Cell Structures
... Surrounds the cell; made of a double layer of specialized lipids, known as phospholipids, with embedded proteins; regulates the movement of substances into and out of the cell; also called the cell membrane. prokaryote A microscopic single-celled organism, including bacteria and cyanobacteria; does ...
... Surrounds the cell; made of a double layer of specialized lipids, known as phospholipids, with embedded proteins; regulates the movement of substances into and out of the cell; also called the cell membrane. prokaryote A microscopic single-celled organism, including bacteria and cyanobacteria; does ...
Cell “Travel Brochure”
... include: beach resort, factory, amusement park, island… Discuss/include a minimum of five cell structures. Some possibilities include but are not limited too: o Nucleus o Lysosomes o Mitochondria o Endoplasmic Reticulum o Cell Membrane o Golgi Apparatus o Cytoplasm o Ribosomes Create an analogy betw ...
... include: beach resort, factory, amusement park, island… Discuss/include a minimum of five cell structures. Some possibilities include but are not limited too: o Nucleus o Lysosomes o Mitochondria o Endoplasmic Reticulum o Cell Membrane o Golgi Apparatus o Cytoplasm o Ribosomes Create an analogy betw ...
Susceptibility of phospholipids of Proteus mirabilis smooth and
... and R 45 strains were therefore easy to follow by measuring luminescence in a reaction mixture containing L-a-DMPC. Fig. 1 shows that the rate of phospholipid hydrolysis by intact and sonicated R 45 ceils was about the same, whereas intact cells of the S 1959 strain remained inactive unless disrupte ...
... and R 45 strains were therefore easy to follow by measuring luminescence in a reaction mixture containing L-a-DMPC. Fig. 1 shows that the rate of phospholipid hydrolysis by intact and sonicated R 45 ceils was about the same, whereas intact cells of the S 1959 strain remained inactive unless disrupte ...
10-1 Cell Growth
... on its DNA. – When a cell is small the info stored in DNA is able to meet all the cell’s needs. – As a cell increases in size, it usually does not make extra copies of DNA. – If the cell were to increase without limit, an info crisis would occur. ...
... on its DNA. – When a cell is small the info stored in DNA is able to meet all the cell’s needs. – As a cell increases in size, it usually does not make extra copies of DNA. – If the cell were to increase without limit, an info crisis would occur. ...
Single-celled vs. Multi
... Vacuoles tend to be large in plant cells and play a role in turgor pressure. When a plant is wellwatered, water collects in cell vacuoles producing rigidity in the plant. Without sufficient water, pressure in the vacuole is reduced and the plant ...
... Vacuoles tend to be large in plant cells and play a role in turgor pressure. When a plant is wellwatered, water collects in cell vacuoles producing rigidity in the plant. Without sufficient water, pressure in the vacuole is reduced and the plant ...
pogil 3
... 11. In the phospholipid bilayer of Model 2, what do the light gray wiggly protrusions, or tails, represent? The spheres? ...
... 11. In the phospholipid bilayer of Model 2, what do the light gray wiggly protrusions, or tails, represent? The spheres? ...
Chapter 7 - OnMyCalendar
... 1. Describe the structure of the cell membrane. 2. By what methods are substances transported across membranes? Fluid Mosaic Model The membrane is a fluid structure with various proteins embedded in or attached to a double layer (bilayer) of phospholipids o Fluid = capable of flowing and easily ch ...
... 1. Describe the structure of the cell membrane. 2. By what methods are substances transported across membranes? Fluid Mosaic Model The membrane is a fluid structure with various proteins embedded in or attached to a double layer (bilayer) of phospholipids o Fluid = capable of flowing and easily ch ...
File - PBL Group 14
... After death, cell components are progressively degraded, and there is widespread leakage of cellular enzymes into the extracellular space and, conversely, entry of extracellular macromolecules from the interstitial space into the dying cells. Finally, the dead cell may become replaced by large masse ...
... After death, cell components are progressively degraded, and there is widespread leakage of cellular enzymes into the extracellular space and, conversely, entry of extracellular macromolecules from the interstitial space into the dying cells. Finally, the dead cell may become replaced by large masse ...
The inner ear The inner ear can be divided into
... receptor cells, which are called hair cells, are arranged in rows and they possess numerous hair like processes that extend into the endolymph of the cochlear duct. As sound vibrations pass through the inner ear, the hairs shear back and forth against the tectorial membrane, and the mechanical defor ...
... receptor cells, which are called hair cells, are arranged in rows and they possess numerous hair like processes that extend into the endolymph of the cochlear duct. As sound vibrations pass through the inner ear, the hairs shear back and forth against the tectorial membrane, and the mechanical defor ...
Growth
... Results expressed as colony forming units (CFU) since it is not absolutely certain that each colony arose from an individual cell Viable cell counts very sensitive: Any viable cell colony Allow: Identification of organisms Isolation of pure cultures ...
... Results expressed as colony forming units (CFU) since it is not absolutely certain that each colony arose from an individual cell Viable cell counts very sensitive: Any viable cell colony Allow: Identification of organisms Isolation of pure cultures ...
2016 Chapter 7 Lecture
... move from HIGH to LOW concentration (down a concentration gradient) Molecules that do so are: small, gases, non-polar ...
... move from HIGH to LOW concentration (down a concentration gradient) Molecules that do so are: small, gases, non-polar ...
Cell Analogy
... and artisans. The poster will include the title, a cell and the analogies around the cell with picture descriptions as well as the text. What does a quality analogy look like? To get full credit for each analogy, think about this: Does the analogy for this structure/process make sense? Are the two ...
... and artisans. The poster will include the title, a cell and the analogies around the cell with picture descriptions as well as the text. What does a quality analogy look like? To get full credit for each analogy, think about this: Does the analogy for this structure/process make sense? Are the two ...
Topic - CarstensenPortfolio
... cells so small?”, “Who first discovers the cell?” “How long till inside of cell could be described?” “What are some things that cells can do for us?” After small discussion, mention cell organelle if it has not been brought up already. All life as we know it is survives because of the functions ...
... cells so small?”, “Who first discovers the cell?” “How long till inside of cell could be described?” “What are some things that cells can do for us?” After small discussion, mention cell organelle if it has not been brought up already. All life as we know it is survives because of the functions ...
Unit 2: Cell Biology Study Guide
... provides strength and support to the cell 12. mitochondria(mitochondrion): cell organelles surrounded by two membranes that break down food molecules 13. chloroplast: an organelle found in plants and algae where photosynthesis occurs 14. hereditary: having to do with the passing of traits from paren ...
... provides strength and support to the cell 12. mitochondria(mitochondrion): cell organelles surrounded by two membranes that break down food molecules 13. chloroplast: an organelle found in plants and algae where photosynthesis occurs 14. hereditary: having to do with the passing of traits from paren ...
CHAPTER 5: CELL STRUCTURE
... protist cells where they direct the assembly of the cytoskeletal microtubules and form the basal bodies that anchor the flagella. The cytoskeleton, composed of actin filaments, microtubules, and intermediate filaments, provides a framework to anchor the organelles and give a cell its shape. Microtub ...
... protist cells where they direct the assembly of the cytoskeletal microtubules and form the basal bodies that anchor the flagella. The cytoskeleton, composed of actin filaments, microtubules, and intermediate filaments, provides a framework to anchor the organelles and give a cell its shape. Microtub ...
Oxidative folding in mitochondria
... 1991, MChem, Chemical Engineering, Univ of Delaware, USA 1993, PhD, (Fulbright and EU Fellow) Chemical Engineering/Biochemistry Univ. of Delaware and Institut Pasteur France ...
... 1991, MChem, Chemical Engineering, Univ of Delaware, USA 1993, PhD, (Fulbright and EU Fellow) Chemical Engineering/Biochemistry Univ. of Delaware and Institut Pasteur France ...
Biotechnology Unit 2: Cellular Biology Essential Cell Biology
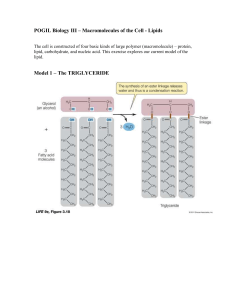
... and if there is more than one double bond it is called a __________________ fatty acid a. The double bonds in unsaturated fatty acids makes the hydrocarbon chains __________________ which makes it difficult for them to stack together easily and therefore typically form __________________ substa ...
... and if there is more than one double bond it is called a __________________ fatty acid a. The double bonds in unsaturated fatty acids makes the hydrocarbon chains __________________ which makes it difficult for them to stack together easily and therefore typically form __________________ substa ...
Cells
... ______________ – Diffusion of water across a membrane. ______________ refers to tendency of cell to gain or lose water. If the solution is Isotonic to the cell – Solute concentration is same on both sides of membrane. No net movement of water. Hypertonic to the cell – Concentration of solu ...
... ______________ – Diffusion of water across a membrane. ______________ refers to tendency of cell to gain or lose water. If the solution is Isotonic to the cell – Solute concentration is same on both sides of membrane. No net movement of water. Hypertonic to the cell – Concentration of solu ...
BIOREACTION AND BIOREACTOR - Universiti Malaysia Perlis
... heart of any industrial fermentation process. • The advantages are mild rxn conditions, high yields and stereospecific compounds. • Bioreactors supply a homogeneous (same throughout) environment by constantly stirring the contents. • Bioreactors give the cells a controlled environment by ensuring th ...
... heart of any industrial fermentation process. • The advantages are mild rxn conditions, high yields and stereospecific compounds. • Bioreactors supply a homogeneous (same throughout) environment by constantly stirring the contents. • Bioreactors give the cells a controlled environment by ensuring th ...
Optogenetics 3.0 Please share
... improvement over earlier versions, and the authors have successfully used it in combination with ChR2. It is likely that a combination of ChR2 and eNpHR3.0 (or Arch) will be sufficient in many cases where bidirectional control of cell membrane potential is desired. A second major breakthrough for op ...
... improvement over earlier versions, and the authors have successfully used it in combination with ChR2. It is likely that a combination of ChR2 and eNpHR3.0 (or Arch) will be sufficient in many cases where bidirectional control of cell membrane potential is desired. A second major breakthrough for op ...
Cytoskeletal Architecture and Cell Morphogenesis
... Figure 3: Spatio-temporal regulation of cell division in fission yeast. Contractile ring Node precursors are composed of the two major components Cdr2 and Mid1. Their assembly is restricted to the middle by Pom1 kinase which forms a gradient emanating from the cell tips. Pom1 lowers Cdr2 affinity for m ...
... Figure 3: Spatio-temporal regulation of cell division in fission yeast. Contractile ring Node precursors are composed of the two major components Cdr2 and Mid1. Their assembly is restricted to the middle by Pom1 kinase which forms a gradient emanating from the cell tips. Pom1 lowers Cdr2 affinity for m ...
Macromolecules of the Cell
... Globular proteins: they are involved in cellular structure. They are folded into compact form. The formation of a-helix or B-sheets depends on the type of amino acids present in the polypeptide. Leucine, methionine, and glutamate are strong a-helix formers, whereas isoleucine, valine, and phenylalan ...
... Globular proteins: they are involved in cellular structure. They are folded into compact form. The formation of a-helix or B-sheets depends on the type of amino acids present in the polypeptide. Leucine, methionine, and glutamate are strong a-helix formers, whereas isoleucine, valine, and phenylalan ...
Weekly PowerPoint
... from one place to another. Do not drag it or push it on the countertop. 3. When focusing on a slide, ALWAYS start with the 4X red objective lens. Once you have the object in focus, then switch to the next higher power objective (10X yellow). Re-focus on the image and then switch to the next highest ...
... from one place to another. Do not drag it or push it on the countertop. 3. When focusing on a slide, ALWAYS start with the 4X red objective lens. Once you have the object in focus, then switch to the next higher power objective (10X yellow). Re-focus on the image and then switch to the next highest ...
Cell Model Expectations
... Cell Model Expectations You will create a 3-D model of a plant or animal cell (your choice) using common materials. You will label the structures on the models with numbers, and provide a key to identify each part of the cell. You will also complete a sheet identifying each organelle, its function, ...
... Cell Model Expectations You will create a 3-D model of a plant or animal cell (your choice) using common materials. You will label the structures on the models with numbers, and provide a key to identify each part of the cell. You will also complete a sheet identifying each organelle, its function, ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.