INTRODUCTION
... ligands in solution, for instance) is called its lability. Those coordination compounds for which such substitution reaction are rapid, called labile, whereas those for which such substitution reactions proceed slowly (or not at all) are called inert. It is to be noted that these terms should not b ...
... ligands in solution, for instance) is called its lability. Those coordination compounds for which such substitution reaction are rapid, called labile, whereas those for which such substitution reactions proceed slowly (or not at all) are called inert. It is to be noted that these terms should not b ...
Applications of trivalent and pentavalent tantalum in organic synthesis
... have very similar chemical properties but not as similar as Zirconiun~(Zr) and Hafnium (Hf). Oxidation states and stereochemistries of Nb and Ta are shown below (Table I). Nb and Ta have very little cationic behaviour, however they can complex well in all the oxidation states viz., 11, 111, IV and V ...
... have very similar chemical properties but not as similar as Zirconiun~(Zr) and Hafnium (Hf). Oxidation states and stereochemistries of Nb and Ta are shown below (Table I). Nb and Ta have very little cationic behaviour, however they can complex well in all the oxidation states viz., 11, 111, IV and V ...
Document
... the first series of the f-block and are called the inner transition elements These elements are frequently called “rare earths,” a name of historical origin but a clear misnomer because several are not rare at all For many uses, the lanthanides do not have to be separated from one another. A mixture ...
... the first series of the f-block and are called the inner transition elements These elements are frequently called “rare earths,” a name of historical origin but a clear misnomer because several are not rare at all For many uses, the lanthanides do not have to be separated from one another. A mixture ...
Complexes Of 5,7,7,12,14,14 - European Scientific Journal
... five coordinated square pyramidal complexes. The complexes cis-[Cd(teta)(NO3)](NO3) and cis-[Cd(tet-b)(NO3)](NO3) underwent axial ligand substitution and anion exchange reaction with KCNS to produce [Cd(teta)(SCN)](SCN) and [Cd(tet-b)(SCN)](SCN) respectively. The square pyramidal complex [CdLI](ClO4 ...
... five coordinated square pyramidal complexes. The complexes cis-[Cd(teta)(NO3)](NO3) and cis-[Cd(tet-b)(NO3)](NO3) underwent axial ligand substitution and anion exchange reaction with KCNS to produce [Cd(teta)(SCN)](SCN) and [Cd(tet-b)(SCN)](SCN) respectively. The square pyramidal complex [CdLI](ClO4 ...
View/Open
... oxygen to be more positive; therefore, the proton is held less strongly. In effect, the benzene ring of phenol acts as if it were an electron-withdrawing group when compared with the cyclohexane ring of cyclohexanol. We can understand this effect by noting that the carbon atom which bears the hydrox ...
... oxygen to be more positive; therefore, the proton is held less strongly. In effect, the benzene ring of phenol acts as if it were an electron-withdrawing group when compared with the cyclohexane ring of cyclohexanol. We can understand this effect by noting that the carbon atom which bears the hydrox ...
Conjugate addition_Clayden
... Conjugate addition of alcohols can be catalysed by acid or base Alcohols undergo conjugate addition only very slowly in the absence of a catalyst: they are not such good nucleophiles as amines for the very reason we have just mentioned in connection with the reactivity of hydroxylamine—oxygen is mor ...
... Conjugate addition of alcohols can be catalysed by acid or base Alcohols undergo conjugate addition only very slowly in the absence of a catalyst: they are not such good nucleophiles as amines for the very reason we have just mentioned in connection with the reactivity of hydroxylamine—oxygen is mor ...
23-24
... complexes, magnetic behavior. Ligand Field Theory (LFT) is much simpler than MO theory (a little more sophisticated than CFT), but it is a very useful theory. ...
... complexes, magnetic behavior. Ligand Field Theory (LFT) is much simpler than MO theory (a little more sophisticated than CFT), but it is a very useful theory. ...
Excited state properties of lanthanide complexes: Beyond ff states
... In the absence of oxygen, Eu2+ ions can be photochemically oxidized by water [34,41,42]. This process prevents the efficient accumulation of Eu2+ as a final product of the Eu(III) photoreduction. However, in the region of the LMCT band of Eu(III) azide complexes the extinction coefficient of Eu2+ is suffic ...
... In the absence of oxygen, Eu2+ ions can be photochemically oxidized by water [34,41,42]. This process prevents the efficient accumulation of Eu2+ as a final product of the Eu(III) photoreduction. However, in the region of the LMCT band of Eu(III) azide complexes the extinction coefficient of Eu2+ is suffic ...
HYPERVALENT IODINE IN CARBON-CARBON BOND
... highly polarized three-center-four-electron (3c-4e) bond, in which the central atom bears a positive charge and two monovalent ligands share the corresponding negative charge. This type of bonding serves to distinguish hypervalent compounds from transition metal complexes in which d-orbital hybridiz ...
... highly polarized three-center-four-electron (3c-4e) bond, in which the central atom bears a positive charge and two monovalent ligands share the corresponding negative charge. This type of bonding serves to distinguish hypervalent compounds from transition metal complexes in which d-orbital hybridiz ...
full paper - Wayne State Chemistry Department
... tris(3,5-di-tert-butylpyrazolato)tetrahydrofuranvanadium(III) (3), respectively, as purple crystalline solids (Scheme 1). Compounds 1⫺3 are air-sensitive in solution and in the solid state, but are thermally stable indefinitely at ambient temperature under argon. The structures of 1⫺3 were assigned ...
... tris(3,5-di-tert-butylpyrazolato)tetrahydrofuranvanadium(III) (3), respectively, as purple crystalline solids (Scheme 1). Compounds 1⫺3 are air-sensitive in solution and in the solid state, but are thermally stable indefinitely at ambient temperature under argon. The structures of 1⫺3 were assigned ...
the general features of transition metal chemistry
... some wavelengths are absorbed by the solution. Copper(II) ions in solution absorb light in the ___ region of the spectrum. The light which passes through the solution and out the other side will have all the colours in it except for the ___. We see this mixture as _____, the complementary colour of ...
... some wavelengths are absorbed by the solution. Copper(II) ions in solution absorb light in the ___ region of the spectrum. The light which passes through the solution and out the other side will have all the colours in it except for the ___. We see this mixture as _____, the complementary colour of ...
Linear hexadentate ligands as iron chelators
... It was found that when the 3LI or 4LI linkers were used in conjunction with methylprotected TAM thiaz (10), the products of the first coupling reaction were water soluble, and were extracted into the aqueous phase with the excess diamine during purification. In these cases, the convergent synthetic ...
... It was found that when the 3LI or 4LI linkers were used in conjunction with methylprotected TAM thiaz (10), the products of the first coupling reaction were water soluble, and were extracted into the aqueous phase with the excess diamine during purification. In these cases, the convergent synthetic ...
Induced Aromaticity and Electron-Count Rules for Bipyramidal and
... system (initially non-aromatic or even non-existent in a free state) through interaction it with a suitable mono- or polyatomic fragment resulting in the completion of closed electronic shell of the composed system. A well-known example of this phenomenon (referred to as metalloaromaticity [4]) is a ...
... system (initially non-aromatic or even non-existent in a free state) through interaction it with a suitable mono- or polyatomic fragment resulting in the completion of closed electronic shell of the composed system. A well-known example of this phenomenon (referred to as metalloaromaticity [4]) is a ...
Chapter 8. Chiral Catalysts
... measured as enantiomeric excess [% ee = (R−S)/(R+S) × 100], depends on electronic and steric factors in a very subtle form. A simple calculation shows that differences in energy of only 2 kcal/mol between these transition states are enough to obtain more than 90% ee, and small changes in any of the ...
... measured as enantiomeric excess [% ee = (R−S)/(R+S) × 100], depends on electronic and steric factors in a very subtle form. A simple calculation shows that differences in energy of only 2 kcal/mol between these transition states are enough to obtain more than 90% ee, and small changes in any of the ...
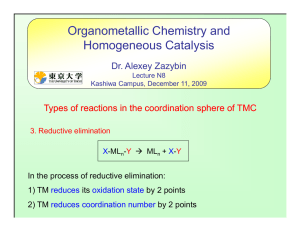
Lecture8
... 1) Retain of the TM oxidation state (hydrocarbyl ligand changes to hydride or acyl ligand changes to alkyl) 2) Vacant place in the coordination sphere of TMC is important for elimination 3) H-atom in the transition state should have an opportunity to reach the M-atom 4) High oxidative state of the T ...
... 1) Retain of the TM oxidation state (hydrocarbyl ligand changes to hydride or acyl ligand changes to alkyl) 2) Vacant place in the coordination sphere of TMC is important for elimination 3) H-atom in the transition state should have an opportunity to reach the M-atom 4) High oxidative state of the T ...
Structural Evaluation and Solution Integrity of Alkali Metal Salt
... The preparation of a variety of salt complexes of [12-MCMn(III)N(shi)-4] (1) provides the structural basis for the first quantitative investigation of the cation and anion selectivity of metallacrowns. The preparation, X-ray crystal structures, and solution integrities of crystalline salts (LiCl2)[1 ...
... The preparation of a variety of salt complexes of [12-MCMn(III)N(shi)-4] (1) provides the structural basis for the first quantitative investigation of the cation and anion selectivity of metallacrowns. The preparation, X-ray crystal structures, and solution integrities of crystalline salts (LiCl2)[1 ...
Organometallic Chemistry between organic and inorganic
... Sometimes, radical abstraction produces a 17-e species (see C103). ...
... Sometimes, radical abstraction produces a 17-e species (see C103). ...
Chapter 3
... cesium atoms (six oxigens, one thiocyanate molecule and two arenes). The last interesting examples again refer to the binding of Cs. In Figure 8 a and b, the two alkali metal complexes with calix[4]arene are shown. In both structures the Cs atom is bound within the cup-shaped cone conformation adopt ...
... cesium atoms (six oxigens, one thiocyanate molecule and two arenes). The last interesting examples again refer to the binding of Cs. In Figure 8 a and b, the two alkali metal complexes with calix[4]arene are shown. In both structures the Cs atom is bound within the cup-shaped cone conformation adopt ...
View/Open - Minerva Access
... for formation of C-C bonds with CO2 as the only coproduct. Here I provide an overview of: key solution phase literature; thermochemical considerations for decarboxylation of esters and thermolysis of esters in the absence of a metal catalyst. Results from my laboratory on the use of multistage ion t ...
... for formation of C-C bonds with CO2 as the only coproduct. Here I provide an overview of: key solution phase literature; thermochemical considerations for decarboxylation of esters and thermolysis of esters in the absence of a metal catalyst. Results from my laboratory on the use of multistage ion t ...
Development of Fluorescence based Biosensor for Estimation of Heavy Metal... Sudha J. Kulkarni Kalpana S. Joshi
... analysis include inductively coupled plasma mass spectroscopy, X-ray absorption spectroscopy, cold vapour atomic absorption spectroscopy and UV visible spectrophotometry [3]. Though precise, these methods are costly and require trained personnel. Also they are laboratory bound. Therefore biosensors ...
... analysis include inductively coupled plasma mass spectroscopy, X-ray absorption spectroscopy, cold vapour atomic absorption spectroscopy and UV visible spectrophotometry [3]. Though precise, these methods are costly and require trained personnel. Also they are laboratory bound. Therefore biosensors ...
Ketones and Aldehydes Reading: Wade chapter 18, sections 18
... 1. Grignard and organolithium addition: Highly basic grignard and organolithium reagents add to carbonyl irreversibly to give alcohols; aldehydes give 2° alcohols and ketones give 3° alcohols; formaldehyde gives a 1° alcohol: ...
... 1. Grignard and organolithium addition: Highly basic grignard and organolithium reagents add to carbonyl irreversibly to give alcohols; aldehydes give 2° alcohols and ketones give 3° alcohols; formaldehyde gives a 1° alcohol: ...
Crystal-Field Theory
... Tetrahedral and Square-Planar Complexes • Square planar complexes can be thought of as follows: start with an octahedral complex and remove two ligands along the z-axis. • As a consequence the four planar ligands are drawn in towards the metal. • Relative to the octahedral field, the orbital is grea ...
... Tetrahedral and Square-Planar Complexes • Square planar complexes can be thought of as follows: start with an octahedral complex and remove two ligands along the z-axis. • As a consequence the four planar ligands are drawn in towards the metal. • Relative to the octahedral field, the orbital is grea ...
Metal carbonyl

Metal carbonyls are coordination complexes of transition metals with carbon monoxide ligands. Metal carbonyls are useful in organic synthesis and as catalysts or catalyst precursors in homogeneous catalysis, such as hydroformylation and Reppe chemistry. In the Mond process, nickel carbonyl is used to produce pure nickel. In organometallic chemistry, metal carbonyls serve as precursors for the preparation of other organometalic complexes.Metal carbonyls are toxic by skin contact, inhalation or ingestion, in part because of their ability to carbonylate hemoglobin to give carboxyhemoglobin, which prevents the binding of O2.