Representative Quiz Questions_Key
... discover that the alien duplex has a significantly higher melting temperature than earth DNA. What interaction would contribute most significantly to this effect? Since the alien DNA is all purines with two rings, you would get more base stacking energy. 5. mRNA structures affect protein translation ...
... discover that the alien duplex has a significantly higher melting temperature than earth DNA. What interaction would contribute most significantly to this effect? Since the alien DNA is all purines with two rings, you would get more base stacking energy. 5. mRNA structures affect protein translation ...
Somatic MEN1 gene mutation does not contribute
... Boggild et al. found LOH on chromosome 11 in as many as about 20% of 88 sporadic adenomas (12). This discrepancy could have been explained by mutation(s) affecting the transcription level of the MEN1 gene. Therefore, we decided to sequence exon 1 and promoter but this experiment failed to reveal any ...
... Boggild et al. found LOH on chromosome 11 in as many as about 20% of 88 sporadic adenomas (12). This discrepancy could have been explained by mutation(s) affecting the transcription level of the MEN1 gene. Therefore, we decided to sequence exon 1 and promoter but this experiment failed to reveal any ...
Protein - standish
... Of those 22 amino acids, your body can make 13 of them without you ever thinking about it. Your body can't make the other nine amino acids, but you can get them by eating protein-rich foods. They are called essential amino acids because it's essential that you get them from the foods you eat. ...
... Of those 22 amino acids, your body can make 13 of them without you ever thinking about it. Your body can't make the other nine amino acids, but you can get them by eating protein-rich foods. They are called essential amino acids because it's essential that you get them from the foods you eat. ...
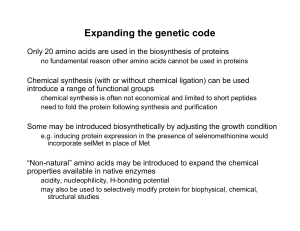
Non-natural amino acid
... acids and loads them onto tRNA E + ATP + AA Î E(AA-AMP) + PPi E(AA-AMP) + tRNA Î AA-tRNA + AMP + E E : alanyl-tRNA synthetase, cysteinyl-tRNA ...
... acids and loads them onto tRNA E + ATP + AA Î E(AA-AMP) + PPi E(AA-AMP) + tRNA Î AA-tRNA + AMP + E E : alanyl-tRNA synthetase, cysteinyl-tRNA ...
Gene regulation - Napa Valley College
... Right-click slide / select “Play” © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... Right-click slide / select “Play” © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
(3-D Molecules (key))
... the button in that section with a movie camera on it to see an animation. a. Change style to “ball and stick” and rotate it. To zoom in, press the Shift key and slide your finger up and down the scroll bar on the right side of your mousepad. How does a glycogen molecule compare in size to a glucose ...
... the button in that section with a movie camera on it to see an animation. a. Change style to “ball and stick” and rotate it. To zoom in, press the Shift key and slide your finger up and down the scroll bar on the right side of your mousepad. How does a glycogen molecule compare in size to a glucose ...
Chapter 7 Body Systems
... Glucose can be burned and used immediately as fuel for energy, stored as glycogen ( primarily in the liver and skeletal muscle), and burned as fuel at a later time, or stored as fat and burned as fuel at a later time. Glucose can be catabolized anaerobically and aerobically. Anaerobically, glucose i ...
... Glucose can be burned and used immediately as fuel for energy, stored as glycogen ( primarily in the liver and skeletal muscle), and burned as fuel at a later time, or stored as fat and burned as fuel at a later time. Glucose can be catabolized anaerobically and aerobically. Anaerobically, glucose i ...
melanoma
... two good copies of each of these tumor suppressor genes, but sometimes you inherit one good copy and one mutated copy. Basically it means that, along with inheriting genes for your red hair or blue eyes, you may have inherited a mutated cell cycle gene. You had it when you were born, so it's not the ...
... two good copies of each of these tumor suppressor genes, but sometimes you inherit one good copy and one mutated copy. Basically it means that, along with inheriting genes for your red hair or blue eyes, you may have inherited a mutated cell cycle gene. You had it when you were born, so it's not the ...
Chapter 12: Inheritance Patterns and Human Genetics
... Section 1 Chromosomes and Inheritance Section 2 Human Genetics ...
... Section 1 Chromosomes and Inheritance Section 2 Human Genetics ...
Lecture 11 - Biosynthesis of Amino Acids
... nucleotides and lipids are very old Biosynthetic (anabolic) pathways share common intermediates with the degradative (catabolic) pathways. The amino acids are the building blocks for proteins and other nitrogen-containing compounds ...
... nucleotides and lipids are very old Biosynthetic (anabolic) pathways share common intermediates with the degradative (catabolic) pathways. The amino acids are the building blocks for proteins and other nitrogen-containing compounds ...
Functional genomics: assigning functions to genome sequences
... • Many (most ?) proteins function in complexes made up of non-homologous proteins • Some (many ?) proteins are crystallizable only with their functional partners Suggests that targeting of non-homologus, functionally linked proteins may offer a useful shortcut to learning protein structures and func ...
... • Many (most ?) proteins function in complexes made up of non-homologous proteins • Some (many ?) proteins are crystallizable only with their functional partners Suggests that targeting of non-homologus, functionally linked proteins may offer a useful shortcut to learning protein structures and func ...
control of the drosophila body pattern
... same. The only change is in the identity of the segments. The results of the studies of these homeotic mutations have revealed much about how segment identity is established. The cloning of the Antp gene led to the discovery of the homeobox, an 180bp DNA fragment characteristic of homeotic genes. Ho ...
... same. The only change is in the identity of the segments. The results of the studies of these homeotic mutations have revealed much about how segment identity is established. The cloning of the Antp gene led to the discovery of the homeobox, an 180bp DNA fragment characteristic of homeotic genes. Ho ...
Gene Section PML (Promyelocytic leukemia) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... successively, from the N- to the C-terminus, by: 1- a proline-rich N-terminus 2- a so-called "tripartite motif", cysteine-histidine rich, composed of a RING finger structure and 2 B box domains, with putative DNAbinding function 3- a coiled-coil motif corresponding to a dimerization interface 4- a b ...
... successively, from the N- to the C-terminus, by: 1- a proline-rich N-terminus 2- a so-called "tripartite motif", cysteine-histidine rich, composed of a RING finger structure and 2 B box domains, with putative DNAbinding function 3- a coiled-coil motif corresponding to a dimerization interface 4- a b ...
here - PHI-base
... Unaffected pathogenicity - the transgenic strain which expresses no or reduced levels of a specific gene product(s) has wild-type disease causing ability Increased virulence (Hypervirulence) - the transgenic strain causes higher levels of disease than the wild-type strain Effector (plant avirulence ...
... Unaffected pathogenicity - the transgenic strain which expresses no or reduced levels of a specific gene product(s) has wild-type disease causing ability Increased virulence (Hypervirulence) - the transgenic strain causes higher levels of disease than the wild-type strain Effector (plant avirulence ...
BNS216 - Staff
... • Each recombinant vector contains a random region of the target chromosome • The number of microbes in the library is large • Thus any gene in the target organism’s genome is present in at least one member of the gene library ...
... • Each recombinant vector contains a random region of the target chromosome • The number of microbes in the library is large • Thus any gene in the target organism’s genome is present in at least one member of the gene library ...
- Journal of Clinical Investigation
... efficient germline mutagen (16), and systematic tests in zebrafish revealed a dose of ENU which induced new mutations at defined “tester” pigmentation loci at rates between one in 300 and one in 2,000 mutagenized genomes (17, 18). Distinct genes are of quite different mutability, but the average rat ...
... efficient germline mutagen (16), and systematic tests in zebrafish revealed a dose of ENU which induced new mutations at defined “tester” pigmentation loci at rates between one in 300 and one in 2,000 mutagenized genomes (17, 18). Distinct genes are of quite different mutability, but the average rat ...
Name of Student: Dominik Sommerfeld
... is also largely determined by molecular recognition of the amino acid sequence surrounding a target P-site. An important aspect of substrate peptide specificity is that the target P-site falls within a consensus sequence motif, which exhibits structural and chemical complementarity to the kinase act ...
... is also largely determined by molecular recognition of the amino acid sequence surrounding a target P-site. An important aspect of substrate peptide specificity is that the target P-site falls within a consensus sequence motif, which exhibits structural and chemical complementarity to the kinase act ...
video slide
... Concept 17.2: Transcription is the DNA-directed synthesis of RNA: a closer look • Transcription, the first stage of gene expression, can be examined in more detail • RNA synthesis is catalyzed by RNA polymerase, which pries the DNA strands apart and hooks together the RNA nucleotides • RNA synthesi ...
... Concept 17.2: Transcription is the DNA-directed synthesis of RNA: a closer look • Transcription, the first stage of gene expression, can be examined in more detail • RNA synthesis is catalyzed by RNA polymerase, which pries the DNA strands apart and hooks together the RNA nucleotides • RNA synthesi ...
Cell Division
... daughter cells enter interphase, during which they grow and prepare for another division. In plants, cell division is mostly confined to specific regions, called meristems. For example, plant stems grow in length by cell division at the tips, or shoot apical meristems. Mitosis provides the mechanism ...
... daughter cells enter interphase, during which they grow and prepare for another division. In plants, cell division is mostly confined to specific regions, called meristems. For example, plant stems grow in length by cell division at the tips, or shoot apical meristems. Mitosis provides the mechanism ...
Table S1.
... D6 – Fatty acid desaturase Required for the synthesis of highly unsaturated fatty acids. D5 – Fatty acid desaturase Required for the synthesis of highly unsaturated fatty acids. Elongation of very long chain fatty acids Participates in the biosynthesis of long chain poly ...
... D6 – Fatty acid desaturase Required for the synthesis of highly unsaturated fatty acids. D5 – Fatty acid desaturase Required for the synthesis of highly unsaturated fatty acids. Elongation of very long chain fatty acids Participates in the biosynthesis of long chain poly ...
Inheritance and Adaptations
... 5. Heredity is the passing on of _____________ from parents to offspring. 6. Crossing a horse and a donkey is an example of ...
... 5. Heredity is the passing on of _____________ from parents to offspring. 6. Crossing a horse and a donkey is an example of ...
report on HMM
... In humans, as in other higher organisms, a DNA molecule consists of two strands that wrap around each other to resemble a twisted ladder whose sides, made of sugar and phosphate molecules, are connected by rungs of nitrogen containing chemicals called bases. Four different bases are present in DNA: ...
... In humans, as in other higher organisms, a DNA molecule consists of two strands that wrap around each other to resemble a twisted ladder whose sides, made of sugar and phosphate molecules, are connected by rungs of nitrogen containing chemicals called bases. Four different bases are present in DNA: ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.