Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Tractography Technical Considerations
... reduced, including motion between acquisitions with different orientations of the diffusion-sensitizing gradients. Another advantage of SS-EPI is its relatively high SNR per unit of scanning time. This is particularly important for DWI because diffusion gradients at high b-values cause considerable ...
... reduced, including motion between acquisitions with different orientations of the diffusion-sensitizing gradients. Another advantage of SS-EPI is its relatively high SNR per unit of scanning time. This is particularly important for DWI because diffusion gradients at high b-values cause considerable ...
Title Spatial resolution measurement for iterative
... and image data domains, while spatial resolution and structural edges are preserved and even improved [9]. In addition, AIDR 3D has four strengths of noise reduction levels (weak, mild, standard, and strong). All data acquisitions were performed with a non-helical scan mode, which was used routinely ...
... and image data domains, while spatial resolution and structural edges are preserved and even improved [9]. In addition, AIDR 3D has four strengths of noise reduction levels (weak, mild, standard, and strong). All data acquisitions were performed with a non-helical scan mode, which was used routinely ...
190047_190047 - espace@Curtin
... covering a range of anatomic locations involving radiosensitive organs and (iii) facilitate comparison with published protocols and diagnostic reference levels. Specific clinical indications were included ...
... covering a range of anatomic locations involving radiosensitive organs and (iii) facilitate comparison with published protocols and diagnostic reference levels. Specific clinical indications were included ...
Multiple Kernel Learning Approach For Medical Image
... modality for studying internal structures of the human body. An x-ray sensitive film or a digital detector is placed behind the patient to capture the x-rays as they are passed through the patient’s body. Different tissues within the body show varying absorption levels of x-rays, e.g., dense bones a ...
... modality for studying internal structures of the human body. An x-ray sensitive film or a digital detector is placed behind the patient to capture the x-rays as they are passed through the patient’s body. Different tissues within the body show varying absorption levels of x-rays, e.g., dense bones a ...
Document
... For homogeneous media, the Fourier Diffraction Theorem is analogous to the central-slice theorem of x-ray CT Heterogeneous media are treated as (we hope) small perturbations of a homogeneous medium, to which an assumption such as the Born approximation or Rytov approximation can be applied BMI I FS0 ...
... For homogeneous media, the Fourier Diffraction Theorem is analogous to the central-slice theorem of x-ray CT Heterogeneous media are treated as (we hope) small perturbations of a homogeneous medium, to which an assumption such as the Born approximation or Rytov approximation can be applied BMI I FS0 ...
C-arm Cone-beam CT - Society Of Interventional Radiology
... system is compact enough to allow mounting on a moving C-arm, thereby allowing the patient to remain stationary during the examination. In a single orbit about the patient, a complete volumetric dataset covering a large anatomic region of interest is generated from which submillimeter isotropic reco ...
... system is compact enough to allow mounting on a moving C-arm, thereby allowing the patient to remain stationary during the examination. In a single orbit about the patient, a complete volumetric dataset covering a large anatomic region of interest is generated from which submillimeter isotropic reco ...
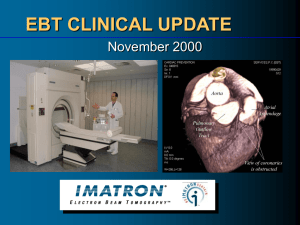
ElectronBeam
... circumference of the body to the X-ray beam, the EBT X-ray beam enters from the back. Thus, anterior structures such as the breast and thyroid are subjected to a lesser dose of radiation (17% of the entrance skin dose). ...
... circumference of the body to the X-ray beam, the EBT X-ray beam enters from the back. Thus, anterior structures such as the breast and thyroid are subjected to a lesser dose of radiation (17% of the entrance skin dose). ...
WP DIGITAL MAMMO rev3 (5)
... computer during a readout sequence. This is known as direct readout, a function of all digital systems, and should not be confused with direct conversion digital detection. Thin film transistor (TFT) arrays are the active electronic readout mechanism commonly used in both direct- and indirect-digita ...
... computer during a readout sequence. This is known as direct readout, a function of all digital systems, and should not be confused with direct conversion digital detection. Thin film transistor (TFT) arrays are the active electronic readout mechanism commonly used in both direct- and indirect-digita ...
WP DIGITAL MAMMO rev3
... computer during a readout sequence. This is known as direct readout, a function of all digital systems, and should not be confused with direct conversion digital detection. Thin film transistor (TFT) arrays are the active electronic readout mechanism commonly used in both direct- and indirect-digita ...
... computer during a readout sequence. This is known as direct readout, a function of all digital systems, and should not be confused with direct conversion digital detection. Thin film transistor (TFT) arrays are the active electronic readout mechanism commonly used in both direct- and indirect-digita ...
Ongoing quality control in digital radiography: Report of AAPM
... previously, this rate should be adjusted to reflect the operator’s clinical practice. Repeated image rates in pediatric imaging departments have been reported to be approximately 3%–5%,7,9 and the task group recommends that a target of 5% be used in pediatric imaging, and 7% as a threshold for inves ...
... previously, this rate should be adjusted to reflect the operator’s clinical practice. Repeated image rates in pediatric imaging departments have been reported to be approximately 3%–5%,7,9 and the task group recommends that a target of 5% be used in pediatric imaging, and 7% as a threshold for inves ...
Coffimator Selection for SPECT Brain Imaging: The
... structed without apodization. Noise measurements and clinical studies were also investigated ...
... structed without apodization. Noise measurements and clinical studies were also investigated ...
ACR White Paper on Radiation Dose in Medicine
... medicine for more than a century. The benefits of noninvasive or minimally invasive procedures are integral to modern patient care and greatly exceed the associated risks. The development of remarkable equipment such as multidetector row CT and the increased utilization of x-ray and nuclear medicine ...
... medicine for more than a century. The benefits of noninvasive or minimally invasive procedures are integral to modern patient care and greatly exceed the associated risks. The development of remarkable equipment such as multidetector row CT and the increased utilization of x-ray and nuclear medicine ...
Full Text
... identify such radiation-induced cancers in a general population are problematic, since excess cancers that occur in populations exposed to high levels of radiation (and consequently are likely to be radiation-induced) cannot be differentiated from naturally occurring cancers by even the most sophist ...
... identify such radiation-induced cancers in a general population are problematic, since excess cancers that occur in populations exposed to high levels of radiation (and consequently are likely to be radiation-induced) cannot be differentiated from naturally occurring cancers by even the most sophist ...
Přednášky z lékařské biofyziky Masarykova univerzita v
... Passage of X-rays through Patient's Body X-rays emitted from a small focal area of the anode propagate in all directions. In the tube envelope, some low energy photons are absorbed. Further absorption of these photons occurs in the primary filter, made of aluminium sheet. It absorbs low energy pho ...
... Passage of X-rays through Patient's Body X-rays emitted from a small focal area of the anode propagate in all directions. In the tube envelope, some low energy photons are absorbed. Further absorption of these photons occurs in the primary filter, made of aluminium sheet. It absorbs low energy pho ...
Understanding image quality and radiation dose in MSCT and
... exposure to obtain a pair of values Var(Smed) and E(Smed). Now, use the relation Var(Nmed) = E(Nmed) with Var(Smed) = k2 ⋅ Var(Nmed) and E(Smed) = k ⋅ E(Nmed) to find k = Var(Smed) / E(Smed). – Electronic noise: Determine Var(Smin) from the subtraction of two dark images. ...
... exposure to obtain a pair of values Var(Smed) and E(Smed). Now, use the relation Var(Nmed) = E(Nmed) with Var(Smed) = k2 ⋅ Var(Nmed) and E(Smed) = k ⋅ E(Nmed) to find k = Var(Smed) / E(Smed). – Electronic noise: Determine Var(Smin) from the subtraction of two dark images. ...
Radiation-Dose-Monitor 11062015.ai
... RDM is compatible with various types of imaging modalities from all manufacturers. It is designed for all medical professionals responsible for the dose cycle (Radiologists, Technologists, Director of Radiology, Medical Physicists, Etc. ). Thanks to its Web-based architecture, multiple control scree ...
... RDM is compatible with various types of imaging modalities from all manufacturers. It is designed for all medical professionals responsible for the dose cycle (Radiologists, Technologists, Director of Radiology, Medical Physicists, Etc. ). Thanks to its Web-based architecture, multiple control scree ...
Detection of Acoustic Schwannoma: Use of Constructive
... screening sequence of the peripheral vestibulocochlear pathway was available to complement the T2-weighted whole-brain survey, which examines the central vestibulocochlear pathways. If a satisfactory screening sequence was available, contrast-enhanced images would be required only when this sequence ...
... screening sequence of the peripheral vestibulocochlear pathway was available to complement the T2-weighted whole-brain survey, which examines the central vestibulocochlear pathways. If a satisfactory screening sequence was available, contrast-enhanced images would be required only when this sequence ...
Fetal Magnetic Resonance Imaging at 3.0 T
... discoveries concerning magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Magnetic resonance imaging is among the most notable of the advanced imaging sciences, with privileged position as being low risk and being a flexible enough modality to acquire a wide variety of information within 1 medical imaging system. It ...
... discoveries concerning magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Magnetic resonance imaging is among the most notable of the advanced imaging sciences, with privileged position as being low risk and being a flexible enough modality to acquire a wide variety of information within 1 medical imaging system. It ...
Installation of Imaging Modalities
... Molecular Imaging / Nuclear Medicine / Gamma Camera • A patient ingests or is injected with a small amount of radioactive material. The radioactive material gives off gamma rays that can be detected by a special camera that produces computerized images ...
... Molecular Imaging / Nuclear Medicine / Gamma Camera • A patient ingests or is injected with a small amount of radioactive material. The radioactive material gives off gamma rays that can be detected by a special camera that produces computerized images ...
Distinguishing Tumefactive Demyelinating Lesions from Glioma or
... irregular border, mass effect, perilesional edema, central necrosis, variable enhancement, variable T2-weighted signal intensity, and involvement of gray matter. However, these are nonspecific MR imaging features shared by gliomas ...
... irregular border, mass effect, perilesional edema, central necrosis, variable enhancement, variable T2-weighted signal intensity, and involvement of gray matter. However, these are nonspecific MR imaging features shared by gliomas ...
Optimisation in general radiography (PDF Available)
... terms of stochastic effects in the long term [14]. It equates the uniform dose to the whole body that would have a similar level of risk and takes account of doses to radio-sensitive organs in different parts of the body. However, the effective dose can only be derived from calculations. These are b ...
... terms of stochastic effects in the long term [14]. It equates the uniform dose to the whole body that would have a similar level of risk and takes account of doses to radio-sensitive organs in different parts of the body. However, the effective dose can only be derived from calculations. These are b ...
Welcome to Advances in Molecular Breast
... imaging (BSGI) and positron emission mammography (PEM). All three capitalize on diagnostic nuclear imaging methods. MBI and BSGI employ gamma cameras specifically designed for breast examination using technetium-99m (Tc-99m) sestamibi, the preferred radiopharmaceutical probe for tumor localization a ...
... imaging (BSGI) and positron emission mammography (PEM). All three capitalize on diagnostic nuclear imaging methods. MBI and BSGI employ gamma cameras specifically designed for breast examination using technetium-99m (Tc-99m) sestamibi, the preferred radiopharmaceutical probe for tumor localization a ...
Upright Open MRI Centres
... supine, non- weight-bearing position and as a result may not detect pathology that becomes visible only when the patient is scanned in an upright position. Upright Open MRI scanners have clear advantages over supine imaging and may be used as first line MRI for the spine or as an adjunct if supine M ...
... supine, non- weight-bearing position and as a result may not detect pathology that becomes visible only when the patient is scanned in an upright position. Upright Open MRI scanners have clear advantages over supine imaging and may be used as first line MRI for the spine or as an adjunct if supine M ...
Magnetic resonance imaging in biomedical research
... antibodies under scanning electron microscope attached to CD8 cells. ...
... antibodies under scanning electron microscope attached to CD8 cells. ...
Positron emission tomography

Positron emission tomography (PET) is a nuclear medicine, functional imaging technique that produces a three-dimensional image of functional processes in the body. The system detects pairs of gamma rays emitted indirectly by a positron-emitting radionuclide (tracer), which is introduced into the body on a biologically active molecule. Three-dimensional images of tracer concentration within the body are then constructed by computer analysis. In modern PET-CT scanners, three dimensional imaging is often accomplished with the aid of a CT X-ray scan performed on the patient during the same session, in the same machine.If the biologically active molecule chosen for PET is fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG), an analogue of glucose, the concentrations of tracer imaged will indicate tissue metabolic activity as it corresponds to the regional glucose uptake. Use of this tracer to explore the possibility of cancer metastasis (i.e., spreading to other sites) is the most common type of PET scan in standard medical care (90% of current scans). However, on a minority basis, many other radioactive tracers are used in PET to image the tissue concentration of other types of molecules of interest. One of the disadvantages of PET scanners is their operating cost.