Metal Complexes Containing Natural and Artificial Radioactive
... member of the actinide series of elements, although it has no 5f electrons in its metallic, gaseous, or ionic forms [1]. Technetium (element 43) possesses two radioactive isotopes with long half-lives: 99Tc (2.12 × 105 years, has practical use) and 98Tc (1.5 × 106 years, it is a rhenium analogue). B ...
... member of the actinide series of elements, although it has no 5f electrons in its metallic, gaseous, or ionic forms [1]. Technetium (element 43) possesses two radioactive isotopes with long half-lives: 99Tc (2.12 × 105 years, has practical use) and 98Tc (1.5 × 106 years, it is a rhenium analogue). B ...
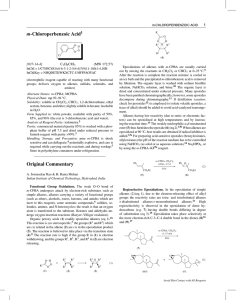
Chloroperbenzoic_aci..
... Epoxidations of alkenes with m-CPBA are usually carried out by mixing the reactants in CH2 Cl2 or CHCl3 at 0–25 ◦ C.9 After the reaction is complete the reaction mixture is cooled in an ice bath and the precipitated m-chlorobenzoic acid is removed by filtration. The organic layer is washed with sodi ...
... Epoxidations of alkenes with m-CPBA are usually carried out by mixing the reactants in CH2 Cl2 or CHCl3 at 0–25 ◦ C.9 After the reaction is complete the reaction mixture is cooled in an ice bath and the precipitated m-chlorobenzoic acid is removed by filtration. The organic layer is washed with sodi ...
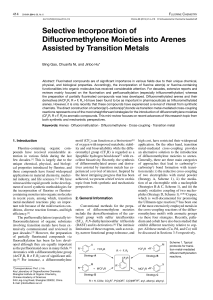
Separation of alcohol/ether/hydrocarbon mixtures in
... bottom product and the hydrocarbons as top product. The alcohol splits up between the top and the bottom so that further alcohol/hydrocarbons and/or alcohol/ether separations have to be performed. The split-up of the alcohol between top and bottom products depends on the nature of the compounds whic ...
... bottom product and the hydrocarbons as top product. The alcohol splits up between the top and the bottom so that further alcohol/hydrocarbons and/or alcohol/ether separations have to be performed. The split-up of the alcohol between top and bottom products depends on the nature of the compounds whic ...
Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry
... which differ from each other in the spatial arrangement of groups about the double bond. Organic and Biological Chemistry ...
... which differ from each other in the spatial arrangement of groups about the double bond. Organic and Biological Chemistry ...
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE General Organic Chemistry I
... Students will gain an understanding of the role that organic chemistry plays in their lives, and the role that organic chemistry plays in the agricultural and medical fields. Students learn how to identify problems and work as a team to solve those problems. Students learn how to predict reactions a ...
... Students will gain an understanding of the role that organic chemistry plays in their lives, and the role that organic chemistry plays in the agricultural and medical fields. Students learn how to identify problems and work as a team to solve those problems. Students learn how to predict reactions a ...
1002_4th Exam_1010620
... D) It involves nuclides with atomic number larger than 83 and mass number larger than 200. Answer: A 41) A nuclide has a decay constant of 4.28 × 10-4 /h. If the activity of a sample is 3.14 × 105 /s, how many atoms of the nuclide are present in the sample? A) 2.34 × 1011 B) 7.34 × 108 C) 1.34 × 102 ...
... D) It involves nuclides with atomic number larger than 83 and mass number larger than 200. Answer: A 41) A nuclide has a decay constant of 4.28 × 10-4 /h. If the activity of a sample is 3.14 × 105 /s, how many atoms of the nuclide are present in the sample? A) 2.34 × 1011 B) 7.34 × 108 C) 1.34 × 102 ...
mc_ch08 - MrBrownsChem1LCHS
... decomposition, single-displacement, and doubledisplacement reactions. • Classify a reaction as a synthesis, decomposition, single-displacement, double-displacement, or combustion reaction. • List three kinds of synthesis reactions and six kinds of decomposition reactions. ...
... decomposition, single-displacement, and doubledisplacement reactions. • Classify a reaction as a synthesis, decomposition, single-displacement, double-displacement, or combustion reaction. • List three kinds of synthesis reactions and six kinds of decomposition reactions. ...
PDF aldehydes and ketones
... Addition of S nucleophiles (addition of NaHSO3) Addition of NaHSO3 to carbonyl/ aldehydic carbon gives solid adduct; these are sulfonates that are water soluble. Only RCHO, methyl ketones, and cyclic ketones react. Carbonyl compounds can be regenerated on treating the adduct with acid or base. R C ...
... Addition of S nucleophiles (addition of NaHSO3) Addition of NaHSO3 to carbonyl/ aldehydic carbon gives solid adduct; these are sulfonates that are water soluble. Only RCHO, methyl ketones, and cyclic ketones react. Carbonyl compounds can be regenerated on treating the adduct with acid or base. R C ...
chemical reaction
... decomposition, single-displacement, and doubledisplacement reactions. • Classify a reaction as a synthesis, decomposition, single-displacement, double-displacement, or combustion reaction. • List three kinds of synthesis reactions and six kinds of decomposition reactions. ...
... decomposition, single-displacement, and doubledisplacement reactions. • Classify a reaction as a synthesis, decomposition, single-displacement, double-displacement, or combustion reaction. • List three kinds of synthesis reactions and six kinds of decomposition reactions. ...
Nucleophilic Substitution and b
... Recall the problem: If reaction occurs only at the C bearing the Cl the other should remain chiral! Hmmmm? But now notice that the intermediate sulfonium ion is achiral. It has a mirror plane of symmetry. Only optically inactive products will result. ...
... Recall the problem: If reaction occurs only at the C bearing the Cl the other should remain chiral! Hmmmm? But now notice that the intermediate sulfonium ion is achiral. It has a mirror plane of symmetry. Only optically inactive products will result. ...
Chapter 18: Ethers and Epoxides
... Proton NMR: H on a C next to ether O is shifted downfield to 3.4 to 4.5 The 1H NMR spectrum of dipropyl ether shows this signal at 3.4 In epoxides, these H’s absorb at 2.5 to 3.5 d in ...
... Proton NMR: H on a C next to ether O is shifted downfield to 3.4 to 4.5 The 1H NMR spectrum of dipropyl ether shows this signal at 3.4 In epoxides, these H’s absorb at 2.5 to 3.5 d in ...
Ethers and Epoxides
... Proton NMR: H on a C next to ether O is shifted downfield to 3.4 to 4.5 The 1H NMR spectrum of dipropyl ether shows this signal at 3.4 In epoxides, these H’s absorb at 2.5 to 3.5 d in ...
... Proton NMR: H on a C next to ether O is shifted downfield to 3.4 to 4.5 The 1H NMR spectrum of dipropyl ether shows this signal at 3.4 In epoxides, these H’s absorb at 2.5 to 3.5 d in ...
Chapter 24. Amines
... • Alkylamines cleave at the C–C bond nearest the nitrogen to yield an alkyl radical and a nitrogencontaining cation ...
... • Alkylamines cleave at the C–C bond nearest the nitrogen to yield an alkyl radical and a nitrogencontaining cation ...
chm238f02.exam2
... (c) Which reagent(s) would you use if you wanted to substitute the alcohol with bromide in the same position and with inversion of configuration, without any rearrangement. ...
... (c) Which reagent(s) would you use if you wanted to substitute the alcohol with bromide in the same position and with inversion of configuration, without any rearrangement. ...
homogeneous catalysis
... Written mainly from a pedagogical point of view, this book is not comprehensive but selective. The material presented was selected on the basis of two criteria. We have tried to include most of the homogeneous catalytic reactions with proven industrial applications and well-established mechanisms. T ...
... Written mainly from a pedagogical point of view, this book is not comprehensive but selective. The material presented was selected on the basis of two criteria. We have tried to include most of the homogeneous catalytic reactions with proven industrial applications and well-established mechanisms. T ...
Chapter 24. Amines
... • Alkylamines cleave at the C–C bond nearest the nitrogen to yield an alkyl radical and a nitrogencontaining cation ...
... • Alkylamines cleave at the C–C bond nearest the nitrogen to yield an alkyl radical and a nitrogencontaining cation ...
CHM238-01 EXAM 2 October 14, 2002 103
... (c) Which reagent(s) would you use if you wanted to substitute the alcohol with bromide in the same position and with inversion of configuration, without any rearrangement. (d) This type of rearrangement can occur when trying to hydrate an alkene in acid. If we add water and acid (acid catalyzed hyd ...
... (c) Which reagent(s) would you use if you wanted to substitute the alcohol with bromide in the same position and with inversion of configuration, without any rearrangement. (d) This type of rearrangement can occur when trying to hydrate an alkene in acid. If we add water and acid (acid catalyzed hyd ...
Bioorganic chemistry-a scientific endeavour in continuous
... combinatory procedures; the polymerase chain reaction (PCR); all of the latest separation and spectroscopic methodology with computer analysis; and the generous use -as reagents -- of bacteria, fungi, enzymes, whole cells, and ground liver microsomes, inter alia. A graduate course in bioorganic chem ...
... combinatory procedures; the polymerase chain reaction (PCR); all of the latest separation and spectroscopic methodology with computer analysis; and the generous use -as reagents -- of bacteria, fungi, enzymes, whole cells, and ground liver microsomes, inter alia. A graduate course in bioorganic chem ...
Chapter 1 Chemical Bonding and Chemical Structure
... • Low molecular weight amines tend to be water soluble whether they are primary, secondary or tertiary • Fewer than 5 carbons usually = solubility in water ...
... • Low molecular weight amines tend to be water soluble whether they are primary, secondary or tertiary • Fewer than 5 carbons usually = solubility in water ...
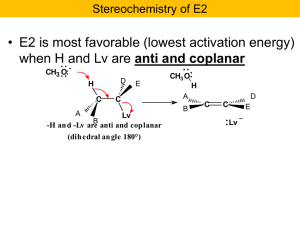
Chapter 11 - Alcohols and Ethers1
... - For this reaction to occur, make sure the stereochemistry of the reactant is in a way that can allow for a center of inversion of, what was originally, the halide atom - Epoxidation is a syn addition that is stereospeci c ...
... - For this reaction to occur, make sure the stereochemistry of the reactant is in a way that can allow for a center of inversion of, what was originally, the halide atom - Epoxidation is a syn addition that is stereospeci c ...
Lectures 4-6
... Collins Oxidation (CrO3 • 2pyridine) TL 1969, 336 - CrO3 (anhydrous) + pyridine (anhydrous) ...
... Collins Oxidation (CrO3 • 2pyridine) TL 1969, 336 - CrO3 (anhydrous) + pyridine (anhydrous) ...
Enantioselective synthesis

Enantioselective synthesis, also called chiral synthesis or asymmetric synthesis, is defined by IUPAC as: a chemical reaction (or reaction sequence) in which one or more new elements of chirality are formed in a substrate molecule and which produces the stereoisomeric (enantiomeric or diastereoisomeric) products in unequal amounts.Put more simply: it is the synthesis of a compound by a method that favors the formation of a specific enantiomer or diastereomer.Enantioselective synthesis is a key process in modern chemistry and is particularly important in the field of pharmaceuticals, as the different enantiomers or diastereomers of a molecule often have different biological activity.