From 3-D Positron Emission Tomography to 3
... PET was originally conceived in the 1950s as a 3D imaging modality with the physical collimation of conventional single-photon emitters replaced by the electronic collimation of coincidence imaging. However, concerns over the high level of scattered photons and the perceived absence of an effective ...
... PET was originally conceived in the 1950s as a 3D imaging modality with the physical collimation of conventional single-photon emitters replaced by the electronic collimation of coincidence imaging. However, concerns over the high level of scattered photons and the perceived absence of an effective ...
From 3-D Positron Emission Tomography to 3
... PET was originally conceived in the 1950s as a 3D imaging modality with the physical collimation of conventional single-photon emitters replaced by the electronic collimation of coincidence imaging. However, concerns over the high level of scattered photons and the perceived absence of an effective ...
... PET was originally conceived in the 1950s as a 3D imaging modality with the physical collimation of conventional single-photon emitters replaced by the electronic collimation of coincidence imaging. However, concerns over the high level of scattered photons and the perceived absence of an effective ...
MRI Visiting Fellowship 15-16.pub
... techniques and developments must be applied in the current clinical practice of the radiologist and the attendees must make these changes in order to maintain certification. The Radiology observership program incorporates our current practice which is ever changing and based upon the latest imaging ...
... techniques and developments must be applied in the current clinical practice of the radiologist and the attendees must make these changes in order to maintain certification. The Radiology observership program incorporates our current practice which is ever changing and based upon the latest imaging ...
Tomotherapy: A "Revolution" in Radiation Therapy
... verification and actual radiation dose delivery. Patients who are treated for cure receive high radiation doses of 60 to 70 Gy, given in 30 to 40 daily fractions at the rate of 5 fractions per week. There are several critical steps in this process. One of these is the use of sophisticated 3-D imagin ...
... verification and actual radiation dose delivery. Patients who are treated for cure receive high radiation doses of 60 to 70 Gy, given in 30 to 40 daily fractions at the rate of 5 fractions per week. There are several critical steps in this process. One of these is the use of sophisticated 3-D imagin ...
A Report of the American Society of Nuclear Cardiology Task Force
... diagnostic accuracy of the most commonly used noninvasive tests. Since the 1990 congressional mandate that women be included in all federally funded cardiovascular trials, a growing body of data continues to support the fact that diagnostic accuracy of noninvasive cardiac tests is different in women ...
... diagnostic accuracy of the most commonly used noninvasive tests. Since the 1990 congressional mandate that women be included in all federally funded cardiovascular trials, a growing body of data continues to support the fact that diagnostic accuracy of noninvasive cardiac tests is different in women ...
PDF - Medical Journal of Australia
... the clinical efficacy of the procedure in the Australian context. Although restricted to specific indications and to eight PET machines, this federal funding does provide greater public access and clinical exposure to the technique. Despite the proven benefits of FDG-PET, imaging is a lengthy proces ...
... the clinical efficacy of the procedure in the Australian context. Although restricted to specific indications and to eight PET machines, this federal funding does provide greater public access and clinical exposure to the technique. Despite the proven benefits of FDG-PET, imaging is a lengthy proces ...
Paper - Columbia CS
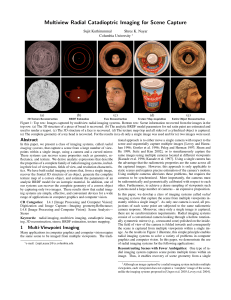
... correspond to different viewing directions for a single lighting condition. We show that one of our radial imaging systems achieves the same goal. It should be noted that a dense sampling of viewing directions is needed to characterize the appearance of specular materials. Our system uses multiple r ...
... correspond to different viewing directions for a single lighting condition. We show that one of our radial imaging systems achieves the same goal. It should be noted that a dense sampling of viewing directions is needed to characterize the appearance of specular materials. Our system uses multiple r ...
Does DICOM work with other standards-development
... Physicians have better access to images and reports when DICOM standards are in place. This allows them to make a faster diagnosis, potentially from anywhere in the world. ...
... Physicians have better access to images and reports when DICOM standards are in place. This allows them to make a faster diagnosis, potentially from anywhere in the world. ...
Isolated Right Sided Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Connection
... atrium (RA) or the innominate vein. Common congenital heart diseases associated with PAPVC include sinus venosus and secundum type atrial septal defects while PAPVC is rarely seen alone. On physical examination, patients with PAPVC may present with an elevated JVP, parasternal lift due to RV enlarge ...
... atrium (RA) or the innominate vein. Common congenital heart diseases associated with PAPVC include sinus venosus and secundum type atrial septal defects while PAPVC is rarely seen alone. On physical examination, patients with PAPVC may present with an elevated JVP, parasternal lift due to RV enlarge ...
Quantifying spatial heterogeneity in dynamic contrast
... IAUC) at each tumour voxel. The tumour may then be summarised as a whole by computing an average value of the chosen parameter. A change in such a summary statistic (such as mean or median values) after drug administration may be used as evidence of drug action. A problem with this approach is that ...
... IAUC) at each tumour voxel. The tumour may then be summarised as a whole by computing an average value of the chosen parameter. A change in such a summary statistic (such as mean or median values) after drug administration may be used as evidence of drug action. A problem with this approach is that ...
Medical X-ray Facility License Application Form
... Certificate of training of the radiologic/x-ray technologist in radiation protection if he/she acts as the radiation protection officer. Certificate of training of the head of the facility in radiology if he is not a FPCR/DPBR for government facilities and in areas with no FPCR/DPBR within 45 km vic ...
... Certificate of training of the radiologic/x-ray technologist in radiation protection if he/she acts as the radiation protection officer. Certificate of training of the head of the facility in radiology if he is not a FPCR/DPBR for government facilities and in areas with no FPCR/DPBR within 45 km vic ...
22 Myocardial Perfusion Imaging with PET, PET/CT, PET/MRI
... reaching their respective detectors 180 degrees apart.3,32 The coincidence electronics in the new advanced PET scanners with TOF electronics are capable of measuring the exact time interval between the two annihilation photons reaching the opposing detectors. The exact location of the annihilation i ...
... reaching their respective detectors 180 degrees apart.3,32 The coincidence electronics in the new advanced PET scanners with TOF electronics are capable of measuring the exact time interval between the two annihilation photons reaching the opposing detectors. The exact location of the annihilation i ...
PET vs. SPECT: in the Context of Ongoing Developments (Review
... This paper intends to compare the abilities of the two major imaging modalities in nuclear medicine imaging: Positron Emission Tomography (PET) and Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT). The motivations are many-fold: (i) To gain a better understanding of the strengths and limitations o ...
... This paper intends to compare the abilities of the two major imaging modalities in nuclear medicine imaging: Positron Emission Tomography (PET) and Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT). The motivations are many-fold: (i) To gain a better understanding of the strengths and limitations o ...
Evolution for Bone
... has been achieved in the development of model-based corrective SPECT image reconstruction methods that include correction for these image quality-degrading factors. The corrective image reconstruction package (also referred to as Resolution Recovery) developed by JHU group provides improved SPECT im ...
... has been achieved in the development of model-based corrective SPECT image reconstruction methods that include correction for these image quality-degrading factors. The corrective image reconstruction package (also referred to as Resolution Recovery) developed by JHU group provides improved SPECT im ...
REVIEWS - Max Planck Institute for Biological Cybernetics
... importance in diagnostic medicine and more recently in basic research. In medicine, MRI is primarily used to produce structural images of organs, including the central nervous system, but it can also provide information on the physico-chemical state of tissues, their vascularization, and perfusion. ...
... importance in diagnostic medicine and more recently in basic research. In medicine, MRI is primarily used to produce structural images of organs, including the central nervous system, but it can also provide information on the physico-chemical state of tissues, their vascularization, and perfusion. ...
Diffuse optical tomography of breast cancer during
... neoadjuvant chemotherapy in a breast cancer patient. This important paper introduced a new clinical application to the field. However, quantification of breast cancer properties from spectroscopic data alone requires assumptions about tissues 共e.g., homogeneous media, etc.兲 which are often questiona ...
... neoadjuvant chemotherapy in a breast cancer patient. This important paper introduced a new clinical application to the field. However, quantification of breast cancer properties from spectroscopic data alone requires assumptions about tissues 共e.g., homogeneous media, etc.兲 which are often questiona ...
Walter et al. (2007) Radiotherapy and Oncology 85
... tissue can be achieved by using photons of lower energy, for example with an X-ray source inside the treatment room emitting photons with a maximum energy of 80–140 keV. While these devices provide images of the bony anatomy with better quality than MV PI can offer, soft tissue information is still ...
... tissue can be achieved by using photons of lower energy, for example with an X-ray source inside the treatment room emitting photons with a maximum energy of 80–140 keV. While these devices provide images of the bony anatomy with better quality than MV PI can offer, soft tissue information is still ...
Why Currently Used Diagnostic Techniques for Heart
... they cannot completely explain the excess CV morbidity and mortality.11 They do contribute, but in a different way or to a lesser extent in comparison with other individuals. For example, adjustment for classic ...
... they cannot completely explain the excess CV morbidity and mortality.11 They do contribute, but in a different way or to a lesser extent in comparison with other individuals. For example, adjustment for classic ...
- Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention
... Metastasis of the liver is sometimes difficult to detect by unenhanced CT or FDG-PET. However, DWI was very useful in the detection of liver metastasis, which had distinguishable decreased diffusion different from benign lesions. It has been reported that MRI has an extremely high degree of sensitiv ...
... Metastasis of the liver is sometimes difficult to detect by unenhanced CT or FDG-PET. However, DWI was very useful in the detection of liver metastasis, which had distinguishable decreased diffusion different from benign lesions. It has been reported that MRI has an extremely high degree of sensitiv ...
- KoreaMed Synapse
... Panoramic radiography was the way to discover the occult pericoronal lesions in the present case as well as the determination of their extension, shape and periphery, size, number, and effects on surrounding structures.25 Although the information acquired from the panoramic radiograph about the inte ...
... Panoramic radiography was the way to discover the occult pericoronal lesions in the present case as well as the determination of their extension, shape and periphery, size, number, and effects on surrounding structures.25 Although the information acquired from the panoramic radiograph about the inte ...
Professional capabilities for medical radiation practice
... Accreditation Committee will consult on the Accreditation standard and an Accreditation process in the middle of the year. The Professional capabilities for medical radiation practice will underpin both the Supervised practice guidelines and the Medical Radiation Practice Accreditation standard. Fee ...
... Accreditation Committee will consult on the Accreditation standard and an Accreditation process in the middle of the year. The Professional capabilities for medical radiation practice will underpin both the Supervised practice guidelines and the Medical Radiation Practice Accreditation standard. Fee ...
Chapter 12: 3D medical Informatics
... distinctive about the architecture of the tissue that he is viewing, but what he is seeing is beyond his experience. He calls a colleague and she places the sample in a 3D confocal microscope to acquire a digital volume image of the sample. Together, they perform some simple computer operations on t ...
... distinctive about the architecture of the tissue that he is viewing, but what he is seeing is beyond his experience. He calls a colleague and she places the sample in a 3D confocal microscope to acquire a digital volume image of the sample. Together, they perform some simple computer operations on t ...
Cancer Imaging With Fluorine-18–Labeled Choline Derivatives
... derivative is most advantageous for clinical use. There have been no direct in vivo comparisons between individual compounds, and previous in vitro comparisons have not controlled for potentially confounding factors, including the presence of synthetic contaminants such as dimethylethanolamine, whic ...
... derivative is most advantageous for clinical use. There have been no direct in vivo comparisons between individual compounds, and previous in vitro comparisons have not controlled for potentially confounding factors, including the presence of synthetic contaminants such as dimethylethanolamine, whic ...
Developing a quality control program for digital mammography
... be necessary, however, on the basis of experience, to validate these tests in terms of their sensitivity and relevance in predicting failures. In addition to the purpose of QC, testing of equipment is carried out when the imaging equipment is installed or commissioned. In this case, a more comprehen ...
... be necessary, however, on the basis of experience, to validate these tests in terms of their sensitivity and relevance in predicting failures. In addition to the purpose of QC, testing of equipment is carried out when the imaging equipment is installed or commissioned. In this case, a more comprehen ...
Professional capabilities for medical radiation practice
... Accreditation Committee will consult on the Accreditation standard and an Accreditation process in the middle of the year. The Professional capabilities for medical radiation practice will underpin both the Supervised practice guidelines and the Medical Radiation Practice Accreditation standard. Fee ...
... Accreditation Committee will consult on the Accreditation standard and an Accreditation process in the middle of the year. The Professional capabilities for medical radiation practice will underpin both the Supervised practice guidelines and the Medical Radiation Practice Accreditation standard. Fee ...
Medical imaging

Medical imaging is the technique and process of creating visual representations of the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention. Medical imaging seeks to reveal internal structures hidden by the skin and bones, as well as to diagnose and treat disease. Medical imaging also establishes a database of normal anatomy and physiology to make it possible to identify abnormalities. Although imaging of removed organs and tissues can be performed for medical reasons, such procedures are usually considered part of pathology instead of medical imaging.As a discipline and in its widest sense, it is part of biological imaging and incorporates radiology which uses the imaging technologies of X-ray radiography, magnetic resonance imaging, medical ultrasonography or ultrasound, endoscopy, elastography, tactile imaging, thermography, medical photography and nuclear medicine functional imaging techniques as positron emission tomography.Measurement and recording techniques which are not primarily designed to produce images, such as electroencephalography (EEG), magnetoencephalography (MEG), electrocardiography (ECG), and others represent other technologies which produce data susceptible to representation as a parameter graph vs. time or maps which contain information about the measurement locations. In a limited comparison these technologies can be considered as forms of medical imaging in another discipline.Up until 2010, 5 billion medical imaging studies had been conducted worldwide. Radiation exposure from medical imaging in 2006 made up about 50% of total ionizing radiation exposure in the United States.In the clinical context, ""invisible light"" medical imaging is generally equated to radiology or ""clinical imaging"" and the medical practitioner responsible for interpreting (and sometimes acquiring) the images is a radiologist. ""Visible light"" medical imaging involves digital video or still pictures that can be seen without special equipment. Dermatology and wound care are two modalities that use visible light imagery. Diagnostic radiography designates the technical aspects of medical imaging and in particular the acquisition of medical images. The radiographer or radiologic technologist is usually responsible for acquiring medical images of diagnostic quality, although some radiological interventions are performed by radiologists.As a field of scientific investigation, medical imaging constitutes a sub-discipline of biomedical engineering, medical physics or medicine depending on the context: Research and development in the area of instrumentation, image acquisition (e.g. radiography), modeling and quantification are usually the preserve of biomedical engineering, medical physics, and computer science; Research into the application and interpretation of medical images is usually the preserve of radiology and the medical sub-discipline relevant to medical condition or area of medical science (neuroscience, cardiology, psychiatry, psychology, etc.) under investigation. Many of the techniques developed for medical imaging also have scientific and industrial applications.Medical imaging is often perceived to designate the set of techniques that noninvasively produce images of the internal aspect of the body. In this restricted sense, medical imaging can be seen as the solution of mathematical inverse problems. This means that cause (the properties of living tissue) is inferred from effect (the observed signal). In the case of medical ultrasonography, the probe consists of ultrasonic pressure waves and echoes that go inside the tissue to show the internal structure. In the case of projectional radiography, the probe uses X-ray radiation, which is absorbed at different rates by different tissue types such as bone, muscle and fat.The term noninvasive is used to denote a procedure where no instrument is introduced into a patient's body which is the case for most imaging techniques used.