proteins imbedded in and on membrane • Together they are called the “Fluid Mosaic Model” ...
Science 8 Questions 1. What does Organelle mean? 2. What is
... 19. What is the job of cilia and flagella? 20. What is the difference between cilia and flagella? 21. What cells have a cell wall? 22. What is the job of the cell wall? 23. What is the job of chloroplast? 24. What is the job of the vacuole? 25. How do plant and animal cells differ in regards to vacu ...
... 19. What is the job of cilia and flagella? 20. What is the difference between cilia and flagella? 21. What cells have a cell wall? 22. What is the job of the cell wall? 23. What is the job of chloroplast? 24. What is the job of the vacuole? 25. How do plant and animal cells differ in regards to vacu ...
To return to the chapter summary click escape or close this document.
... What kind of transport is shown? Explain how you know. ...
... What kind of transport is shown? Explain how you know. ...
Diffusion and Osmosis Lab
... through cellular membranes ! To connect the concepts of diffusion and osmosis to the cell structure and function Pre-lab questions or research - Remember to write complete sentences. Assume the reader doesn’t know the questions. 1. Diffusion is the movement of a solute from an area of higher concent ...
... through cellular membranes ! To connect the concepts of diffusion and osmosis to the cell structure and function Pre-lab questions or research - Remember to write complete sentences. Assume the reader doesn’t know the questions. 1. Diffusion is the movement of a solute from an area of higher concent ...
Worksheet - Moore Public Schools
... Centriole (animal cells only): Each centriole is a ring of 15. ____________________________ groups of fused microtubules. There are 16. ____________________________ microtubules in each group. Microtubules (and centrioles) are part of the cytoskeleton. In the complete animal cell centrosome, the two ...
... Centriole (animal cells only): Each centriole is a ring of 15. ____________________________ groups of fused microtubules. There are 16. ____________________________ microtubules in each group. Microtubules (and centrioles) are part of the cytoskeleton. In the complete animal cell centrosome, the two ...
anatomy test ch 3 cells and tissues
... 2. A red blood cell placed in a hypotonic solution would ________________. 3. ________ tissue protects and provides an energy reserve. 4. ____________ is the sight of protein synthesis 5. _______________ is composed largely of nonliving extracellular matrix, important in protection and support 6. __ ...
... 2. A red blood cell placed in a hypotonic solution would ________________. 3. ________ tissue protects and provides an energy reserve. 4. ____________ is the sight of protein synthesis 5. _______________ is composed largely of nonliving extracellular matrix, important in protection and support 6. __ ...
Biology Hoonors Cell Structure and Function Quiz
... 8. Cell membranes are made up of (cellulose / phospholipids). 9. The (cell wall / cell membrane) regulates what enters and exits the cell. 10. The (mitochondria / lysosomes) release energy from glucose. 11. Without ribosomes, a cell would not be able to produce (proteins / carbohydrates). 12. Cells ...
... 8. Cell membranes are made up of (cellulose / phospholipids). 9. The (cell wall / cell membrane) regulates what enters and exits the cell. 10. The (mitochondria / lysosomes) release energy from glucose. 11. Without ribosomes, a cell would not be able to produce (proteins / carbohydrates). 12. Cells ...
ch7 FA 11 - Cal State LA
... • Structures important for cell-cell adhesion – Adherens junctions (30nm gap between cells) • Cadherin-cadherin interactions in belt-like strips holding two cells together • Cytoplasmic domains link via beta-catenin and alpha-catenin to the cytoskeleton ...
... • Structures important for cell-cell adhesion – Adherens junctions (30nm gap between cells) • Cadherin-cadherin interactions in belt-like strips holding two cells together • Cytoplasmic domains link via beta-catenin and alpha-catenin to the cytoskeleton ...
Eukaryotic Cells - christophersonbiology
... proteins. Made up of a system of tubes, vesicles, and covered with ribosomes ...
... proteins. Made up of a system of tubes, vesicles, and covered with ribosomes ...
Homeostasis, Transport, and Bioenergetics
... higher concentration to one of lower concentration by random molecular motion. B. Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of lower concentration to one of higher concentration by random molecular motion. C. Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to on ...
... higher concentration to one of lower concentration by random molecular motion. B. Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of lower concentration to one of higher concentration by random molecular motion. C. Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to on ...
Essay 2
... transport nutrients in and waste out of the cell because of the low surface area to volume ratio. However, some of these useful organelles were once prokaryotes. Chloroplasts and mitochondria, for example, are clearly prokaryotic endosymbionts, with telltale small and exclusively freefloating ribos ...
... transport nutrients in and waste out of the cell because of the low surface area to volume ratio. However, some of these useful organelles were once prokaryotes. Chloroplasts and mitochondria, for example, are clearly prokaryotic endosymbionts, with telltale small and exclusively freefloating ribos ...
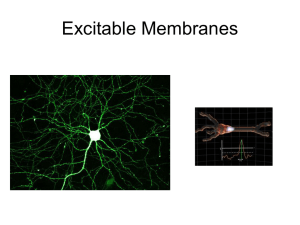
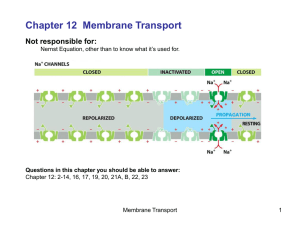
What is “membrane potential”
... Not responsible for: Nernst Equation, other than to know what it’s used for. ...
... Not responsible for: Nernst Equation, other than to know what it’s used for. ...
Placement-of-PROKERA-for-Dry-Eye
... such as recurrent corneal erosion, epithelium basement membrane dystrophy (EBMD), and Salzmann nodular degeneration - In conjunction with epithelial debridement and/or superficial keratectomy to promote rapid healing and restore vision d) Keratitis due to exposure and moderate and severe dry eye - T ...
... such as recurrent corneal erosion, epithelium basement membrane dystrophy (EBMD), and Salzmann nodular degeneration - In conjunction with epithelial debridement and/or superficial keratectomy to promote rapid healing and restore vision d) Keratitis due to exposure and moderate and severe dry eye - T ...
Structures and Functions in living organisms
... • Some chemicals can pass through this barrier and the cell can control what comes in and out. • It is selectively permeable. ...
... • Some chemicals can pass through this barrier and the cell can control what comes in and out. • It is selectively permeable. ...
3D Visualization of Thylakoid Membrane
... Proper biogenesis of the chloroplast is essential for all photosynthetic plant cells. As germinating seedlings are exposed to light, etioplasts in young mesophyll cells become chloroplasts in the developing seedling. The chloroplast thylakoids develop from a paracrystalline tubular structure that is ...
... Proper biogenesis of the chloroplast is essential for all photosynthetic plant cells. As germinating seedlings are exposed to light, etioplasts in young mesophyll cells become chloroplasts in the developing seedling. The chloroplast thylakoids develop from a paracrystalline tubular structure that is ...
DW#4 CellsAlive Websearch
... Centriole (animal cells only): Each centriole is a ring of 15. ____________________________ groups of fused microtubules. There are 16. ____________________________ microtubules in each group. Microtubules (and centrioles) are part of the cytoskeleton. In the complete animal cell centrosome, the two ...
... Centriole (animal cells only): Each centriole is a ring of 15. ____________________________ groups of fused microtubules. There are 16. ____________________________ microtubules in each group. Microtubules (and centrioles) are part of the cytoskeleton. In the complete animal cell centrosome, the two ...
Cell Cycle and Mitosis - Willimon-PHS
... have been duplicated, the cell enters another shorter growth period in which mitochondria and ...
... have been duplicated, the cell enters another shorter growth period in which mitochondria and ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.