Equilibrium-Phase High Spatial Resolution Contrast
... magnetic resonance angiography (CE-MRA) at 1.5T using a blood pool contrast agent for the preoperative evaluation of deep inferior epigastric artery perforator branches (DIEP), and (ii) to compare image quality with conventional first-pass CEMRA. Methods: Twenty-three consecutive patients were inclu ...
... magnetic resonance angiography (CE-MRA) at 1.5T using a blood pool contrast agent for the preoperative evaluation of deep inferior epigastric artery perforator branches (DIEP), and (ii) to compare image quality with conventional first-pass CEMRA. Methods: Twenty-three consecutive patients were inclu ...
Electronic portal imaging devices: a review and
... imaging source. This is followed by a concise historical review and perspective on the various classes of technologies that have been developed to meet these requirements. A more detailed operational description is then provided for the two first-generation portal imaging technologies that were comm ...
... imaging source. This is followed by a concise historical review and perspective on the various classes of technologies that have been developed to meet these requirements. A more detailed operational description is then provided for the two first-generation portal imaging technologies that were comm ...
Sirona offers the right 3D choice for every dentist
... GALILEOS sets new standards by offering the lowest radiation dosage with superior image quality.** The intuitive operation and optimized clinical workflow provide efficiency in both, dentistry and 3D diagnostics. GALILEOS represents the future of dentistry and is now available in 2 versions – both o ...
... GALILEOS sets new standards by offering the lowest radiation dosage with superior image quality.** The intuitive operation and optimized clinical workflow provide efficiency in both, dentistry and 3D diagnostics. GALILEOS represents the future of dentistry and is now available in 2 versions – both o ...
usrenal
... • Small isoechoic massses miss by US • Equivocal CT scan more sensitive in small lesion detection • CT for staging purposes • Identify primary & other smaller metastases not identified on US ...
... • Small isoechoic massses miss by US • Equivocal CT scan more sensitive in small lesion detection • CT for staging purposes • Identify primary & other smaller metastases not identified on US ...
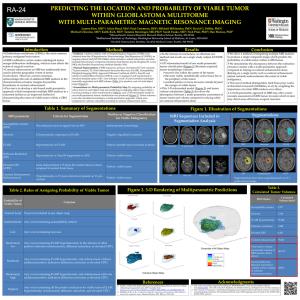
predicting the location and probability of viable tumor within
... MO) and Swedish Neuroscience Institute (Seattle, WA). Manual Segmentations. 8 MRI sequences, primary and derived [T1 pre-contrast, T1 post-contrast, T2, Fluid Attenuated Inversion Recovery (FLAIR), Susceptibility ...
... MO) and Swedish Neuroscience Institute (Seattle, WA). Manual Segmentations. 8 MRI sequences, primary and derived [T1 pre-contrast, T1 post-contrast, T2, Fluid Attenuated Inversion Recovery (FLAIR), Susceptibility ...
Meandering Main Pancreatic Duct in a Case of Recurrent Acute
... episodes of acute pancreatitis for last 2 years. Contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the abdomen was performed with magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) at the time of first episode, which showed necrotic collection in pancreatic head region. Main pancreatic duct was ...
... episodes of acute pancreatitis for last 2 years. Contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the abdomen was performed with magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) at the time of first episode, which showed necrotic collection in pancreatic head region. Main pancreatic duct was ...
ACR-SNM-SPR- Practice Guideline for the Performance of
... The American College of Radiology, with more than 30,000 members, is the principal organization of radiologists, radiation oncologists, and clinical medical physicists in the United States. The College is a nonprofit professional society whose primary purposes are to advance the science of radiology ...
... The American College of Radiology, with more than 30,000 members, is the principal organization of radiologists, radiation oncologists, and clinical medical physicists in the United States. The College is a nonprofit professional society whose primary purposes are to advance the science of radiology ...
Technical Standard for Diagnostic Procedures Using
... 1. Certification in Radiology, Diagnostic Radiology, Nuclear Radiology, or Nuclear Medicine by one of the following organizations: the American Board of Radiology (ABR), the American Board of Nuclear Medicine, the American Osteopathic Board of Radiology, the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons ...
... 1. Certification in Radiology, Diagnostic Radiology, Nuclear Radiology, or Nuclear Medicine by one of the following organizations: the American Board of Radiology (ABR), the American Board of Nuclear Medicine, the American Osteopathic Board of Radiology, the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons ...
Image Quality and Dose Comparison between
... • A: CBCT - entire volumetric dataset collected with single rotation • B: Conventional CT - requires z-direction translation ...
... • A: CBCT - entire volumetric dataset collected with single rotation • B: Conventional CT - requires z-direction translation ...
Artefacts in cone beam CT - Scientific Research Publishing
... a high energy X-ray photon and one of the outer shell electrons of an atom. This outer shell electron is bound with very little energy to the atom so when the X-ray photon collides with it, the electron is ejected from the atom. Because energy and momentum are both conserved in this collision, the e ...
... a high energy X-ray photon and one of the outer shell electrons of an atom. This outer shell electron is bound with very little energy to the atom so when the X-ray photon collides with it, the electron is ejected from the atom. Because energy and momentum are both conserved in this collision, the e ...
Abdominal Imaging: Use of High- Concentration Contrast Media
... Abdominal Imaging in MDCT Since its clinical introduction in 1989, volumetric CT scanning has resulted in a revolution in diagnostic imaging. Spiral CT has improved over the last few years, with faster gantry rotation, more powerful X-ray tubes, and improved interpolation algorithms, but the greates ...
... Abdominal Imaging in MDCT Since its clinical introduction in 1989, volumetric CT scanning has resulted in a revolution in diagnostic imaging. Spiral CT has improved over the last few years, with faster gantry rotation, more powerful X-ray tubes, and improved interpolation algorithms, but the greates ...
New Technologies in 3D Conformal Radiation Therapy: Introduction
... The best way of determining the PTV and OAR is on the basis of multiple-modality 3D image data sets such as X-ray computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance (MRI and MRS), and PET. Routinely, Xray CT is the most common tomographic imaging method (see Chaps. 7–8, 13). The registration of all these ...
... The best way of determining the PTV and OAR is on the basis of multiple-modality 3D image data sets such as X-ray computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance (MRI and MRS), and PET. Routinely, Xray CT is the most common tomographic imaging method (see Chaps. 7–8, 13). The registration of all these ...
syngo Workplaces
... Manual interruption possible once desired anatomy has been imaged CARE Dose4D – minimizing dose, maximizing quality – patient by patient Automated real-time tube current adjustment for best diagnostic image quality at lowest possible dose, independent of patient size and anatomy Fully automated dose ...
... Manual interruption possible once desired anatomy has been imaged CARE Dose4D – minimizing dose, maximizing quality – patient by patient Automated real-time tube current adjustment for best diagnostic image quality at lowest possible dose, independent of patient size and anatomy Fully automated dose ...
Characterization of Metabolic Differences between Benign and
... Network for Translational Research in Optical Imaging grants (nos. U54-CA105480-01 and U54-CA136400), a UCI Cancer Center grant (no. P30-CA62203), a Laser Microbeam and Medical Program grant (no. P41-RR01192), and a National Institutes of Health Laboratory for Fluorescence ...
... Network for Translational Research in Optical Imaging grants (nos. U54-CA105480-01 and U54-CA136400), a UCI Cancer Center grant (no. P30-CA62203), a Laser Microbeam and Medical Program grant (no. P41-RR01192), and a National Institutes of Health Laboratory for Fluorescence ...
Ultrasonic and X-ray Tomographic Imaging of Highly Contrasting
... microstructure characterization of concrete usually have a large penetrating capability and high resolution up to 5-10 micrometers. Compared with other imaging methods, XCT has several advantages including the ability to acquire 3D data set, no need for sample preparation, and non-destruction to sui ...
... microstructure characterization of concrete usually have a large penetrating capability and high resolution up to 5-10 micrometers. Compared with other imaging methods, XCT has several advantages including the ability to acquire 3D data set, no need for sample preparation, and non-destruction to sui ...
Procedure Guideline for Tumor Imaging with 18F
... PET is a tomographic scintigraphic technique in which a computer-generated image of local radioactive tracer distribution in tissues is produced through the detection of annihilation photons that are emitted when radionuclides introduced into the body decay and release positrons. 18FFDG PET is a tom ...
... PET is a tomographic scintigraphic technique in which a computer-generated image of local radioactive tracer distribution in tissues is produced through the detection of annihilation photons that are emitted when radionuclides introduced into the body decay and release positrons. 18FFDG PET is a tom ...
Funding the Future The Kay
... Pam Goldblatt, BS, RT(R)(M) joined the Crawford Long Hospital Breast with Emory for 4 years in the Breast Imaging Center and has 22 years Center in 2003 with 10 years of experience. experience as a technologist. Ann West, RT(R)(M) has a total of 36 years as a registered technologist. She Susan W. Ho ...
... Pam Goldblatt, BS, RT(R)(M) joined the Crawford Long Hospital Breast with Emory for 4 years in the Breast Imaging Center and has 22 years Center in 2003 with 10 years of experience. experience as a technologist. Ann West, RT(R)(M) has a total of 36 years as a registered technologist. She Susan W. Ho ...
Cone Beam Computed Tomography in Endodontics: An Overview.
... region is complicated due to the complex anatomy and the varying radio density of the tissues. The classic 2 dimensional radiographic technique do provide an excellent representation of the tissues, but are limited in differentiating superimposing structures. This drawback has been be overcome by Co ...
... region is complicated due to the complex anatomy and the varying radio density of the tissues. The classic 2 dimensional radiographic technique do provide an excellent representation of the tissues, but are limited in differentiating superimposing structures. This drawback has been be overcome by Co ...
this PDF file - Jurnal Teknologi
... emits energy at the resonance frequency of the nuclei, the RF excitation irritates the nuclei’s net magnetization vector (NMV) to flip. When the RF pulse is turn off, the NMV returns to the original axes and releases high energy excess in the form of waves and induces a current in the receiver coil. ...
... emits energy at the resonance frequency of the nuclei, the RF excitation irritates the nuclei’s net magnetization vector (NMV) to flip. When the RF pulse is turn off, the NMV returns to the original axes and releases high energy excess in the form of waves and induces a current in the receiver coil. ...
seven things to know about radioisotopes
... therapeutic doses of radioisotopes (these are only used for cancer treatment and other kinds of therapy, never for diagnosis) are kept isolated in their hospital rooms until the patient’s exposure to the worker and public is reduced to a safe level. The nurses, doctors and porters charged with their ...
... therapeutic doses of radioisotopes (these are only used for cancer treatment and other kinds of therapy, never for diagnosis) are kept isolated in their hospital rooms until the patient’s exposure to the worker and public is reduced to a safe level. The nurses, doctors and porters charged with their ...
Philips SPECT/CT Systems
... Image Quality and Acquisition Speed Astonish provides constant image quality with wide range of count statistics 5 Observers: A relative image quality (RIQ) score with respect to a standard image (64x64x64 matrix, clinical counts, FBP reconstruction) was assigned to each image by each observer (3: ...
... Image Quality and Acquisition Speed Astonish provides constant image quality with wide range of count statistics 5 Observers: A relative image quality (RIQ) score with respect to a standard image (64x64x64 matrix, clinical counts, FBP reconstruction) was assigned to each image by each observer (3: ...
MR Imaging of Scrotal Tumors and Pseudotumors1
... axial fat-suppressed T1-weighted images are obtained. High-resolution dual-echo (in-phase and out-of-phase) axial T1-weighted spoiled gradient-echo sequences are also used to identify fat-water admixtures. These sequences also help to depict hemorrhage because hemosiderin will be most conspicuous on ...
... axial fat-suppressed T1-weighted images are obtained. High-resolution dual-echo (in-phase and out-of-phase) axial T1-weighted spoiled gradient-echo sequences are also used to identify fat-water admixtures. These sequences also help to depict hemorrhage because hemosiderin will be most conspicuous on ...
Pre-print
... Dynamic MRI requires rapid data acquisition to provide an appropriate combination of spatial resolution, temporal resolution, and volumetric coverage for clinical studies. For example, rapid imaging speed is needed for dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE) examinations, in which fast signal-intensity chan ...
... Dynamic MRI requires rapid data acquisition to provide an appropriate combination of spatial resolution, temporal resolution, and volumetric coverage for clinical studies. For example, rapid imaging speed is needed for dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE) examinations, in which fast signal-intensity chan ...
DOC - Investor Relations
... were up 1.4% over the fourth quarter of 2010. However, TechneLite sales have not returned to pre-shortage levels due to a number of reasons including — first of all, change in staffing and utilization practices which allow radiopharmacies to prepare more unit doses of Technetium-based radiopharmaceu ...
... were up 1.4% over the fourth quarter of 2010. However, TechneLite sales have not returned to pre-shortage levels due to a number of reasons including — first of all, change in staffing and utilization practices which allow radiopharmacies to prepare more unit doses of Technetium-based radiopharmaceu ...
Medical imaging

Medical imaging is the technique and process of creating visual representations of the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention. Medical imaging seeks to reveal internal structures hidden by the skin and bones, as well as to diagnose and treat disease. Medical imaging also establishes a database of normal anatomy and physiology to make it possible to identify abnormalities. Although imaging of removed organs and tissues can be performed for medical reasons, such procedures are usually considered part of pathology instead of medical imaging.As a discipline and in its widest sense, it is part of biological imaging and incorporates radiology which uses the imaging technologies of X-ray radiography, magnetic resonance imaging, medical ultrasonography or ultrasound, endoscopy, elastography, tactile imaging, thermography, medical photography and nuclear medicine functional imaging techniques as positron emission tomography.Measurement and recording techniques which are not primarily designed to produce images, such as electroencephalography (EEG), magnetoencephalography (MEG), electrocardiography (ECG), and others represent other technologies which produce data susceptible to representation as a parameter graph vs. time or maps which contain information about the measurement locations. In a limited comparison these technologies can be considered as forms of medical imaging in another discipline.Up until 2010, 5 billion medical imaging studies had been conducted worldwide. Radiation exposure from medical imaging in 2006 made up about 50% of total ionizing radiation exposure in the United States.In the clinical context, ""invisible light"" medical imaging is generally equated to radiology or ""clinical imaging"" and the medical practitioner responsible for interpreting (and sometimes acquiring) the images is a radiologist. ""Visible light"" medical imaging involves digital video or still pictures that can be seen without special equipment. Dermatology and wound care are two modalities that use visible light imagery. Diagnostic radiography designates the technical aspects of medical imaging and in particular the acquisition of medical images. The radiographer or radiologic technologist is usually responsible for acquiring medical images of diagnostic quality, although some radiological interventions are performed by radiologists.As a field of scientific investigation, medical imaging constitutes a sub-discipline of biomedical engineering, medical physics or medicine depending on the context: Research and development in the area of instrumentation, image acquisition (e.g. radiography), modeling and quantification are usually the preserve of biomedical engineering, medical physics, and computer science; Research into the application and interpretation of medical images is usually the preserve of radiology and the medical sub-discipline relevant to medical condition or area of medical science (neuroscience, cardiology, psychiatry, psychology, etc.) under investigation. Many of the techniques developed for medical imaging also have scientific and industrial applications.Medical imaging is often perceived to designate the set of techniques that noninvasively produce images of the internal aspect of the body. In this restricted sense, medical imaging can be seen as the solution of mathematical inverse problems. This means that cause (the properties of living tissue) is inferred from effect (the observed signal). In the case of medical ultrasonography, the probe consists of ultrasonic pressure waves and echoes that go inside the tissue to show the internal structure. In the case of projectional radiography, the probe uses X-ray radiation, which is absorbed at different rates by different tissue types such as bone, muscle and fat.The term noninvasive is used to denote a procedure where no instrument is introduced into a patient's body which is the case for most imaging techniques used.