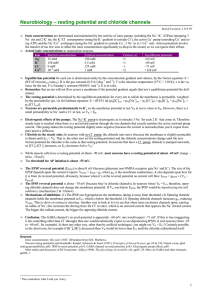
resting potential and chloride channels
... small permeability to Na+ and to Cl– at rest, so VR > EK. Electrogenic effects of the pumps. The Na+/K+ pump is electrogenic as it extrudes 3 Na+ for each 2 K+ that come in. Therefore steady state is reached when there is a net inward current through the ion channels that exactly matches the active ...
... small permeability to Na+ and to Cl– at rest, so VR > EK. Electrogenic effects of the pumps. The Na+/K+ pump is electrogenic as it extrudes 3 Na+ for each 2 K+ that come in. Therefore steady state is reached when there is a net inward current through the ion channels that exactly matches the active ...
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell
... Functions of microtubules Shaping the cell Guiding movement of organelles Separating chromosomes during cell division ...
... Functions of microtubules Shaping the cell Guiding movement of organelles Separating chromosomes during cell division ...
10 Plant and Animal Cells
... chloroplasts in the plant cells, but the nuclei are not easily discernible. While the plant cells shown in image 3 do not contain chloroplasts, their nuclei and other cell parts are visible. Having seen both plant cell images, students should be able to draw a composite plant cell exhibiting all of ...
... chloroplasts in the plant cells, but the nuclei are not easily discernible. While the plant cells shown in image 3 do not contain chloroplasts, their nuclei and other cell parts are visible. Having seen both plant cell images, students should be able to draw a composite plant cell exhibiting all of ...
The Ear
... Is formed by the lateral wall of the inner ear. The greater part of the wall shows a rounded projection, called the promontory, which results from the underlying first turn of the ...
... Is formed by the lateral wall of the inner ear. The greater part of the wall shows a rounded projection, called the promontory, which results from the underlying first turn of the ...
ppt
... Is formed by the lateral wall of the inner ear. The greater part of the wall shows a rounded projection, called the promontory, which results from the underlying first turn of the ...
... Is formed by the lateral wall of the inner ear. The greater part of the wall shows a rounded projection, called the promontory, which results from the underlying first turn of the ...
The Cell Cycle and Cellular Reproduction
... Rigid cell walls outside plasma membrane do not permit furrowing ...
... Rigid cell walls outside plasma membrane do not permit furrowing ...
Unit 1 Notes
... Specificity of Enzymes During an enzyme controlled reaction the substances involved – the substrates – become joined to the surface of the enzyme molecule. The chemical reaction then takes place very rapidly. The spot on the enzyme molecule where the catalytic activity takes place is called the ____ ...
... Specificity of Enzymes During an enzyme controlled reaction the substances involved – the substrates – become joined to the surface of the enzyme molecule. The chemical reaction then takes place very rapidly. The spot on the enzyme molecule where the catalytic activity takes place is called the ____ ...
Flagellar Movement Although the precise mechanism by which
... produces runs, which are movements of a cell in a single direction for some time. If more than one flagellum is present, the flagella align and rotate together as a bundle. Tumbles are abrupt, random changes in direction resulting from clockwise flagellar rotation where each flagellum rotates independen ...
... produces runs, which are movements of a cell in a single direction for some time. If more than one flagellum is present, the flagella align and rotate together as a bundle. Tumbles are abrupt, random changes in direction resulting from clockwise flagellar rotation where each flagellum rotates independen ...
Ergastic
... Cell biology Ergastic Substances Cystoliths are similar to druse crystals but hang from cell wall outgrowths. Rather than calcium oxalate, cystoliths are made of calcium carbonate. They occur in only a few families (Moraceae, Acanthaceae, and Cucurbitaceae) contained in an epidermal cell type calle ...
... Cell biology Ergastic Substances Cystoliths are similar to druse crystals but hang from cell wall outgrowths. Rather than calcium oxalate, cystoliths are made of calcium carbonate. They occur in only a few families (Moraceae, Acanthaceae, and Cucurbitaceae) contained in an epidermal cell type calle ...
7. Development of digestive system I. Yolk sac. Primitive gut
... from the surface epithelium; it splits into 5 dental buds in each quadrant o the dental buds are connected with the oral epithelium and form the primordia of the ectodermal components of teeth o the dental buds develop into caps with outer and inner dental epithelium (ameloblasts) and inner core (st ...
... from the surface epithelium; it splits into 5 dental buds in each quadrant o the dental buds are connected with the oral epithelium and form the primordia of the ectodermal components of teeth o the dental buds develop into caps with outer and inner dental epithelium (ameloblasts) and inner core (st ...
FREE Sample Here
... B) Glucose entering the cell down its concentration gradient provides energy for uptake of sodium ions against the electrochemical gradient. C) Sodium ions can move down their electrochemical gradient through the cotransporter whether or not glucose is present outside the cell. D) The cotransporter ...
... B) Glucose entering the cell down its concentration gradient provides energy for uptake of sodium ions against the electrochemical gradient. C) Sodium ions can move down their electrochemical gradient through the cotransporter whether or not glucose is present outside the cell. D) The cotransporter ...
Are you really going out with a virus?
... 5. Which of the cells in the diagram above is a plant cell? Why? Cell 1, because it has a cell wall 6. Which of the cells in the diagram above is an animal cell? Why? Cell 2, because it does not have a cell wall 7. What organelle is #3 (Cell 1) pointing to? Cell membrane 8. What organelle # ...
... 5. Which of the cells in the diagram above is a plant cell? Why? Cell 1, because it has a cell wall 6. Which of the cells in the diagram above is an animal cell? Why? Cell 2, because it does not have a cell wall 7. What organelle is #3 (Cell 1) pointing to? Cell membrane 8. What organelle # ...
Cytoskeletal elements in bacteria
... FtsZ for this process [15]. FtsZ forms a ring structure in the middle of the cell (slightly off-centre in C. crescentus) (Figure 1a), and recruits all other known cell division proteins to this site [14]. Jan Löwe’s group demonstrated that FtsZ is a tubulin ortholog [16], which in eukaryotic cells ...
... FtsZ for this process [15]. FtsZ forms a ring structure in the middle of the cell (slightly off-centre in C. crescentus) (Figure 1a), and recruits all other known cell division proteins to this site [14]. Jan Löwe’s group demonstrated that FtsZ is a tubulin ortholog [16], which in eukaryotic cells ...
Cells in tight spaces: the role of cell shape in cell function
... in the branched growth of the single cells (Fig. 2 A). Through the use of microscale confinement, a shape change diverted a polarization cue, demonstrating the link between localized protein deposition and polarized growth. Studies in these confining geometries, particularly in microbes and in vitro ...
... in the branched growth of the single cells (Fig. 2 A). Through the use of microscale confinement, a shape change diverted a polarization cue, demonstrating the link between localized protein deposition and polarized growth. Studies in these confining geometries, particularly in microbes and in vitro ...
What is the neuron`s resting potential?
... • Resting neurons are polarized due to the distribution of ions around the neuron’s membrane. • Sodium ions (Na+), potassium ions (K+), chloride ions (Cl-) and negatively charged protein ions are distributed unevenly across the neuron’s membrane. • The ratio of negative to positive charges is great ...
... • Resting neurons are polarized due to the distribution of ions around the neuron’s membrane. • Sodium ions (Na+), potassium ions (K+), chloride ions (Cl-) and negatively charged protein ions are distributed unevenly across the neuron’s membrane. • The ratio of negative to positive charges is great ...
MEMBRANE PROTEINS SYNTHESIZED BY
... the isolated enzyme forms stable interactions with high affinity for a limited number of sites on the cytoplasmic face of the membrane (21). Rabbit reticulocytes contain, with possibly one or two exceptions (22), the same proteins in their membranes as do rabbit erythrocytes. We recently showed that ...
... the isolated enzyme forms stable interactions with high affinity for a limited number of sites on the cytoplasmic face of the membrane (21). Rabbit reticulocytes contain, with possibly one or two exceptions (22), the same proteins in their membranes as do rabbit erythrocytes. We recently showed that ...
Integr. Comp. Biol., 43:55–63 Epithelium—the primary building block
... cells from its epithelium into the extracellular matrix) from which organ development becomes possible. The primary building block providing for complex differentiation, then, is epithelium. It is the epithelial tissue type that sets the Eumetazoa apart from the sponges, and it is epithelia in the B ...
... cells from its epithelium into the extracellular matrix) from which organ development becomes possible. The primary building block providing for complex differentiation, then, is epithelium. It is the epithelial tissue type that sets the Eumetazoa apart from the sponges, and it is epithelia in the B ...
Effects of Nonequilibrium Atmospheric Pressure Plasmas on the
... atm makes the decontamination process practical and inexpensive. In addition, the fact that the gas temperature in such discharges remains relatively low makes their use suitable for applications where medium preservation is desired. Unfortunately, the drive to develop a practical means of decontami ...
... atm makes the decontamination process practical and inexpensive. In addition, the fact that the gas temperature in such discharges remains relatively low makes their use suitable for applications where medium preservation is desired. Unfortunately, the drive to develop a practical means of decontami ...
"Dot and Slot Blotting of DNA". In: Current Protocols in Molecular
... Dot and Slot Blotting of DNA Dot and slot blotting are simple techniques for immobilizing bulk unfractionated DNA on a nitrocellulose or nylon membrane. Hybridization analysis (UNIT 2.10) can then be carried out to determine the relative abundance of target sequences in the blotted DNA preparations. ...
... Dot and Slot Blotting of DNA Dot and slot blotting are simple techniques for immobilizing bulk unfractionated DNA on a nitrocellulose or nylon membrane. Hybridization analysis (UNIT 2.10) can then be carried out to determine the relative abundance of target sequences in the blotted DNA preparations. ...
Generation and propagation of axon potentials
... Image source: http://www.daviddarling.info/encyclopedia/N/neuron.html COSC422 ...
... Image source: http://www.daviddarling.info/encyclopedia/N/neuron.html COSC422 ...
CELLULAR TRANSpoRT PRACTICE
... Read the passage below. Notice that the sentences are numbered. Then answer the questions that follow. The diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane is called osmosis. Like other forms of diffusion, osmosis involves the movement of a substance—water—down its concentration gradient. ...
... Read the passage below. Notice that the sentences are numbered. Then answer the questions that follow. The diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane is called osmosis. Like other forms of diffusion, osmosis involves the movement of a substance—water—down its concentration gradient. ...
File - BINZHOU MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
... Sidney Altman and Thomas Cech were awarded the Nobel Prize for Biochemistry in 1989 ...
... Sidney Altman and Thomas Cech were awarded the Nobel Prize for Biochemistry in 1989 ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.























