CARESTREAM OnSight 3D Extremity System
... Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) and American College of Radiology (ACR). "Radiation Dose in X-Ray and CT Exams." Patient Safety. N.p., n.d. Web. 29 Nov. 2016. Curvebm. "Weight Bearing CT Archives - CurveBeam." CurveBeam. N.p., n.d. Web. 29 Nov. 2016. "What Is a CT Scan (CAT Scan)? Defin ...
... Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) and American College of Radiology (ACR). "Radiation Dose in X-Ray and CT Exams." Patient Safety. N.p., n.d. Web. 29 Nov. 2016. Curvebm. "Weight Bearing CT Archives - CurveBeam." CurveBeam. N.p., n.d. Web. 29 Nov. 2016. "What Is a CT Scan (CAT Scan)? Defin ...
X-Ray Optics Development for Biomedical Imaging Applications at
... Given the energy range covered and the spatially dispersed energies measured, a multiple energy algorithm [10] was implemented to extract composition information from the energies. This method fully accounts for the energy dependent shape of the absorption of materials. An example of the use of this ...
... Given the energy range covered and the spatially dispersed energies measured, a multiple energy algorithm [10] was implemented to extract composition information from the energies. This method fully accounts for the energy dependent shape of the absorption of materials. An example of the use of this ...
the First Positron Emission tomography–Magnetic Resonance
... S Ka, G Lo, V Ai, et al Table. Magnetic resonance imaging protocols and their sequence parameters. ...
... S Ka, G Lo, V Ai, et al Table. Magnetic resonance imaging protocols and their sequence parameters. ...
WHOLE-BODY IMAGING WITH PET/MRI
... plays an important role in the diagnosis and management of patients with cancer. PET facilitates the evaluation of metabolic and molecular characteristics of a wide variety of cancers, but it is limited in its ability to visualize anatomical structures. Whole-body magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is ...
... plays an important role in the diagnosis and management of patients with cancer. PET facilitates the evaluation of metabolic and molecular characteristics of a wide variety of cancers, but it is limited in its ability to visualize anatomical structures. Whole-body magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is ...
Modern physics concepts The Photon Concept
... provide a very good image of soft tissue • CAT scans expose the patient to a large dose of x-rays, which can have long term side effects it is an invasive diagnostic • Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) can provide high resolution images of soft tissue inside a body, and does not use any ionizing ra ...
... provide a very good image of soft tissue • CAT scans expose the patient to a large dose of x-rays, which can have long term side effects it is an invasive diagnostic • Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) can provide high resolution images of soft tissue inside a body, and does not use any ionizing ra ...
X-Rays - LSU School of Medicine
... sterility. Also referred to as “non-stochastic” effects The effect may (potentially) occur following any amount of exposure – there is no threshold. Examples include cancer and genetic defects. ...
... sterility. Also referred to as “non-stochastic” effects The effect may (potentially) occur following any amount of exposure – there is no threshold. Examples include cancer and genetic defects. ...
Junior Radiology
... sterility. Also referred to as “non-stochastic” effects The effect may (potentially) occur following any amount of exposure – there is no threshold. Examples include cancer and genetic defects. ...
... sterility. Also referred to as “non-stochastic” effects The effect may (potentially) occur following any amount of exposure – there is no threshold. Examples include cancer and genetic defects. ...
PDF - Affiliates in Imaging
... colon cancer screenings, screening for vitamin deficiencies during pregnancy, screenings for diabetes, high cholesterol, high blood pressure and tobacco cessation counseling will be covered under these rules along with standard vaccines and immunizations. Plans are also allowed to use reasonable med ...
... colon cancer screenings, screening for vitamin deficiencies during pregnancy, screenings for diabetes, high cholesterol, high blood pressure and tobacco cessation counseling will be covered under these rules along with standard vaccines and immunizations. Plans are also allowed to use reasonable med ...
Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) and Magnetic
... Imaging of the vasculature system using MRI techniques Can be 3-D No contrast required ...
... Imaging of the vasculature system using MRI techniques Can be 3-D No contrast required ...
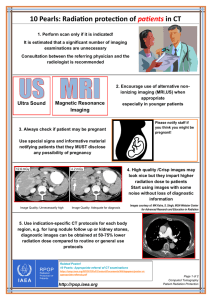
10 Pearls: Radiation protection of patients in CT - RPOP
... 3. Always check if patient may be pregnant Use special signs and informative material notifying patients that they MUST disclose any possibility of pregnancy ...
... 3. Always check if patient may be pregnant Use special signs and informative material notifying patients that they MUST disclose any possibility of pregnancy ...
Clinical Performance of a Spatiotemporally Accelerated Motion
... injection. The acquisition parameters were: TE 1.2-1.4 ms, TR 3.0-3.4 ms, bandwidth 100 kHz, slice thickness 1.0-2.4 mm, and S/I FOV 26-38 cm. The average acquisition time for each temporal phase was 8.5 s (range: 5.5-14.1 s). All imaging was performed completely free-breathing. Single dose contrast ...
... injection. The acquisition parameters were: TE 1.2-1.4 ms, TR 3.0-3.4 ms, bandwidth 100 kHz, slice thickness 1.0-2.4 mm, and S/I FOV 26-38 cm. The average acquisition time for each temporal phase was 8.5 s (range: 5.5-14.1 s). All imaging was performed completely free-breathing. Single dose contrast ...
Strategic Imaging Service Review
... Clinical Radiology is a core component of modern healthcare. Imaging services have become critical in improving patient outcomes and accordingly have ...
... Clinical Radiology is a core component of modern healthcare. Imaging services have become critical in improving patient outcomes and accordingly have ...
L34.ppt - University of Iowa Physics
... images taken at many different angles and positions • an x-ray source and an array of electronic detectors rotates around the patient as the patient slowly moves through the ring. ...
... images taken at many different angles and positions • an x-ray source and an array of electronic detectors rotates around the patient as the patient slowly moves through the ring. ...
Are you looking for a career in healthcare as a MRI Technologist that
... We offer a competitive benefit package that includes three comprehensive health plan design options, flexible spending plan, voluntary short-term disability, employer-paid long-term disability, voluntary long term care, employee assistance program, tuition assistance, and more! We also offer up to 2 ...
... We offer a competitive benefit package that includes three comprehensive health plan design options, flexible spending plan, voluntary short-term disability, employer-paid long-term disability, voluntary long term care, employee assistance program, tuition assistance, and more! We also offer up to 2 ...
X-RAY - lucascarter
... X-rays reveal structural information about the material through which it passes or falls over. It can therefore be used to detect structural deficits or cracks in metal objects that are likely to be missed by the human eye. It is also used to reveal stress related changes in building materials for b ...
... X-rays reveal structural information about the material through which it passes or falls over. It can therefore be used to detect structural deficits or cracks in metal objects that are likely to be missed by the human eye. It is also used to reveal stress related changes in building materials for b ...
RADIOLOGICAL PHYSICS CENTER
... IGRT is defined here to include only those procedures where imaging is used in combination with computer-assisted manual or automatic registration with the planning-CT image. Use of MV EPID or film images as a visual comparison to DRRs does not meet this definition. ...
... IGRT is defined here to include only those procedures where imaging is used in combination with computer-assisted manual or automatic registration with the planning-CT image. Use of MV EPID or film images as a visual comparison to DRRs does not meet this definition. ...
Algoritmo propuesto para el diagnóstico por imagen del
... Multiple Myeloma: A Consensus Statement. MA. Dimopoulos, J. Hillengass, S. Usmani, E. Zamagni, et al. • Purpose The aim of International Myeloma Working Group was to develop practical recommendations for the use of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in multiple myeloma (MM). • Methods An interdiscipli ...
... Multiple Myeloma: A Consensus Statement. MA. Dimopoulos, J. Hillengass, S. Usmani, E. Zamagni, et al. • Purpose The aim of International Myeloma Working Group was to develop practical recommendations for the use of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in multiple myeloma (MM). • Methods An interdiscipli ...
Novel Technologies in Radiotherapy: Protons and Magnetic
... – Restoration of the precession of the nuclei in the static B field ...
... – Restoration of the precession of the nuclei in the static B field ...
L34.ppt - University of Iowa Physics
... images taken at many different angles and positions • an x-ray source and an array of electronic detectors rotates around the patient as the patient slowly moves through the ring. ...
... images taken at many different angles and positions • an x-ray source and an array of electronic detectors rotates around the patient as the patient slowly moves through the ring. ...
Phase Contrast Mammography System REGIUS MODEL 190
... Radiology Information System Digital Color Printer LD-5100 The report integration-type picture archiving communication system (PACS) and radiology information system (RIS) realize the integration of image information and medical charts. ...
... Radiology Information System Digital Color Printer LD-5100 The report integration-type picture archiving communication system (PACS) and radiology information system (RIS) realize the integration of image information and medical charts. ...
medical imaging and radiation sciences
... The Bachelor of Science Degree in Medical Imaging is designed to give students the skills needed to become tomorrow’s leaders in the field of medical imaging. Through preparation for more advanced work in specialty areas such as computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MR), quality mana ...
... The Bachelor of Science Degree in Medical Imaging is designed to give students the skills needed to become tomorrow’s leaders in the field of medical imaging. Through preparation for more advanced work in specialty areas such as computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MR), quality mana ...
Medical imaging

Medical imaging is the technique and process of creating visual representations of the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention. Medical imaging seeks to reveal internal structures hidden by the skin and bones, as well as to diagnose and treat disease. Medical imaging also establishes a database of normal anatomy and physiology to make it possible to identify abnormalities. Although imaging of removed organs and tissues can be performed for medical reasons, such procedures are usually considered part of pathology instead of medical imaging.As a discipline and in its widest sense, it is part of biological imaging and incorporates radiology which uses the imaging technologies of X-ray radiography, magnetic resonance imaging, medical ultrasonography or ultrasound, endoscopy, elastography, tactile imaging, thermography, medical photography and nuclear medicine functional imaging techniques as positron emission tomography.Measurement and recording techniques which are not primarily designed to produce images, such as electroencephalography (EEG), magnetoencephalography (MEG), electrocardiography (ECG), and others represent other technologies which produce data susceptible to representation as a parameter graph vs. time or maps which contain information about the measurement locations. In a limited comparison these technologies can be considered as forms of medical imaging in another discipline.Up until 2010, 5 billion medical imaging studies had been conducted worldwide. Radiation exposure from medical imaging in 2006 made up about 50% of total ionizing radiation exposure in the United States.In the clinical context, ""invisible light"" medical imaging is generally equated to radiology or ""clinical imaging"" and the medical practitioner responsible for interpreting (and sometimes acquiring) the images is a radiologist. ""Visible light"" medical imaging involves digital video or still pictures that can be seen without special equipment. Dermatology and wound care are two modalities that use visible light imagery. Diagnostic radiography designates the technical aspects of medical imaging and in particular the acquisition of medical images. The radiographer or radiologic technologist is usually responsible for acquiring medical images of diagnostic quality, although some radiological interventions are performed by radiologists.As a field of scientific investigation, medical imaging constitutes a sub-discipline of biomedical engineering, medical physics or medicine depending on the context: Research and development in the area of instrumentation, image acquisition (e.g. radiography), modeling and quantification are usually the preserve of biomedical engineering, medical physics, and computer science; Research into the application and interpretation of medical images is usually the preserve of radiology and the medical sub-discipline relevant to medical condition or area of medical science (neuroscience, cardiology, psychiatry, psychology, etc.) under investigation. Many of the techniques developed for medical imaging also have scientific and industrial applications.Medical imaging is often perceived to designate the set of techniques that noninvasively produce images of the internal aspect of the body. In this restricted sense, medical imaging can be seen as the solution of mathematical inverse problems. This means that cause (the properties of living tissue) is inferred from effect (the observed signal). In the case of medical ultrasonography, the probe consists of ultrasonic pressure waves and echoes that go inside the tissue to show the internal structure. In the case of projectional radiography, the probe uses X-ray radiation, which is absorbed at different rates by different tissue types such as bone, muscle and fat.The term noninvasive is used to denote a procedure where no instrument is introduced into a patient's body which is the case for most imaging techniques used.