Tertiary Structure
... Functions of Proteins • Enzymatic catalysis most chemical reactions in the cell are carried out by enzymes ,which are globular proteins. They increase the rate of chemical reactions by reducing the energy of activation. • Transport and storage small molecules are moved throughout the cell by specif ...
... Functions of Proteins • Enzymatic catalysis most chemical reactions in the cell are carried out by enzymes ,which are globular proteins. They increase the rate of chemical reactions by reducing the energy of activation. • Transport and storage small molecules are moved throughout the cell by specif ...
Biosynthesis of heme in mammals
... upregulated by the peroxisome proliferator-activated coactivator 1α (PGC-1α) [14]. PGC-1α is a coactivator of nuclear receptors and transcription factors [15]. The effects of PGC-1α are mediated by interactions with NRF-1 (nuclear regulatory factor 1) and FOX01 (a fork head family member) with the A ...
... upregulated by the peroxisome proliferator-activated coactivator 1α (PGC-1α) [14]. PGC-1α is a coactivator of nuclear receptors and transcription factors [15]. The effects of PGC-1α are mediated by interactions with NRF-1 (nuclear regulatory factor 1) and FOX01 (a fork head family member) with the A ...
Bioreg2017_Replication3_V4
... DNA replication is coordinated with other genomic processes Replication of chromatin and chromatin states -- nucleosome structure and chromatin states are disrupted by the replication fork and must be faithfully duplicated after passage of the replication fork -- changes in chromatin states are ass ...
... DNA replication is coordinated with other genomic processes Replication of chromatin and chromatin states -- nucleosome structure and chromatin states are disrupted by the replication fork and must be faithfully duplicated after passage of the replication fork -- changes in chromatin states are ass ...
chapter 23
... of cellulose make up plant cell walls. More than 50% of the total organic matter in the world is cellulose. People cannot digest cellulose, but when we eat fiber, which is cellulose, it speeds the movement of food through the digestive tract. Microorganisms that can digest cellulose are present in t ...
... of cellulose make up plant cell walls. More than 50% of the total organic matter in the world is cellulose. People cannot digest cellulose, but when we eat fiber, which is cellulose, it speeds the movement of food through the digestive tract. Microorganisms that can digest cellulose are present in t ...
Study Guide Questions Midterm 2
... 14. What are the differences among VLDL, LDL, IDL, and HDL – not just their composition but what they carry/deliver/pick up? 15. Why do people use Olestra? 16. Name some diseases/health risks associated with ...
... 14. What are the differences among VLDL, LDL, IDL, and HDL – not just their composition but what they carry/deliver/pick up? 15. Why do people use Olestra? 16. Name some diseases/health risks associated with ...
Pharmacogenetics
... half-life is relatively short. 85% of the drug is cleared. What is not cleared by DPD is then broken down and eliminated. Anything that is not actively catabolized goes into the anabolic pathway. (Note: For 30 years, they anabolic steroid was studied because that is where the anti-tumor effect came ...
... half-life is relatively short. 85% of the drug is cleared. What is not cleared by DPD is then broken down and eliminated. Anything that is not actively catabolized goes into the anabolic pathway. (Note: For 30 years, they anabolic steroid was studied because that is where the anti-tumor effect came ...
Chapter 4: Modification of Mendelian Ratios
... Phenotypes are the combined result of both genetics and the environment within which genes are expressed. ...
... Phenotypes are the combined result of both genetics and the environment within which genes are expressed. ...
AP Bio DNA Sim Lab
... world to access via the Internet. Why is this information important? Being able to identify the precise location and sequence of human genes will allow us to better understand genetic diseases. In addition, learning about the sequence of genes in other species helps us understand evolutionary relati ...
... world to access via the Internet. Why is this information important? Being able to identify the precise location and sequence of human genes will allow us to better understand genetic diseases. In addition, learning about the sequence of genes in other species helps us understand evolutionary relati ...
A Mathematical Theory of Natural and Artificial Selection. Part V
... Hence provided that zn is small the probability of escaping extinction is much smaller than k. I have been unable to evaluate it exactly, but it seems from a comparison with the case of a dominant factor, that the value of zn such that the factor is as likely to survive as to be extinguished, is of ...
... Hence provided that zn is small the probability of escaping extinction is much smaller than k. I have been unable to evaluate it exactly, but it seems from a comparison with the case of a dominant factor, that the value of zn such that the factor is as likely to survive as to be extinguished, is of ...
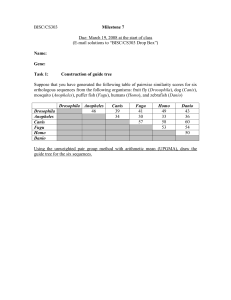
Milestone7
... Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is a virus with a single-stranded RNA genome that is 9749 nucleotides long. Because RNA replication is highly error prone when compared to DNA replication, the HIV virus is constantly mutating. Many of these nucleotide changes result in non-functional viruses, but ...
... Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is a virus with a single-stranded RNA genome that is 9749 nucleotides long. Because RNA replication is highly error prone when compared to DNA replication, the HIV virus is constantly mutating. Many of these nucleotide changes result in non-functional viruses, but ...
Carbon and Biological Molecules Functional Groups Functional
... • Disruption of tertiary structure • Caused by heat, change in pH, salts, dehydration, etc. • Can be reversible or permanent ...
... • Disruption of tertiary structure • Caused by heat, change in pH, salts, dehydration, etc. • Can be reversible or permanent ...
Factor V Leiden
... Leiden, the Netherlands: hence the name factor V Leiden. The mutation results from a substitution of glutamine for arginine at position 506 in the protein. This is one of three sites where APC normally cleaves activated factor V, inactivating it. The APC cleavage site is altered by this mutation, re ...
... Leiden, the Netherlands: hence the name factor V Leiden. The mutation results from a substitution of glutamine for arginine at position 506 in the protein. This is one of three sites where APC normally cleaves activated factor V, inactivating it. The APC cleavage site is altered by this mutation, re ...
Next lectures: Differential Gene expression
... Motifs shared by transcription factors and chromatin proteins • The “histone fold” – Histone H3 and TAF(II)-40 – Histone H4 and TAF(II)-60 – Histone H2B and CBF (CCAAT binding factor) • Wolffe and Pruss (1996) Deviant nucleosomes: the functional specialization of chromatin. Trends ...
... Motifs shared by transcription factors and chromatin proteins • The “histone fold” – Histone H3 and TAF(II)-40 – Histone H4 and TAF(II)-60 – Histone H2B and CBF (CCAAT binding factor) • Wolffe and Pruss (1996) Deviant nucleosomes: the functional specialization of chromatin. Trends ...
Why don’t antibodies get rid of HIV?
... • DNA replication ensures that genetic information is passed on unchanged from a cell to its descendents. • The major thing cells do with genetic information is use it to encode PROTEINS. • Every cell contains all of an organism’s genes, so each cell could (in theory) make every protein. But which p ...
... • DNA replication ensures that genetic information is passed on unchanged from a cell to its descendents. • The major thing cells do with genetic information is use it to encode PROTEINS. • Every cell contains all of an organism’s genes, so each cell could (in theory) make every protein. But which p ...
ii. history of genetics
... thousands of years, it wasn’t until the 1800s that scientific studies were carried out to develop an explanation for this. Today we know that we resemble our parents because of heredity which is the set of characteristics we _______, our parents receive from __________. The study of genetics heredit ...
... thousands of years, it wasn’t until the 1800s that scientific studies were carried out to develop an explanation for this. Today we know that we resemble our parents because of heredity which is the set of characteristics we _______, our parents receive from __________. The study of genetics heredit ...
Stamm revision
... characterisation of core spliceosomal proteins of unknown function [12,13], however, these large scale screens require access to high through-put robotic equipment. We describe here methods to perform genetic screens between pairs of genes in any laboratory. ...
... characterisation of core spliceosomal proteins of unknown function [12,13], however, these large scale screens require access to high through-put robotic equipment. We describe here methods to perform genetic screens between pairs of genes in any laboratory. ...
3. Protein Structure and Function – Bio 20-1
... ▫ Chou-Fasman: each amino acid is assigned a "propensity" for forming helices or sheets ▫ Chou-Fasman is only modestly successful and doesn't predict how sheets and helices arrange ▫ George Rose may be much closer to solving the ...
... ▫ Chou-Fasman: each amino acid is assigned a "propensity" for forming helices or sheets ▫ Chou-Fasman is only modestly successful and doesn't predict how sheets and helices arrange ▫ George Rose may be much closer to solving the ...
Genetic recombination in bacteria: horizon of the beginnings
... together are about 33 kb long and consist of about 40 genes. The tra locus includes the pilin gene and regulatory genes, which together form pili on the cell surface, polymeric proteins that can attach themselves to the surface of F- bacteria and initiate the conjugation. Several proteins coded for ...
... together are about 33 kb long and consist of about 40 genes. The tra locus includes the pilin gene and regulatory genes, which together form pili on the cell surface, polymeric proteins that can attach themselves to the surface of F- bacteria and initiate the conjugation. Several proteins coded for ...
17 - Rutgers Chemistry
... bacterial gene that evolved to protect bacteria against the antibiotic chloramphenicol (CAM). The gene encodes for a protein, chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT), that can add an acetyl group (from acetyl CoA) at one or both of the hydroxyl groups on chloramphenicol. This action prevents chloram ...
... bacterial gene that evolved to protect bacteria against the antibiotic chloramphenicol (CAM). The gene encodes for a protein, chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT), that can add an acetyl group (from acetyl CoA) at one or both of the hydroxyl groups on chloramphenicol. This action prevents chloram ...
DNA and Gene Expression (chaps 12-15)
... A. DNA is double-stranded rather than single-stranded. B. DNA contains the sugar deoxyribose. C. DNA contains thymine instead of uracil. D. DNA is only found in eukaryotic cells. E. DNA is capable of forming many different sequences. ...
... A. DNA is double-stranded rather than single-stranded. B. DNA contains the sugar deoxyribose. C. DNA contains thymine instead of uracil. D. DNA is only found in eukaryotic cells. E. DNA is capable of forming many different sequences. ...
Todd Eckdahl - Davidson College
... Minor Groove Binding Drugs Anti-tumor properties Conformational change in the 3D structure of DNA Prior Knowledge of MGBD/DNA interaction As models for minor groove binding proteins ...
... Minor Groove Binding Drugs Anti-tumor properties Conformational change in the 3D structure of DNA Prior Knowledge of MGBD/DNA interaction As models for minor groove binding proteins ...
Nuclear Architecture, Chromosome Territories, Chromatin Dynamics
... Precipitation of DNA probes and Setup of hybridization solution A hybridization area covered by 12 x 12 mm coverslip requires 3 µl of hybridization mixture. We prepare a final volume of 12 µl hybridization solution, sufficient for 4 hybridizations (or 3 hybridizations on 15 x 15 mm cover slips respe ...
... Precipitation of DNA probes and Setup of hybridization solution A hybridization area covered by 12 x 12 mm coverslip requires 3 µl of hybridization mixture. We prepare a final volume of 12 µl hybridization solution, sufficient for 4 hybridizations (or 3 hybridizations on 15 x 15 mm cover slips respe ...
source file - MIMG — UCLA
... 1. This step requires that you create additional boxes and headings. While in EDIT mode, simply copy/paste then modify the text. 2. Include full name of ...
... 1. This step requires that you create additional boxes and headings. While in EDIT mode, simply copy/paste then modify the text. 2. Include full name of ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.